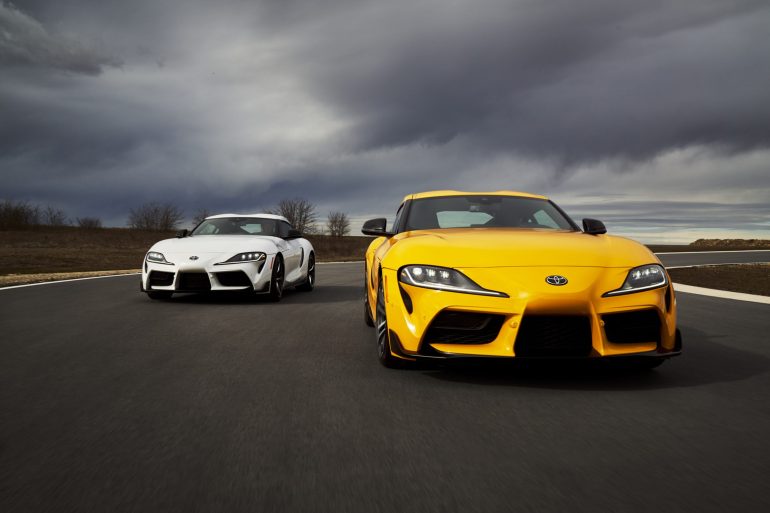
Toyota Supra
1978 - Present
The Toyota Supra: a legend whispered across generations. It's more than just a car, it's a force of power and precision that turns heads and begs to be unleashed. Made famous in video games and adored by gearheads worldwide, the Toyota Supra is a real-life icon. Buckle up and explore the legacy of this legendary sports car.
Overview / Featured / Supra Generations / Models In-Depth / Image Gallery / More Updates
The Toyota Supra - A Brief History
In April 1978, Toyota introduced the world to the Supra name, crafting a new branch from the second-generation Celica coupé that was longer, wider, and packed more punch under the hood. This new variant was distinguished by the A40 chassis code and was aimed directly at the grand tourer segment, primarily to compete with the then-dominant Datsun Z-cars in the Japanese and North American markets. The transformation included swapping the Celica's four-cylinder engine lineup for a more refined six-cylinder engine, marking the inception of the Toyota Supra’s storied journey.
The saga continued with the debut of the A60 Celica XX (Celica Supra for the international market) in July 1981, now based on the third-generation Celica's platform. This iteration sharpened its focus on performance, making its European market debut in August 1982. The UK market, in particular, experienced a sense of exclusivity due to the Supra’s limited availability, capped at 100 units monthly.
Distinguishing itself from the standard Celica coupe with a longer wheelbase and a pronounced front end, the Supra was equipped with a new 2.8-liter 5M-GE twin-cam engine. This generation introduced features like retractable headlights, wider wheel arches, and, crucially, independent rear suspension, enhancing its appeal among enthusiasts.
While the first-generation Supra saw limited action on the racetrack, its successor, the A60, boasted a more illustrious motorsport career. Notably, in the British Saloon Car Championship, Win Percy showcased the Celica Supra's capabilities, securing a notable victory in 1984 and paving the way for further success in rally and touring car championships.
By December 1985, as Toyota rolled out the fourth-generation Celica, the Supra embarked on a solo journey, diverging from the Celica line. The A70 Supra emerged in February 1986, shedding the XX moniker and introducing a coupe body slightly shorter than its predecessor but no less capable. Featuring an all-new design and a double wishbone suspension, the Supra narrowed the gap between a sports car and a cruiser, offering a range of straight-six engines that highlighted its performance pedigree.
The Supra’s evolution continued with the launch of the A70, culminating in the special edition 3.0GT Turbo A, which set the stage for Toyota's foray into Group A racing and rallied competitions. By the time the third-generation phased out, the Supra had firmly established itself as a force to be reckoned with, both on and off the racetrack.
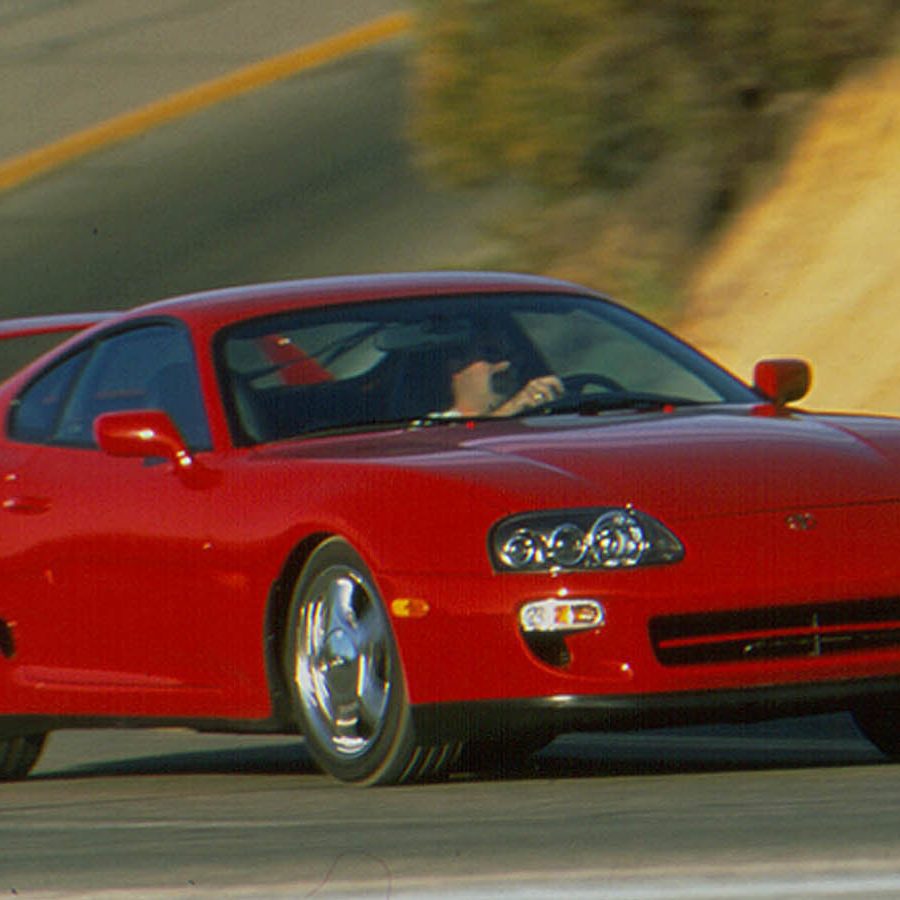
The A80 Supra, unveiled at the 1993 Chicago Motor Show, represented a significant leap forward, drawing inspiration from the 2000GT and signaling Toyota's ambitious vision for its sports car lineage. This fourth-generation model was lighter, faster, and more agile, setting new standards for performance and engineering excellence.
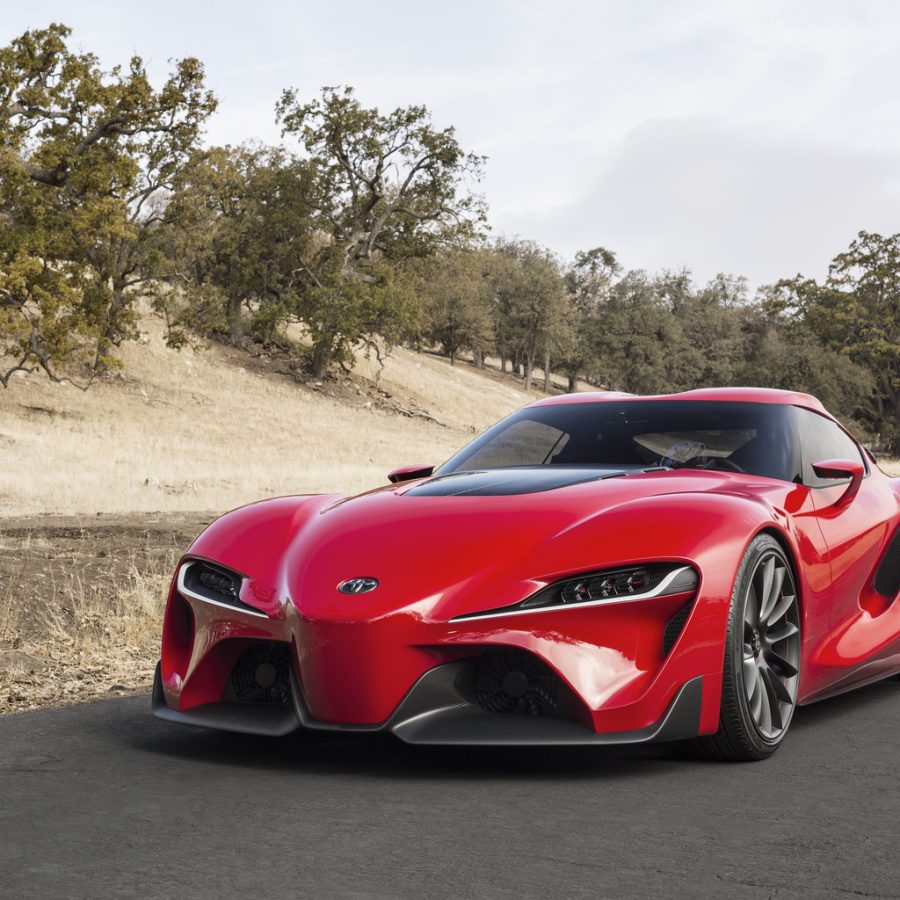
After a brief hiatus, the anticipation for the fifth-generation Supra reached fever pitch, culminating in the reveal of the Toyota GR Supra Racing Concept in 2018. This announcement marked the return of Toyota’s most iconic sports car, reigniting the passion of Supra enthusiasts worldwide.
The latest iteration of the Supra, now in full production, pays homage to its rich heritage while embracing the future. Despite sharing underpinnings with BMW, the new Supra retains a distinct Toyota identity, powered by a 3.0-liter turbocharged engine that echoes the glory of its predecessors.
The journey of the Toyota Supra, from its inception in 1978 to its latest avatar, encapsulates a legacy of innovation, performance, and enduring appeal, continuing to captivate the hearts of car enthusiasts around the globe.
Toyota Supra Basics
Generation 1 (A40/A50)
Called the Celica Supra in most markets, it ran from 1978 to 1981.
Generation 2 (A60)
Also a Celica Supra, this generation was produced from 1982 to 1986.
Generation 3 (A70)
The first generation to truly be called just "Toyota Supra" (no Celica prefix), produced from 1986 to 1993.
Generation 4 (A80)
Perhaps the most iconic generation, known for its curves and power. Production ran from 1993 to 2002 (ended in 1998 for the US market).
Generation 5 (A90)
After a long hiatus, the Supra returned in 2019 (as a 2020 model year) and continues production to this day.
Did You Know?
The first two generations of the Supra were technically called the Celica Supra, as they were based on the Celica platform.
A bright orange, heavily modified MK IV Supra became one of the most famous cars in cinema thanks to its starring role in "The Fast and the Furious" franchise.
The latest Supra shares its platform and engine with the BMW Z4, showcasing a successful collaboration between the two auto giants.
"Toyota proves they can build more than just sensible cars. The Supra is a serious contender."
Car and Driver (1987, on the rise of the A70)
Toyota Supra Generations
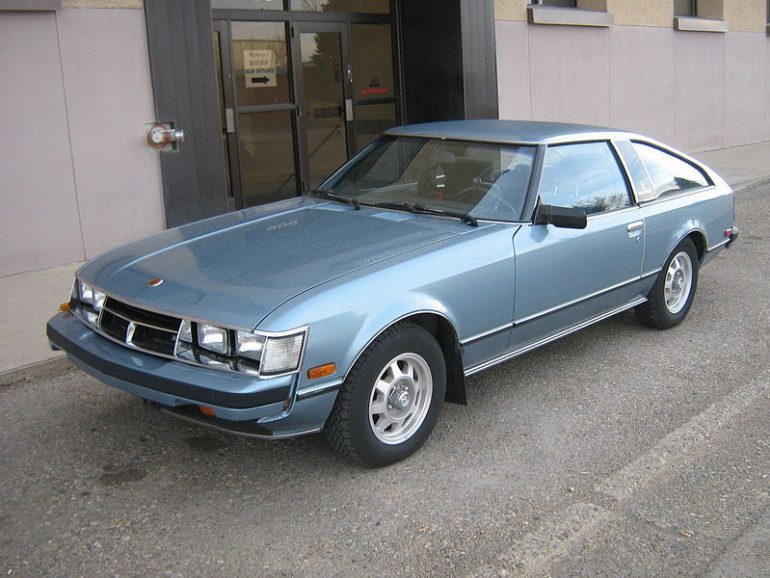

Toyota Supra (A40/A50) Basics
Model code: A40/A50
Also called: Toyota Celica XX (Japan), Toyota Celica Supra
Production: April 1978 – June 1981
Model years: 1979–1981
Assembly: Japan: Tahara, Aichi
Engine: 1988 cc M-EU Inline 6
Engine: 2563 cc 4M-E Inline 6
Engine: 2759 cc 5M-E Inline 6
Transmission: 5-speed manual
Transmission: 4-speed A40D auto
Transmission: 4-speed A43D auto
Wheelbase: 2,630 mm
Length: 4,600–4,615 mm
Width: 1,650 mm
Height: 1,290–1,310 mm
Curb weight: 1,150–1,270 kg
Did You Know?
The first-generation Supra was officially called the Celica Supra
From the very beginning, the Supra came equipped with an inline-6 cylinder engine
Depending on the trim level, the A40/A50 Supra could be equipped with a super futuristic (for the early 1980s) digital instrument cluster.
The first-generation Supra still appeared in movies like "Back to the Future" and popular video games like the original Gran Turismo.
1st Generation Toyota Supra
A40/A50 (1978 - 1981)
Toyota didn’t launch the Supra nameplate as a stand-alone. Instead, Toyota added a Supra badge to the Toyota Celica after extensively reworking the four-cylinder Celica to accept an inline-six engine. Celica Supra coupes slated for export were powered by a 2.6-liter I6 making 110 hp.
Launched in the U.S. market in 1979, the debut of the first-generation Toyota Supra came at a time when the fashion of the era was marked by polyester - a choice as questionably fashionable as the Supra itself was initially perceived. After the exclusive 2000GT, Toyota had taken a long pause from creating accessible six-cylinder sports cars, allowing the Datsun 240Z to dominate the segment unchallenged.
The A40, as the first generation was known, essentially built upon the Celica's foundation but introduced a longer wheelbase and updated aesthetics. Its initial 2.6-liter engine, relatively modest by today's standards, produced 110bhp. To navigate Japanese displacement taxes, the domestic market received a smaller 2.0-liter engine. This was a departure from the norm, as Japanese domestic market versions of sports cars typically received more powerful engines than their international counterparts. In Japan, the car was known as the Celica XX, aligning it with its Celica roots, while internationally, it gained the Supra moniker.
The 2.6-liter single-overhead-cam inline-six engine was basically borrowed from the Cressida sedan. This engine, equipped with Bosch fuel injection and impressed with its smoothness, perfect for a GT-cruiser. Toyota offered a five-speed manual transmission or a four-speed automatic. The Supra boasted an array of features not found on the Celica, from rear disc brakes to an optional eight-track player, described in contemporary reviews as a Celica adorned with "schmaltz." It was a bit of a pioneer, being the first car to incorporate a navigation computer in 1981.
The first-generation Supra was more of a grand tourer than a pure sports car, aiming to compete with the Datsun Z cars rather than outpace them on the track. It established the Supra identity: a distinct, rear-wheel-drive coupe with a straight-six engine, focusing on driver enjoyment and setting a foundation for the evolution of the Supra legacy.
2nd Generation Toyota Supra
A60 (1981 - 1985)
The early 1980s marked a pivotal era for Toyota as it unveiled the second-generation Supra (A60), a model that would further cement the Supra nameplate in the annals of sports car history. Launched between 1981 and 1985, the A60 was not merely a continuation of its predecessor but a bold stride towards a blend of performance, luxury, and technological innovation. This period witnessed Toyota's endeavor to position the Supra as a standout model within the burgeoning sports coupe segment, aiming to outshine its rivals with a concoction of sportiness and sophistication.
The transition from the first-generation A40 to the A60 Supra was dramatic and deliberate. Toyota aimed to differentiate the Supra more distinctly from its Celica sibling, with which it had shared much of its underpinnings. The A60 emerged with a profile that was sleeker, more aerodynamic, and aggressively styled to match its performance upgrades. While the Celica transitioned to front-wheel drive in its later iterations, the Supra steadfastly retained its rear-wheel-drive layout, a testament to its sports car ethos.
The A60 boasted a design that was both contemporary and forward-thinking. Its angular lines, pop-up headlights, and a more pronounced front air dam gave it a formidable presence. The Supra's interior also saw significant upgrades, with a focus on driver comfort and convenience. Features such as adjustable lumbar support seats, automatic climate control, and an advanced audio system highlighted Toyota's commitment to blending performance with luxury.
Under the hood, the A60 Supra was initially equipped with a 2.8-liter inline-six engine, known as the 5M-GE, capable of producing 145 horsepower. This was a significant uptick from its predecessor, offering a more engaging driving experience. By mid-generation, this powertrain was further refined to extract more power, culminating in the introduction of the 161-horsepower 5M-GE in 1984. This engine was paired with either a 5-speed manual or a 4-speed automatic transmission, providing a blend of performance and driving pleasure that was rare for its time.
Toyota didn't hold back on incorporating technology into the A60 Supra. One of the standout features was the introduction of the TEMS (Toyota Electronic Modulated Suspension) system in 1983, a cutting-edge development that allowed drivers to adjust the suspension settings from within the cockpit. This feature, combined with the Supra's independent rear suspension, ensured that the vehicle offered both a comfortable ride and sharp handling characteristics, making it a versatile performer on and off the track.
The A60 Supra also made its mark in motorsports, particularly in touring car championships. Its performance on the track helped to solidify the Supra's reputation as a capable sports car, not just in terms of straight-line speed but also in handling and reliability.
The legacy of the A60 Supra is significant; it represented a time when Toyota was bold and innovative, pushing the boundaries of what was expected from a Japanese sports coupe. It laid the groundwork for the Supra's evolution into a performance icon and played a crucial role in Toyota's motorsport history. The A60 Supra remains a beloved classic, cherished by enthusiasts for its blend of style, performance, and technological prowess.
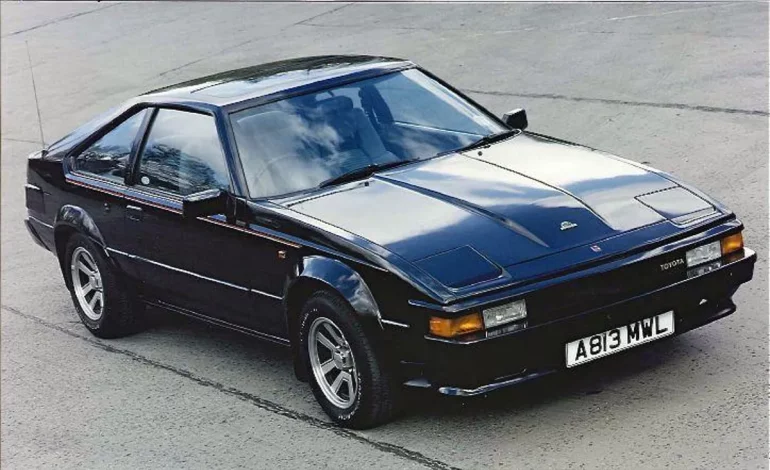

Toyota Supra (A60) Basics
Model code: A60
Also called: Toyota Celica XX (Japan), Toyota Celica Supra
Production: Jul 1981 – Dec 1985
Model years: 1982 - 1986
Assembly: Japan: Tahara
Engine: 1988 cc 1G-EU I6
Engine: 1988 cc 1G-GEU 24v I6
Engine: 1988 cc turbo Inline 6
Engine: 2759 cc 5M-E Inline 6
Engine: 2759 cc 5M-GE Inline 6
Trans: 5-speed W55 manual
Trans: 5-speed W57 manual
Trans: 5-speed W58 manual
Trans: 4-speed A43DL auto
Trans: 4-speed A43DE auto
Wheelbase: 2,614 mm
Length: 4,661 mm
Width: 1,695 mm, 1,720 mm (2.8 L)
Height: 1,321 mm
Curb weight: 1,361 kg (3,000 lb)
Did You Know?
The A60 marked the official separation of the Supra from the Celica, becoming its own standalone model.
The Supra A60 upped the horsepower game, featuring a potent 2.8-liter inline-6 engine, especially in its later model years.
Toyota offered two distinct variants: the P-Type (Performance) with a sporty focus, and the L-Type (Luxury) offering more comfort features.
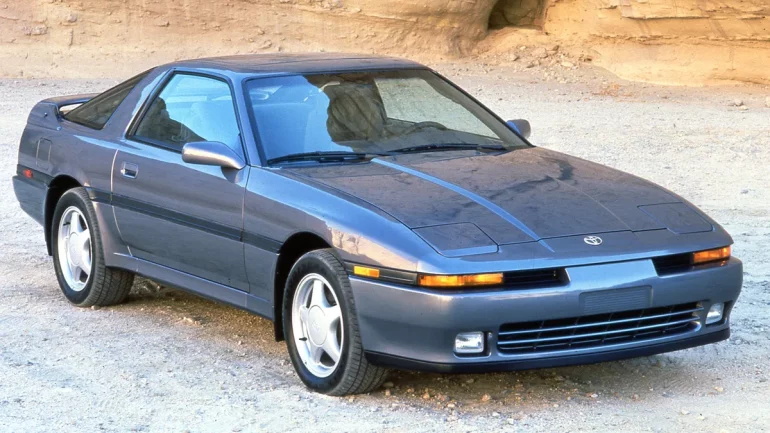

Toyota Supra (A70) Basics
Model code: A70
Production: Feb 1986 – Apr 1993
Model years: 1986–1993
Assembly: Japan: Tahara
Engine: 1988 cc 1G-EU I6
Engine: 1988 cc 1G-FE I6
Engine: 1988 cc 1G-GEU Inline 6
Engine: 1988 cc 1G-GTE twin-turbo Inline 6
Engine: 2491 cc 1JZ-GTE twin-turbo Inline 6
Engine: 2954 cc 7M-GE Inline 6
Engine: 2954 cc 7M-GTE turbo Inline 6
Trans: 5-speed W58 manual
Trans: 5-speed R154 manual
Trans: 4-speed auto
Wheelbase: 2,596 mm
Length: 4,620 mm
Width: 1,690 mm, 1,760 mm (3.0 L)
Height: 1,310 mm (1986–1988), 1,300 mm (1989–1993)
Curb weight: 1,460–1,640 kg (manual), 1,580–1,720 kg (auto)
Did You Know?
The A70 Supra is synonymous with those classic 1980s pop-up headlights, a defining feature of the era.
The introduction of the turbocharged 7M-GTE engine turned the A70 into a true performance machine.
Supra models were available with a targa-style removable roof panel for open-air driving thrills.
3rd Generation Toyota Supra
A70 (1986 - 1993)
The late 1980s and early 1990s represent a golden era in the world of performance cars, with automakers pushing the envelope in technology, power, and design. It was within this vibrant context that the third-generation Toyota Supra, known as the A70, made its debut in 1986. Marking a significant departure from its predecessors, the A70 embarked on a bold journey to redefine the Supra legacy, elevating it into the realm of sports car royalty.
Transitioning from the second-generation A60, the A70 Supra was envisioned as a standalone model, decisively shedding its Celica ties to assert a distinct identity. This generation was not just an evolution; it was a revolution in design, performance, and ambition. Toyota was set on crafting a Supra that could rival the best from Europe and America, and the A70 was its champion.
The A70 Supra introduced a more mature and refined design language. Its body was sleeker, with rounded edges replacing the angular lines of the past. The pop-up headlights remained, preserving a link to the Supra lineage, but the overall silhouette was more aerodynamic, reducing drag and enhancing performance. The interior, too, was a leap forward, offering a cockpit that balanced sporty engagement with luxury, featuring higher-quality materials and advanced electronic gadgets that were impressive for its time.
At the heart of the A70's transformation was its powertrain. The introduction of the 3.0-liter inline-six engine, available in both naturally aspirated (7M-GE) and turbocharged (7M-GTE) forms, was a game-changer. The turbocharged variant, in particular, pushed the boundaries of Toyota's engineering prowess, delivering up to 232 horsepower and 254 lb-ft of torque, numbers that commanded respect on the street and track alike. This engine, coupled with either a 5-speed manual or a 4-speed automatic transmission, provided the thrust and responsiveness that sports car enthusiasts craved.
The A70 Supra was at the forefront of automotive technology. It featured the TEMS (Toyota Electronic Modulated Suspension), an advanced system that allowed drivers to adjust the suspension settings for optimal ride quality and handling. Additionally, the Supra was one of the first vehicles to offer ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) and a limited-slip differential as standard, enhancing safety and performance.
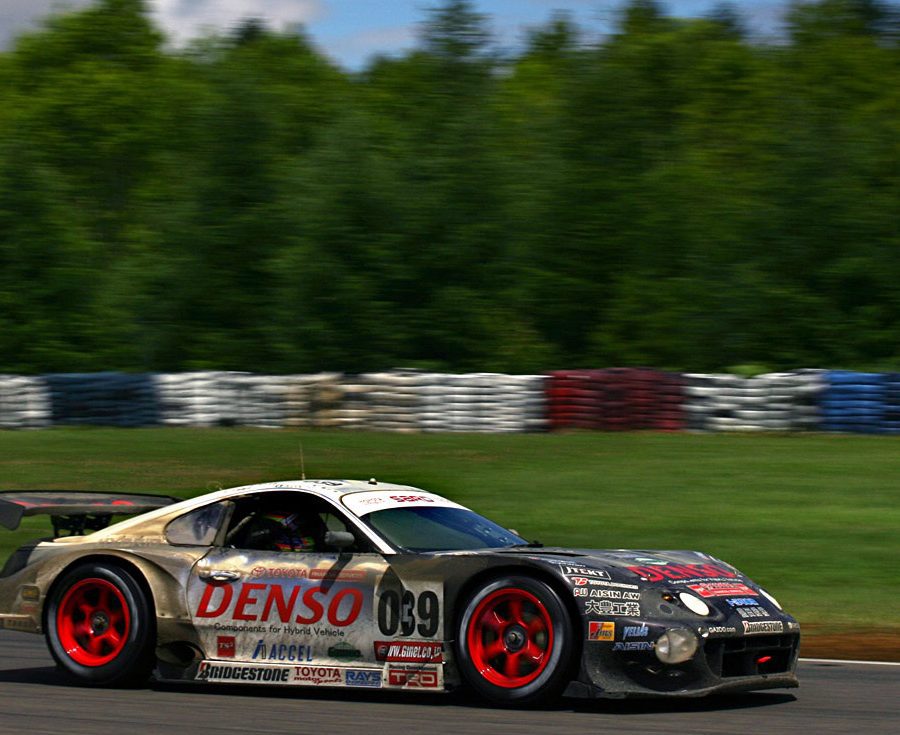
Toyota's ambition for the A70 Supra extended beyond the showroom into the fiercely competitive world of motorsports. The Supra found success in various racing disciplines, from endurance races to touring car championships. These achievements not only bolstered the Supra's reputation as a performance car but also served as a testament to its reliability and engineering excellence.
The A70 Supra's production run until 1993 marked a pivotal chapter in Toyota's history, a period during which the company dared to dream big and challenge the status quo. It significantly contributed to the Supra becoming synonymous with high performance, technological innovation, and driving pleasure.
More than just a model update, the third-generation Supra was a bold statement of intent from Toyota. It showcased the automaker's commitment to building world-class sports cars and laid the foundation for future Supra generations to build upon. The A70 Supra remains a revered icon, celebrated for its contributions to the sports car genre and its enduring legacy in automotive culture.
4th Generation Toyota Supra
A80 (1993 - 2002)
When it comes to Japanese sports cars, few models have achieved the mythical status of the fourth-generation Toyota Supra, codenamed A80. Introduced in 1993, the A80 Supra was a tour de force of Toyota's engineering prowess, design philosophy, and vision for the ultimate sports car. It not only pushed the boundaries of performance but also set new benchmarks for automotive excellence, becoming a legend in the process.
The A80 marked a radical departure from its predecessors in terms of design. Sculpted with an aerodynamic body that seemed to slice through the air with ease, it featured smooth, flowing lines that exuded speed even at a standstill. The iconic rounded front and the notable rear spoiler became defining features of the Supra silhouette. These elements weren't just for show; they contributed to the car's exceptional aerodynamics, allowing it to perform as brilliantly as it looked.
At the heart of the A80 Supra was the now-legendary 2JZ engine, a powerhouse that would cement the Supra's place in automotive lore. The naturally aspirated 2JZ-GE and the turbocharged 2JZ-GTE variants offered performance that could rival and often surpass that of cars twice its price. The 2JZ-GTE, in particular, was a masterpiece, capable of producing 320 horsepower in its US-spec version, with a robust design that became the darling of tuners worldwide for its ability to handle massive power upgrades.
The A80 wasn't just about straight-line speed; it was engineered to excel in every aspect of driving. Its front-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout, along with a lightweight, yet rigid body structure, provided a perfect balance and agility. The advanced suspension setup, electronic aids, and a focus on driver engagement made the Supra a joy to drive, whether on the open road or carving through corners on the track.
The Supra's prowess wasn't confined to public roads; it also made its mark on the racetrack. Competing in various forms of motorsport, including the All Japan Grand Touring Car Championship (JGTC) and the Le Mans 24 Hours, the A80 Supra demonstrated its capabilities against the world's best, often emerging victorious. These achievements in the racing world helped to solidify the Supra's reputation as a high-performance sports car.
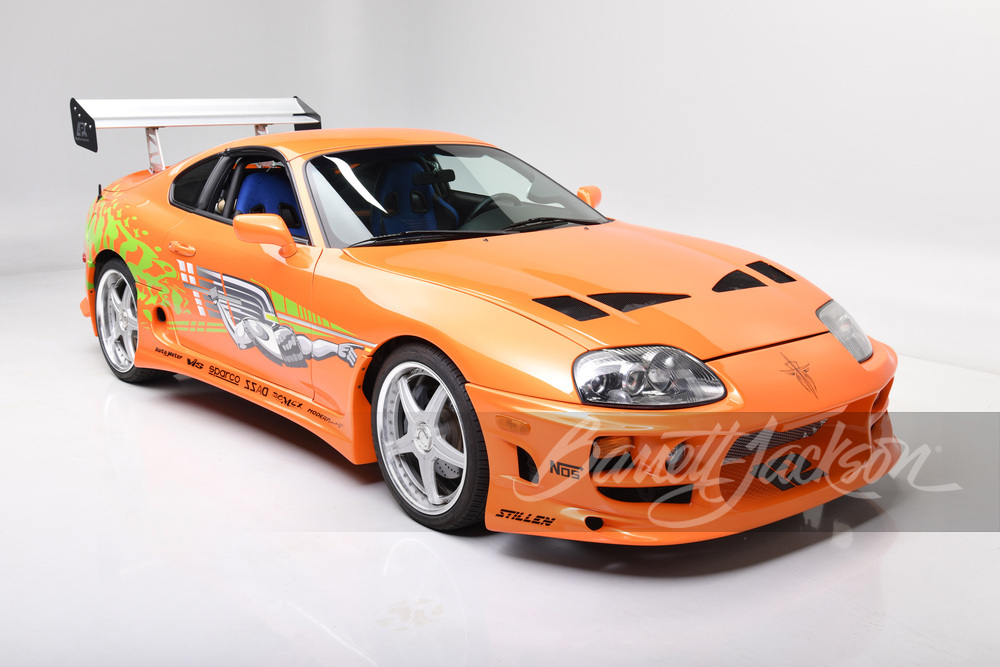
Beyond its technical specifications and racing success, the A80 Supra became a cultural icon. It starred in movies, video games, and TV shows, most notably in the "Fast and Furious" franchise, where it gained a global following. Its popularity in the tuning and modding community has remained unmatched, with enthusiasts around the world still revering the A80 for its performance potential and iconic status.
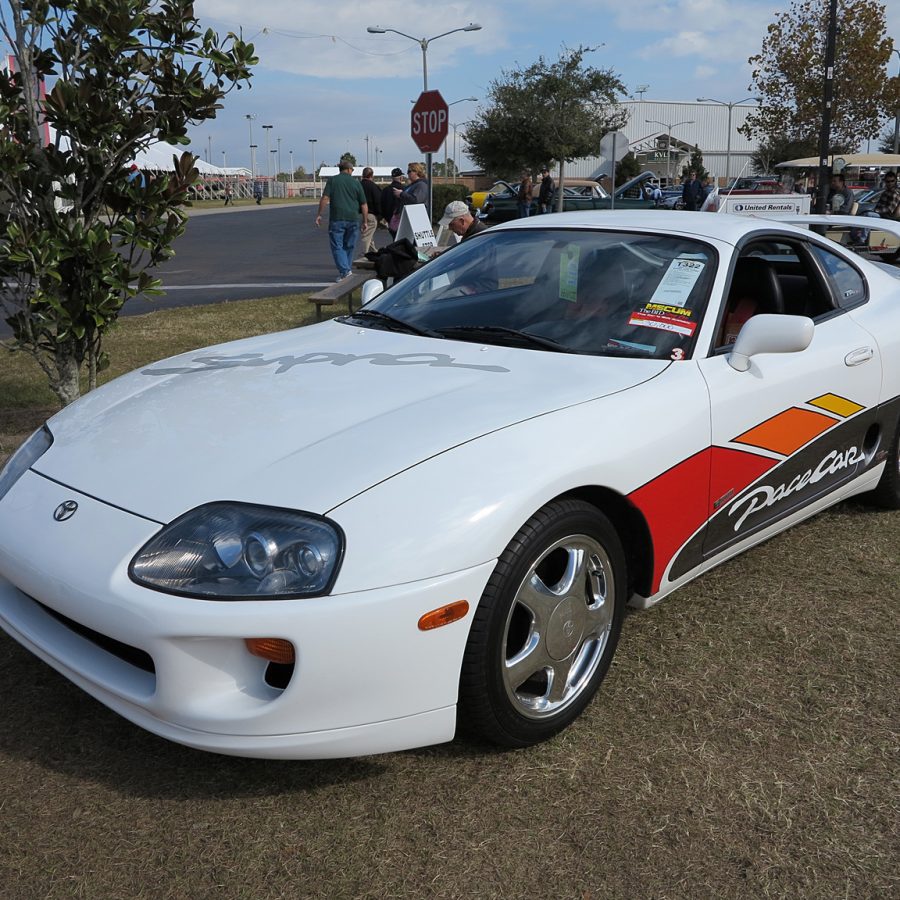
The production of the A80 Toyota Supra ended in 2002, but its legacy endures. It represented the zenith of Toyota's commitment to building a world-class sports car, combining breathtaking performance with reliability and advanced technology.
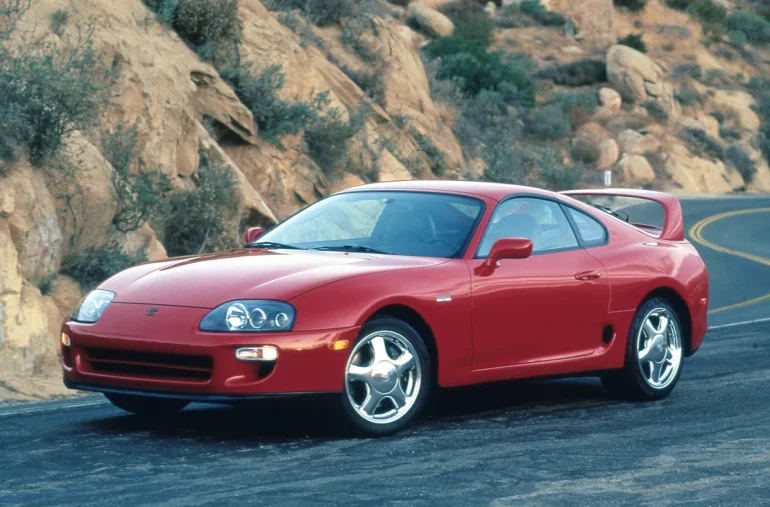

Toyota Supra (A80) Basics
Model code: A80
Production: May 1993 – Aug 2002
Model years: 1994–1998 (North America)
Assembly: Japan
Designer: Isao Tsuzuki
Engine: 2997 cc 2JZ-GE Inline 6
Engine: 2997 cc 2JZ-GTE twin-turbo Inline 6
Trans: 5-speed W58 manual
Trans: 6-speed V16x manual
Trans: 4-speed A340E auto
Wheelbase: 2,550 mm
Length: 4,515–4,520 mm
Width: 1,810 mm
Height: 1,275 mm
Curb weight: 1,410–1,510 kg (naturally aspirated), 1,490–1,570 kg (turbo)
Did You Know?
Thanks to its role in "The Fast and the Furious", the A80, especially in bright orange with wild modifications, is one of the most recognizable movie cars of all time.
The twin-turbocharged 2JZ-GTE engine is synonymous with tuning potential, allowing enthusiasts to unlock incredible horsepower levels.
Supra enthusiasts fiercely debate the merits of the 6-speed manual versus the automatic, with purists often favoring the manual.
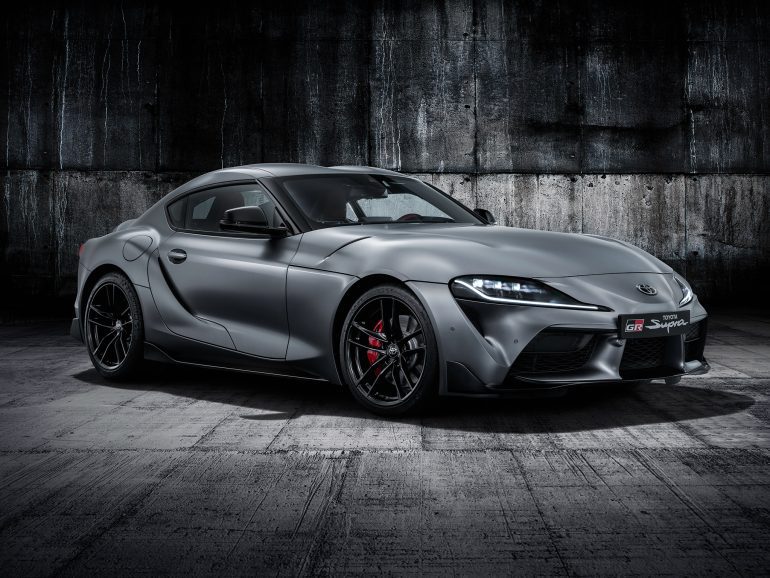

Toyota Supra (J29/DB) Basics
Manufacturer: Toyota
Model code: J29 DB, A90/A91 (for marketing purposes)
Production: Mar 2019 – present
Model years: 2020 - present
Assembly: Austria
Designer: Nobuo Nakamura
Body style: 3-door liftback coupe
Layout: Front-engine, RWD
Engine: 1,998 cc BMW B48B20 turbo I4
Engine: 2,998 cc BMW B58B30C turbo I6
Engine: 2,998 cc BMW B58B30O1 turbo I6
Engine: 2,998 cc BMW B58B30M1 turbo I6
Trans: 8-speed ZF auto
Trans: 6-speed ZF manual
Wheelbase: 2,470 mm
Length: 4,380 mm
Width: 1,865 mm
Height: 1,290–1,295 mm
Curb weight: 1,410–1,520 kg
Did You Know?
The A90 Supra shares its platform, engine, and many components with the BMW Z4, representing a unique collaboration between two automotive giants.
The A90 marked the return of the Supra nameplate after a long hiatus, generating immense excitement among fans.
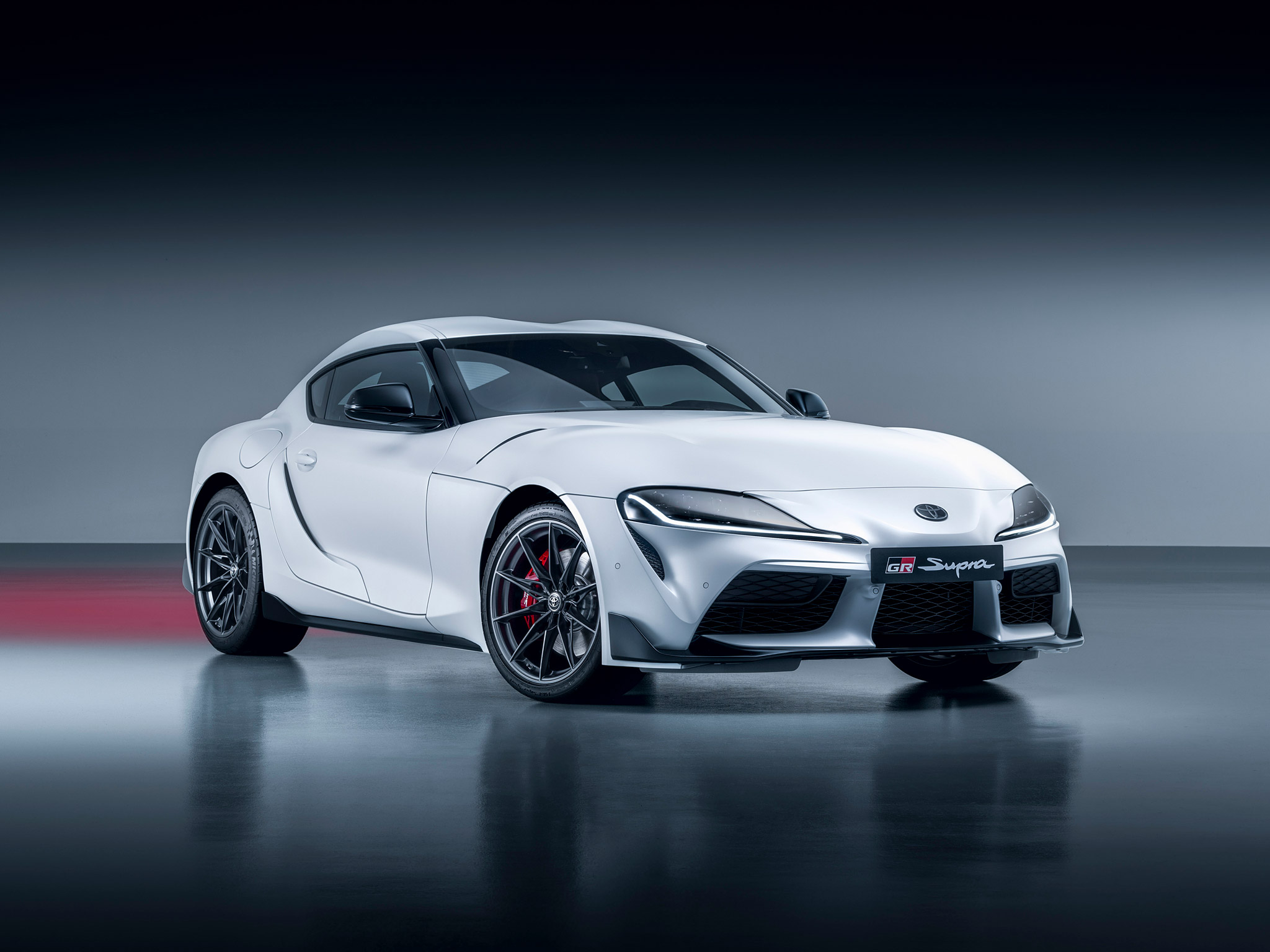
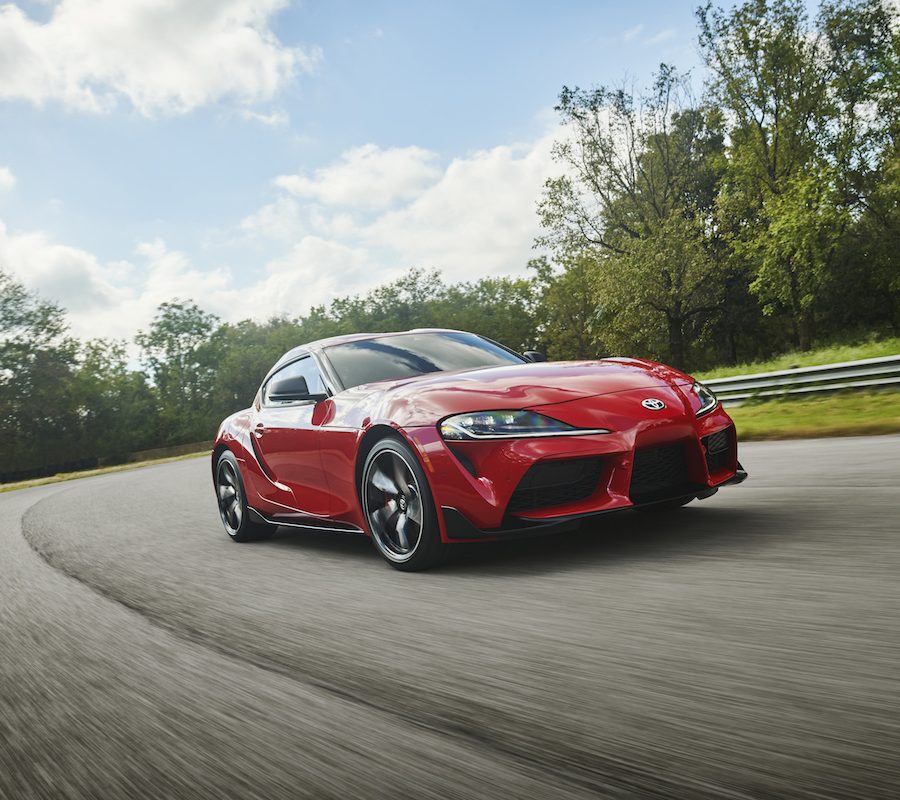
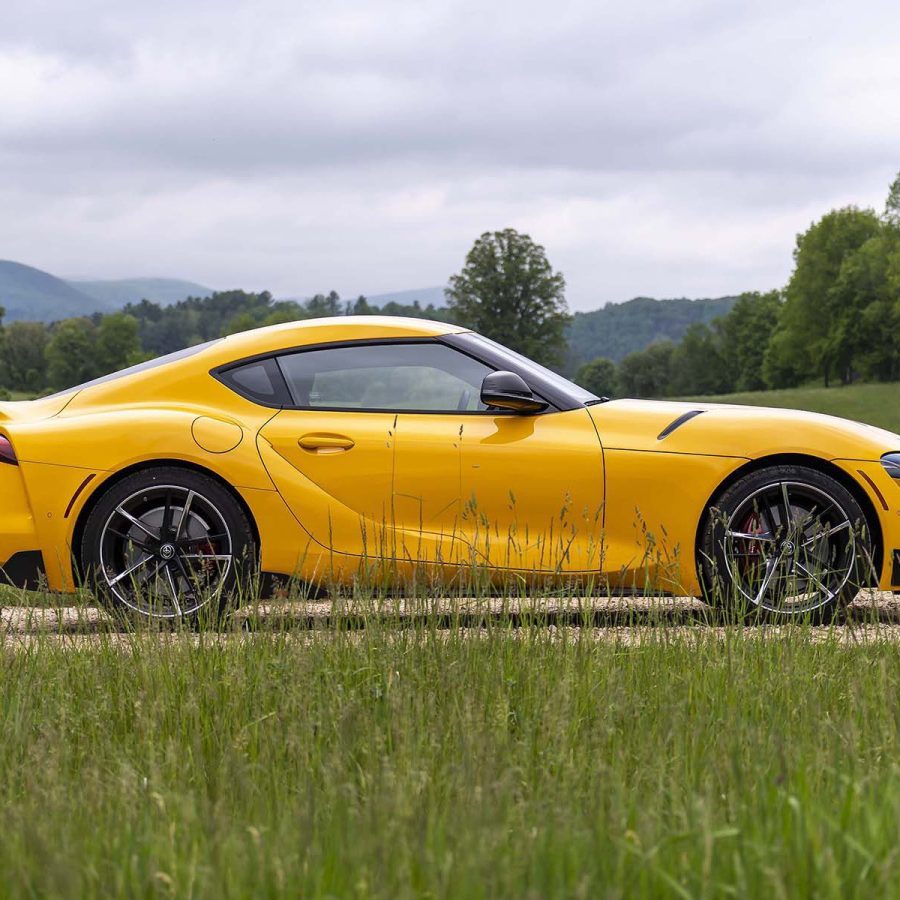
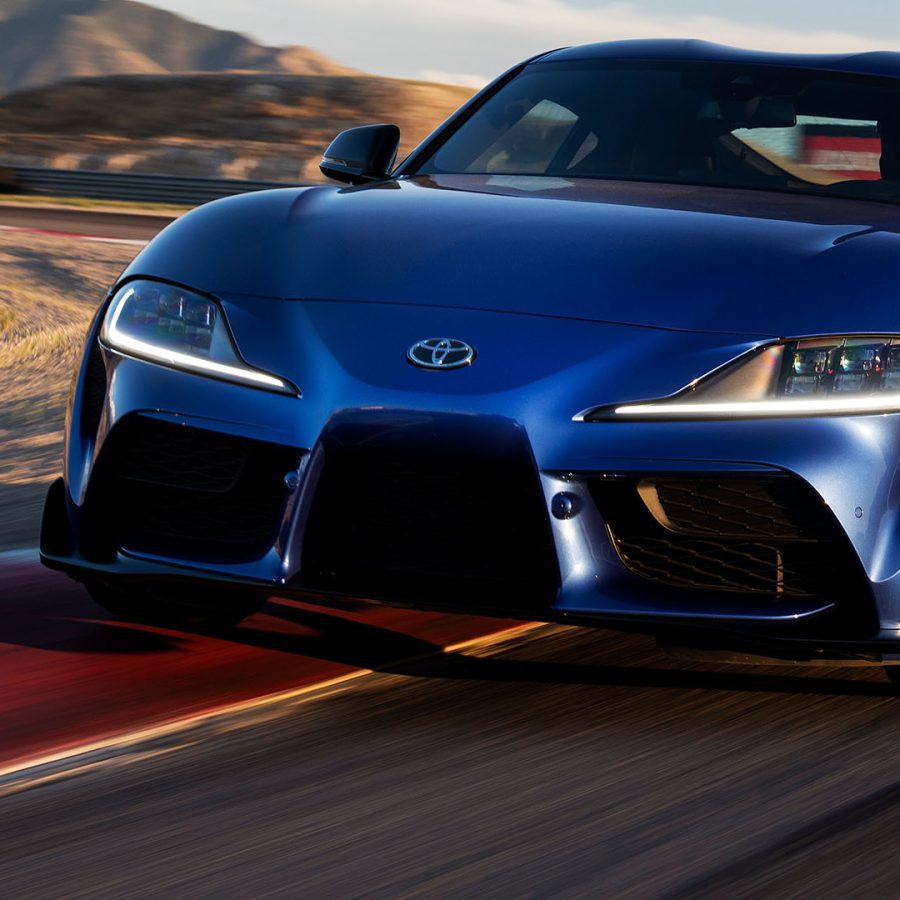
5th Generation Toyota Supra (2019 - Present)
After a hiatus that felt like an eternity to enthusiasts worldwide, the Toyota Supra made a triumphant return in 2019 as the fifth-generation A90. This iteration was not just a revival of a storied nameplate but a statement of Toyota’s commitment to the sports car market, blending heritage with modernity in a global collaboration that has sparked as much debate as it has admiration.
The A90 Supra is the fruit of a collaborative venture between Toyota and BMW, sharing its platform with the BMW Z4. This partnership leveraged BMW's expertise in producing refined, high-performance inline-six engines and rear-wheel-drive dynamics, with Toyota's legendary reputation for quality, durability, and reliability. While some purists initially expressed concerns about the BMW partnership diluting the Supra's Japanese identity, the final product has been widely praised for its performance, handling, and distinct character.
The A90 Supra's design is a forward-looking reinterpretation of its predecessors, especially drawing inspiration from the fourth-generation A80 with its long hood, compact body, and double-bubble roof. It also pays homage to the 2000GT with its sweeping lines and sports car stance. The design has been a point of contention among enthusiasts, with some lauding its aggressive, futuristic look, while others yearned for a closer visual connection to the A80 Supra.
Powering the fifth-generation Supra is a BMW-sourced 3.0-liter turbocharged inline-six engine that delivers 382 horsepower and 368 lb-ft of torque in its latest iteration. This power unit is renowned for its immediate response, flexibility, and, most importantly, its tuning potential—a hallmark of the Supra legacy. The engine is paired with an 8-speed automatic transmission, which, despite the absence of a manual option, has been praised for its quick shifts and intuitive operation.
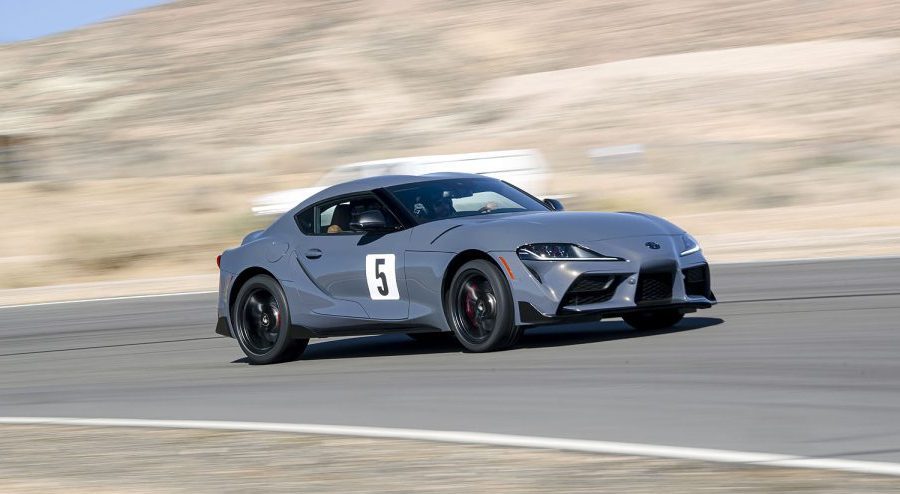
The A90 Supra's performance on the road and track has been met with acclaim from critics and drivers alike. Its finely tuned chassis, rear-wheel-drive layout, and balanced weight distribution provide a driving experience that is both exhilarating and accessible. Reviewers have highlighted the car's agility, precision, and engaging driving dynamics, which stand up to competitors far beyond its price range.
Since its launch, Toyota has been proactive in refining and updating the Supra to enhance its appeal and performance. Notably, the 2021 model year saw an increase in power from the original 335 horsepower to 382, alongside chassis tweaks for improved handling. Toyota also introduced a 2.0-liter turbocharged four-cylinder variant, offering a more accessible entry point to the Supra lineup without sacrificing the joy of driving.
The fifth-generation Supra's reception has been largely positive, with praise for its performance, handling, and the sheer joy it brings to driving. However, it has not been without its detractors, some of whom critique its BMW underpinnings and the perceived departure from its pure Japanese heritage. Yet, even among the debates, the Supra has reestablished its place in the automotive world, being featured in racing events, video games, and automotive media, and reigniting passion for Toyota's sports car legacy.
Our Favorite Toyota Supra Images
"The Supra is back, and it's better than ever. A true successor to the legends of the past."
The Drive (2020 initial review)