Horch
Research, History, Reviews, Media & More
Introduction / Featured Stories / Model Guides / News & Updates
Horch: The Pioneers of German Luxury Automobiles
Horch is a legendary name in the history of German automotive engineering, known for its luxurious, innovative cars that set new standards in design and performance during the early 20th century. Founded by August Horch, a visionary engineer who had previously worked under Karl Benz, the brand quickly established itself as a leader in the luxury car market. This post explores the founding of Horch, its rich history, the iconic car models it produced, and the milestones that have defined its journey in the automotive world.
The Founding Vision: August Horch and the Birth of Horch Cars
Horch was founded in 1899 by August Horch in Cologne, Germany. As a former engineer for Karl Benz, Horch had gained valuable experience in the burgeoning automotive industry. His ambition was to create high-quality automobiles that combined innovation with luxury. After establishing A. Horch & Cie. Motorwagenwerke AG, Horch moved the company to Zwickau in 1904, which became the brand's new home.
Horch's approach to car manufacturing was characterized by meticulous craftsmanship and engineering excellence. From the outset, Horch cars were designed to be luxurious and reliable, appealing to the affluent market of the time. August Horch’s commitment to quality and innovation quickly set the brand apart from its competitors.
The Evolution of Horch: A Legacy of Innovation and Luxury
Horch’s journey from its founding in 1899 to becoming a cornerstone of German luxury automobiles is marked by a series of significant developments and groundbreaking car models:
Early Success and the Birth of a Rival (1900s-1910s):
Horch’s early models were well-received for their quality and performance. However, a dispute with business partners in 1909 led August Horch to leave the company he founded. Undeterred, he started a new company under the name Audi, a Latin translation of his surname "Horch" (meaning "listen" in German). Despite the split, Horch continued to thrive, producing luxury vehicles that were highly regarded for their craftsmanship and engineering.
The Formation of Auto Union (1932):
In 1932, Horch became part of Auto Union, a merger of four German car manufacturers: Audi, DKW, Wanderer, and Horch. This merger was a strategic move to pool resources and technological expertise during the challenging economic conditions of the time. The four interlinked rings of the Auto Union logo, which remains Audi’s emblem today, symbolize this union. Horch became the luxury division of Auto Union, focusing on high-end, prestigious vehicles.
The First V8-Powered Car in Germany (1926):
Horch made automotive history in 1926 by introducing the Horch 303, the first German car to be powered by a V8 engine. The 303 set new standards for power and performance in luxury automobiles and established Horch as a leader in innovative engineering. The success of the 303 paved the way for subsequent models that continued to push the boundaries of luxury and performance.
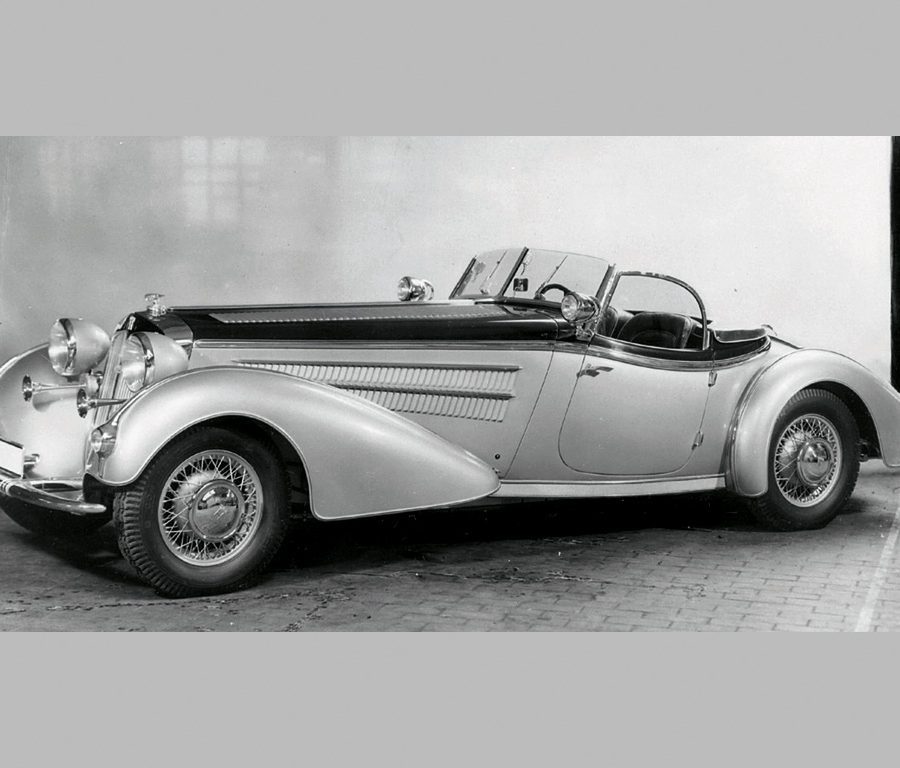
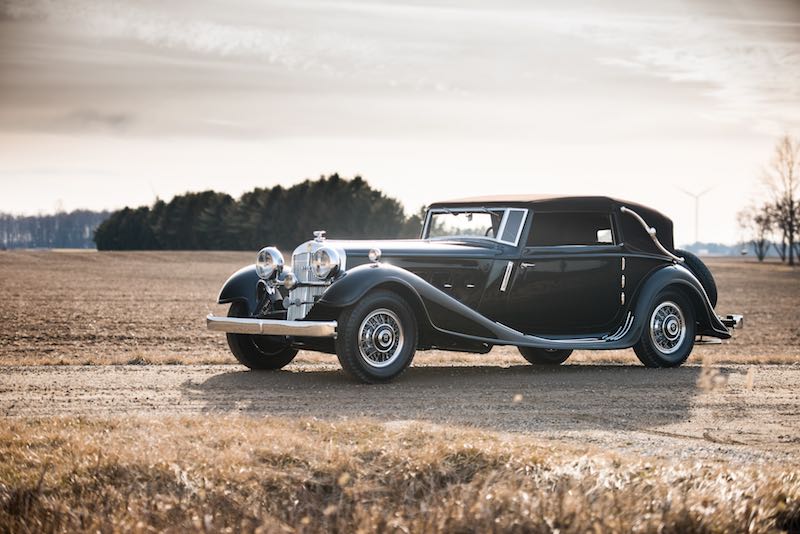
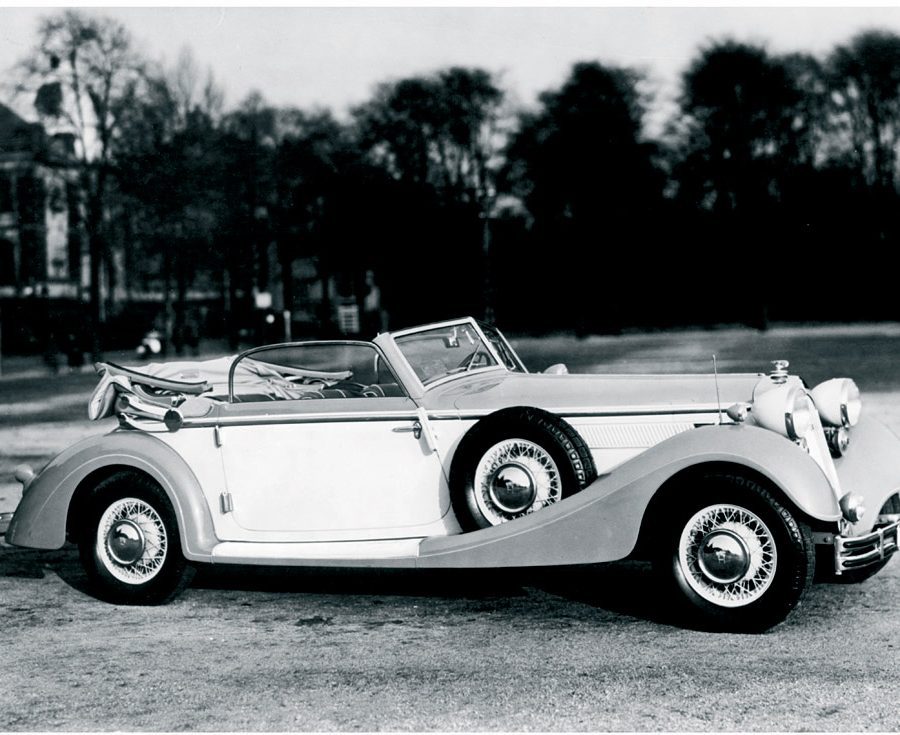
Horch 853: The Epitome of Luxury (1930s):
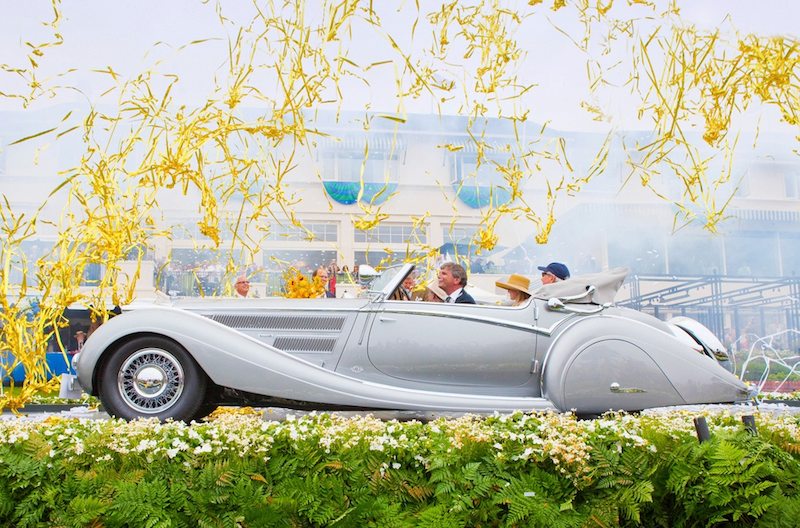
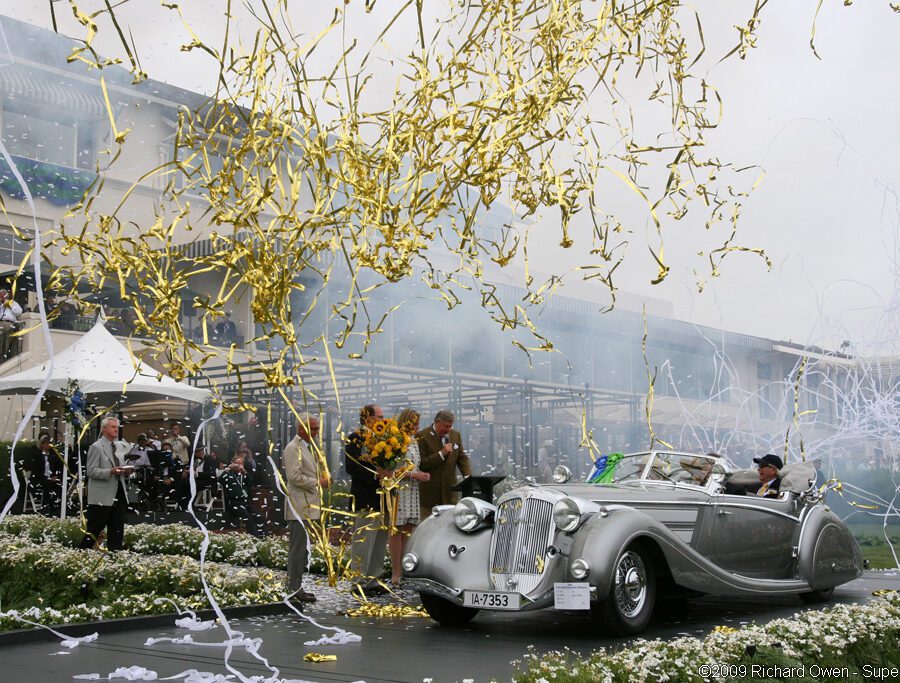
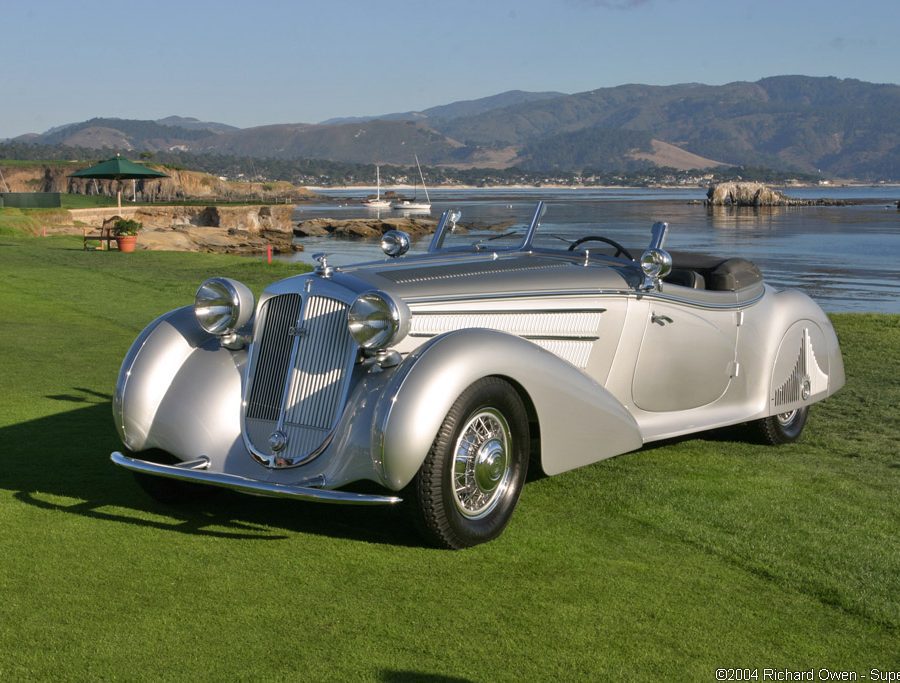
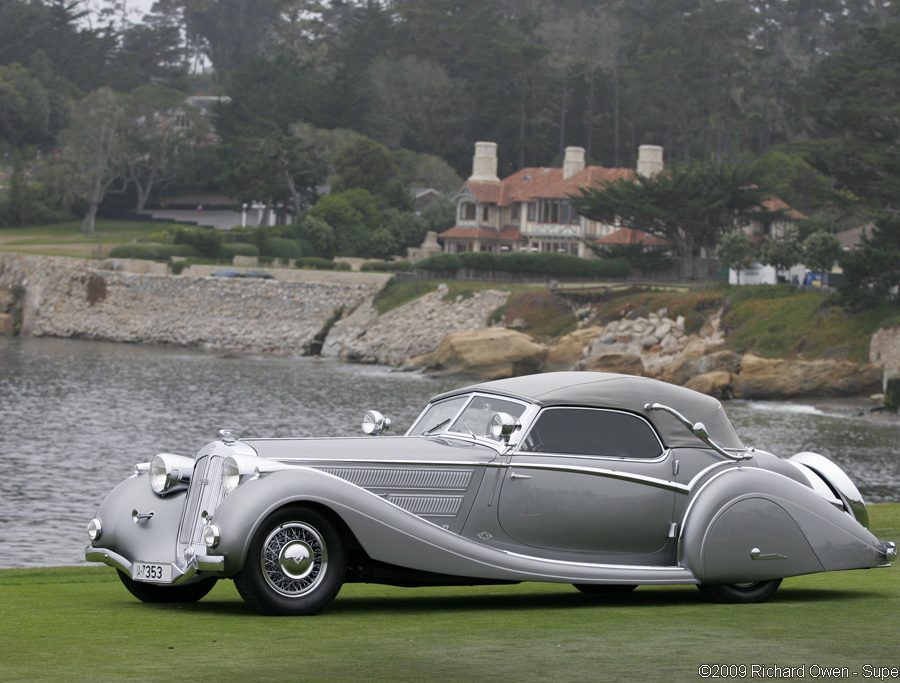
The Horch 853, introduced in the 1930s, is perhaps the most famous model ever produced by the brand. The 853 was a luxurious, large touring car with an inline 8-cylinder engine, delivering smooth performance and a top speed of over 85 mph. Known for its elegant design, advanced engineering, and opulent interior, the Horch 853 quickly became a status symbol among the German elite, including high-ranking military officers and industrialists. It remains one of the most iconic pre-war luxury cars and is highly prized by collectors today.
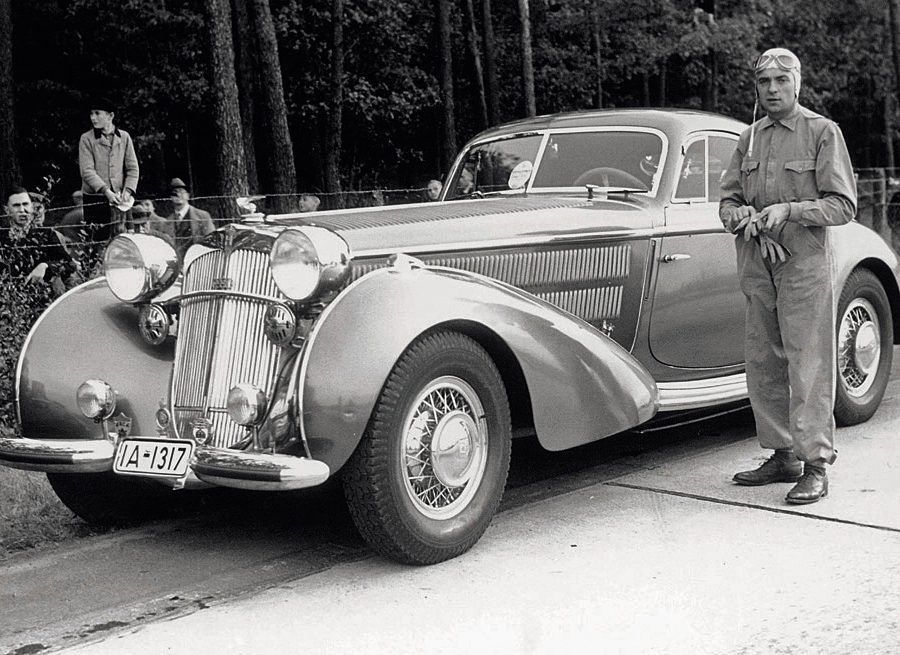
Horch in Motorsport: Showcasing Reliability and Performance:
Horch also made a mark in motorsport, participating in various early automotive races and competitions. The brand’s cars were known for their reliability and performance, often finishing well in endurance races. These successes helped to cement Horch’s reputation as a builder of robust and high-performance cars.
Post-War Challenges and East German Production (1940s-1950s):
After World War II, the Horch factory was located in East Germany, under Soviet control. The factory was nationalized and continued to produce cars under the name "VEB Horch Automobilwerk Zwickau." These post-war Horch models were primarily designed for government officials and were not available to the general public. The economic and political challenges of post-war Germany, combined with the shifting focus of the East German automotive industry, led to the decline of the Horch brand as a producer of luxury cars.
From Horch to Trabant: An Unlikely Evolution:
The Horch factory in Zwickau eventually became part of VEB Sachsenring Automobilwerke Zwickau, the manufacturer responsible for producing the Trabant, one of the most famous East German cars. While the Trabant was a far cry from the luxurious Horch cars of the pre-war era, this transition reflects the dramatic changes in the German automotive industry during the mid-20th century.
Special Milestones and Achievements
Throughout its history, Horch achieved several significant milestones that have left a lasting impact on the automotive world:
Innovative Engineering and Design: Horch was known for its advanced engineering solutions, such as the use of V8 engines, overhead camshafts, and lightweight alloy components. These innovations set Horch apart from its competitors and established the brand as a leader in luxury car manufacturing.
Luxury and Prestige: Horch cars were the epitome of luxury in their time, often chosen by the German elite for their elegance, comfort, and performance. The Horch 853, in particular, remains an icon of pre-war automotive luxury and craftsmanship.
Contribution to Auto Union and Modern Audi: As a founding member of Auto Union, Horch played a key role in the development of what would eventually become Audi. The high standards of quality, innovation, and performance set by Horch continue to influence Audi’s approach to car manufacturing today.
Collector’s Favorites: Today, classic Horch cars are highly prized by collectors and enthusiasts. Models like the Horch 853 Cabriolet are considered masterpieces of automotive design and craftsmanship and often fetch high prices at auctions, reflecting their historical significance and enduring appeal.
The Enduring Legacy of Horch
Horch’s legacy is one of luxury, innovation, and a commitment to excellence in automotive engineering. While the brand ceased to exist as an independent car manufacturer after World War II, its influence continues to be felt in the automotive world. The standards set by Horch for quality, performance, and design have become benchmarks for modern luxury car manufacturers, particularly within the Volkswagen Group, which owns Audi.
Today, Horch is remembered not only for its contributions to early automotive design and engineering but also for its role in shaping the luxury car market. The brand’s commitment to innovation, luxury, and performance remains a source of inspiration for car enthusiasts and manufacturers alike.
Horch Cars
Founded: 1904
Defunct: 1932 / 1959
Fate: Merged with DKW, Wanderer, and Audi to form Auto Union
Successor: Auto Union (1932–1969), Audi NSU Auto Union (1969–1985), Audi AG (1985–present)
Headquarters: Saxony, Germany
Key people: August Horch (founder)
Did You Know
Horch was founded in 1899 by August Horch, a German engineer who had previously worked under Karl Benz. August Horch was one of the pioneering figures in the early automotive industry, and his experience with Benz helped him establish his own car company, initially named A. Horch & Cie.
After a dispute with his business partners in 1909, August Horch left his own company and started a new one. However, he was not allowed to use his name "Horch" for the new venture. Instead, he translated "Horch" (which means "listen" in German) into Latin, resulting in the name "Audi." Thus, Audi was born as a direct successor to Horch.
In 1926, Horch became the first German manufacturer to introduce a V8 engine in a production car, the Horch 303. This model set new standards for power and performance in luxury automobiles and established Horch as a leader in automotive innovation.
The Horch factory in Zwickau, East Germany, eventually became part of VEB Sachsenring Automobilwerke Zwickau, the manufacturer responsible for producing the Trabant, one of the most famous East German cars. Thus, Horch indirectly contributed to the production lineage that led to the Trabant.