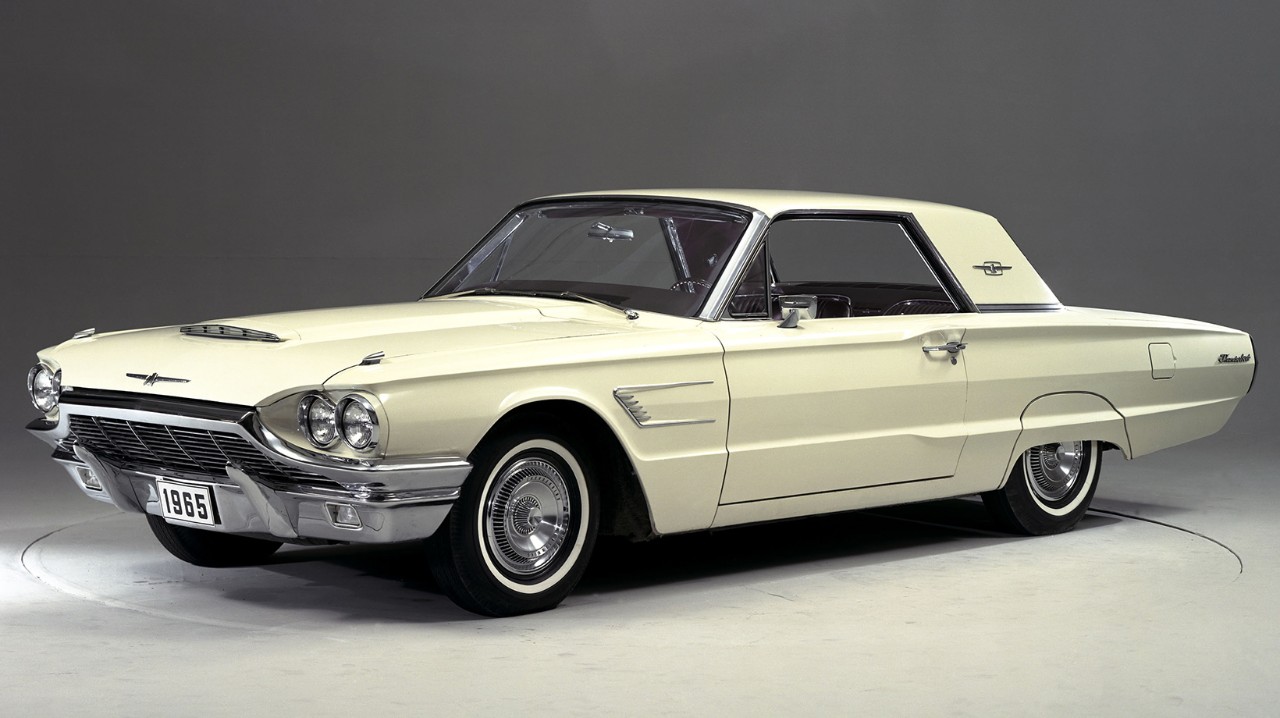
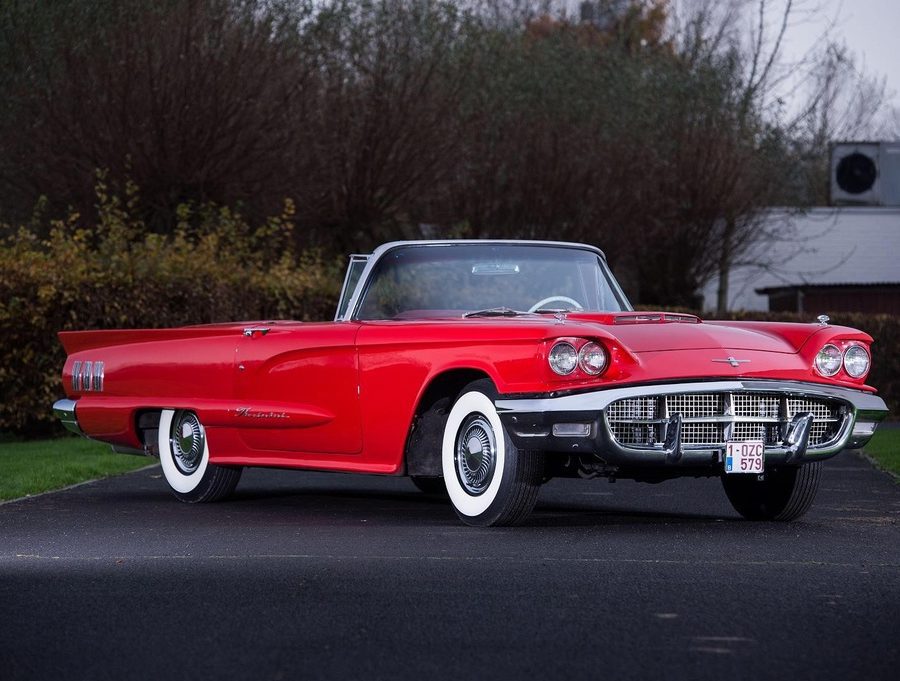
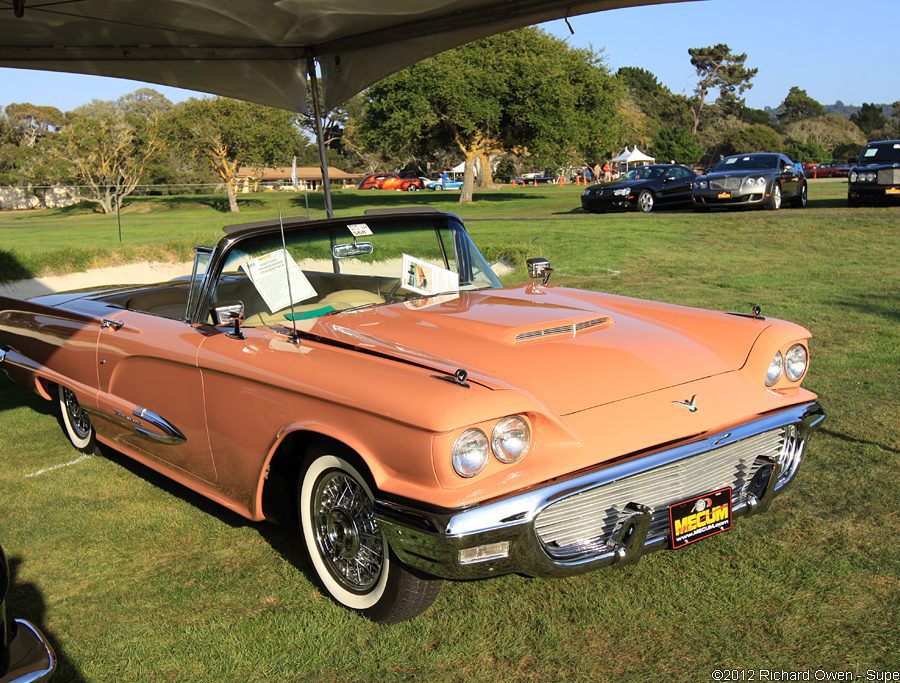
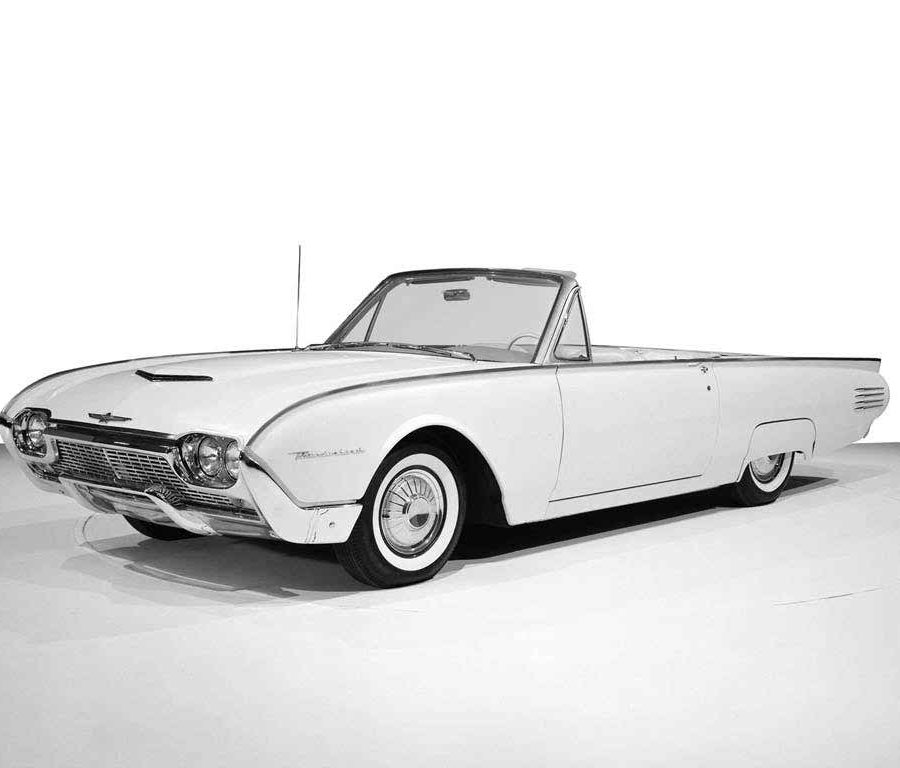
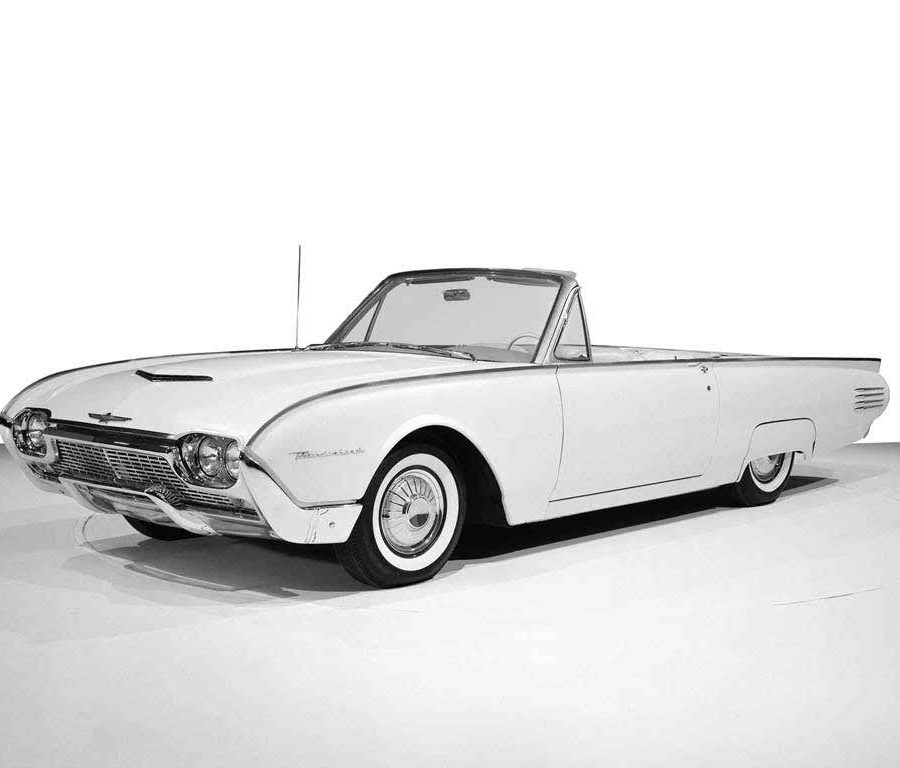
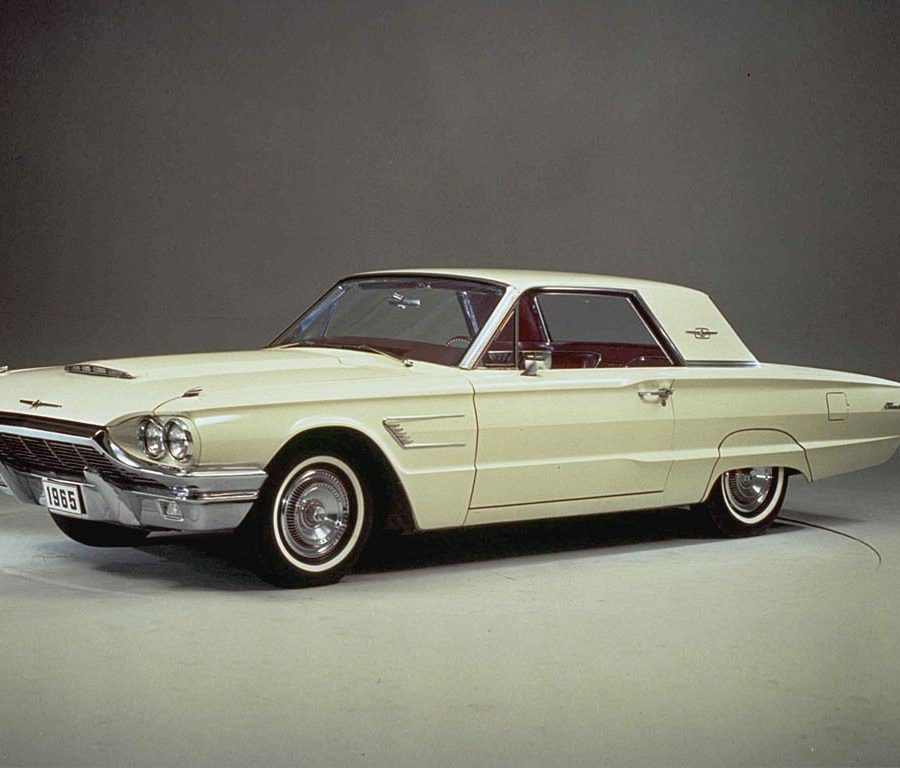
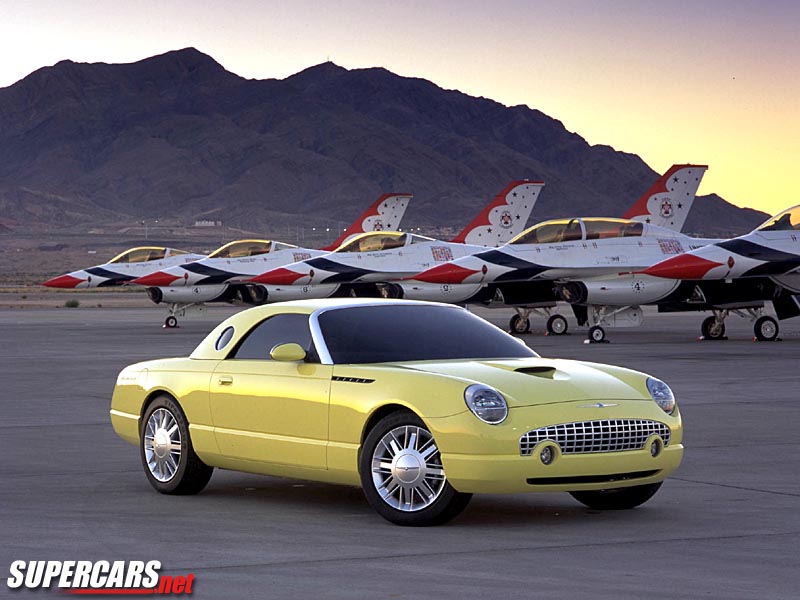
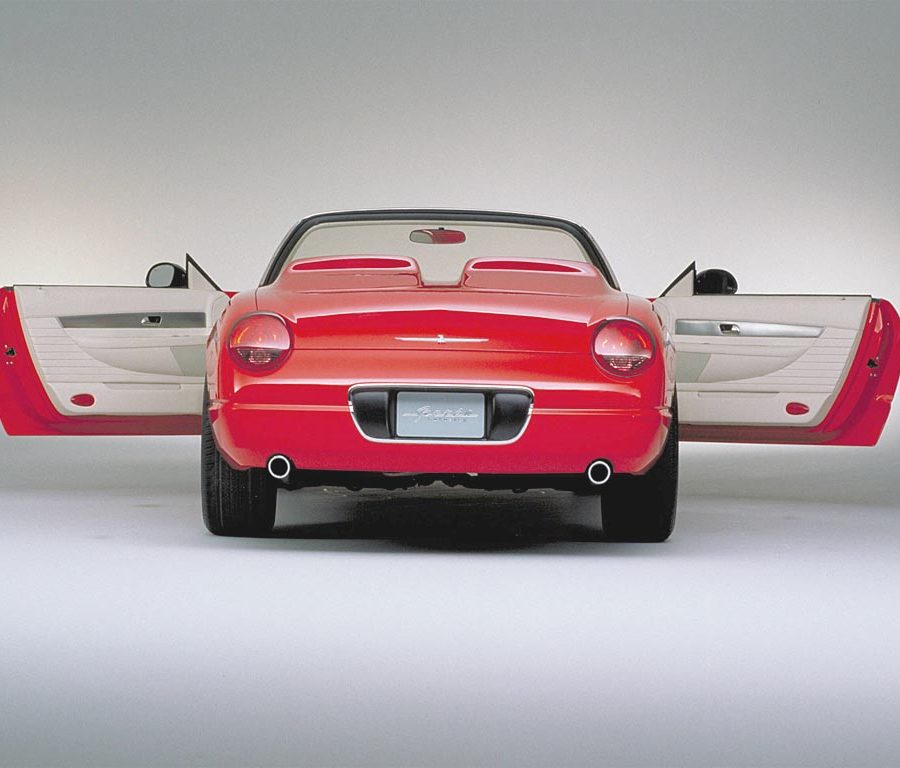
Ford Thunderbird
1955–1997 / 2002–2005
The Ford Thunderbird, affectionately nicknamed the 'T-Bird', debuted in 1954 as a sporty, two-seater convertible. Conceived as a response to Chevrolet's Corvette, it emphasized personal luxury over out-and-out performance. With its distinctive design and focus on comfort and style, the Thunderbird carved out its own niche in the automotive market, becoming an American icon over the following decades through new generations and design philosophies.
Overview / Featured / The Generations / Models In-Depth / Image Gallery / More Updates
Overview
The Ford Thunderbird was the brainchild of George Walker and Louis D. Crusoe, who envisioned a sporty model to expand Ford Motor Company’s lineup. They proposed the idea of a "true Ford sports car" for the 1955 model year, aiming for a car with a sleek, two-passenger design and a canvas top that would maximize standard production components. The design goals included a weight of 2,525 pounds, an Interceptor V-8 engine, balanced weight distribution, superior acceleration, and a top speed of over 100 miles per hour—all while maintaining recognizable Ford characteristics.
As production neared completion, Ford faced a dilemma: they hadn’t named the car. Despite over 5,000 suggestions like Beaver, Detroiter, Runabout, and Savile, none resonated with the team. Crusoe, in a bid to inspire creativity, offered a $250 suit to anyone who could suggest a compelling name. Alden Giberson, a Ford stylist, suggested “Thunderbird,” which the team quickly embraced.
The Thunderbird debuted on February 20, 1954, at Detroit’s first post-war auto show, presenting itself not solely as a sports car but as a stylish, personal vehicle. It began production at the Dearborn Assembly Plant in September of that year, retailing between $2,695 and $4,000. Buyers immediately gravitated to the Thunderbird, describing it as a "morale builder" that was fun and sporty to drive.
Throughout its production, the Thunderbird evolved significantly, introducing features like enhanced safety options, additional engine choices, Dial-O-Matic power seats, a speed-sensitive radio, an optional four-seat layout, expanded interior space, a flatter roofline, and a rear window. The Thunderbird also made its mark in racing, entering NASCAR in 1959 and winning six races that season. The redesigned Thunderbird returned to NASCAR in 1982 and amassed 150 top-division wins, including four Daytona 500 victories. Elements of the Thunderbird also found use in Ford Motorsports’ other performance projects.
Over the decades, the Thunderbird’s design and purpose shifted, eventually becoming a luxury icon. Production ceased in the mid-1990s, though Ford introduced a Heritage Edition in the early 2000s. The Thunderbird celebrated its 50th anniversary in 2005, even as Ford announced it would be discontinued and the nameplate retired.
The Thunderbird left a lasting legacy, remembered for its blend of speed, agility, luxury, and cultural influence. Frequently referenced in pop culture, the Thunderbird, or “T-Bird,” stands as a testament to Ford’s innovation and its ability to create a unique vehicle that shaped both the brand and automotive history.
The Ford Thunderbird
Manufacturer: Ford Motor Company
Production: Oct 1954 – Sep 1997, June 2001 – July 2005
Model years: 1955–1997, 2002–2005
Layout: Front-engine, RWD
"It wasn't about raw power, but effortless cool. The Thunderbird defined personal luxury."
Supercars.net
Ford Thunderbird Generations
The Ford Thunderbird stands as a true icon in automotive history, embodying the evolution of American car culture over nearly five decades. Introduced in 1955, the Thunderbird quickly made its mark with its blend of sporty style and personal luxury, setting it apart from other vehicles of its time. Over the years, Ford adapted the Thunderbird to match shifting trends and consumer desires, producing eleven distinctive generations that each tell a unique part of the brand's story. In this section, we will guide you through all eleven Thunderbird generations, starting with the debut of the original in 1955 and leading up to its revival in 2002. From its early days as a two-seat roadster to its later years as a luxurious grand tourer, each generation reflects Ford’s commitment to innovation, style, and performance. Join us on this journey to explore the Thunderbird’s transformations, including key design changes, technological advancements, and the cultural impact that helped solidify its legendary status in American automotive history.
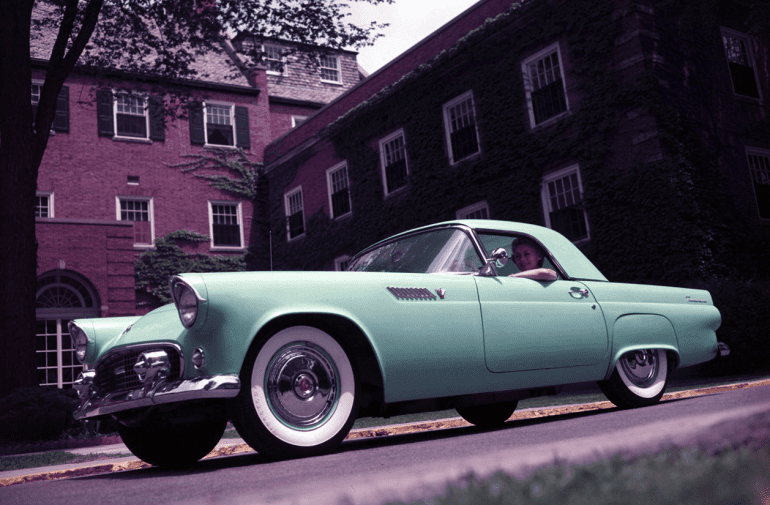
1st Gen Basics
Production: Sep 1954 - Nov 1957
Model years: 1955–1957
Body style: 2-door roadster
Layout: Front-engine, RWD
Engine: 292 cu in (4.8 L) Y-block V8, 312 cu in (5.1 L) Y-block V8
Transmission: 3-speed auto, 3-speed manual, 3-speed overdrive manual
Wheelbase: 102 in (2,591 mm)
Length: 175.3 in (4,453 mm) (1955), 185.2 in (4,704 mm) (1956), 181.4 in (4,608 mm) (1957)
Width 70.3 in (1,786 mm)
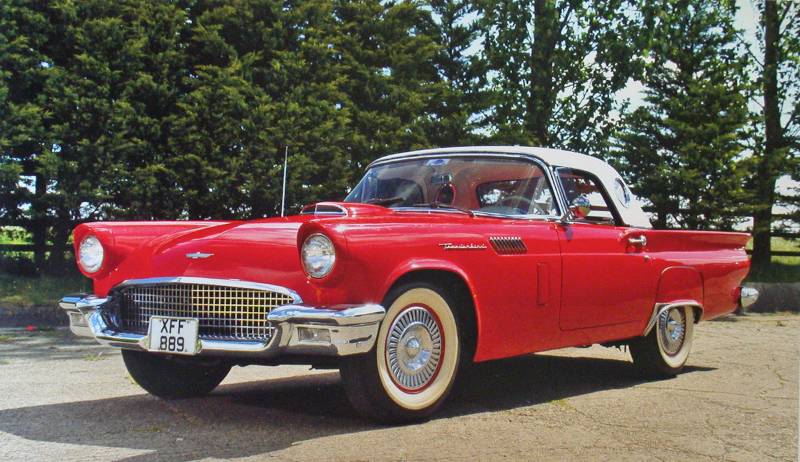
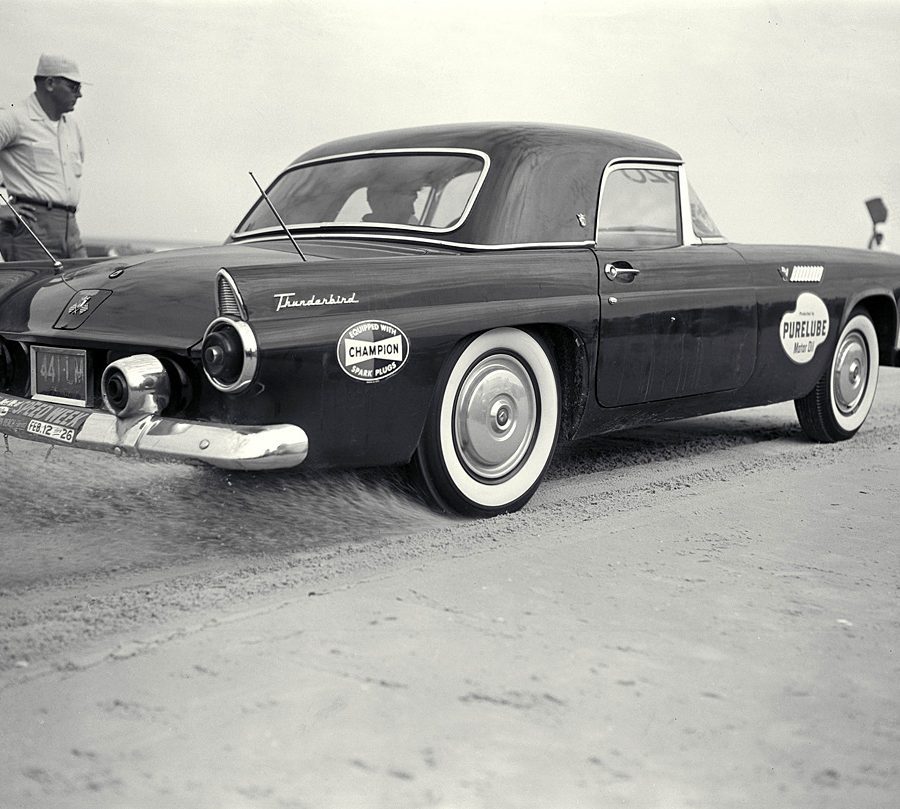
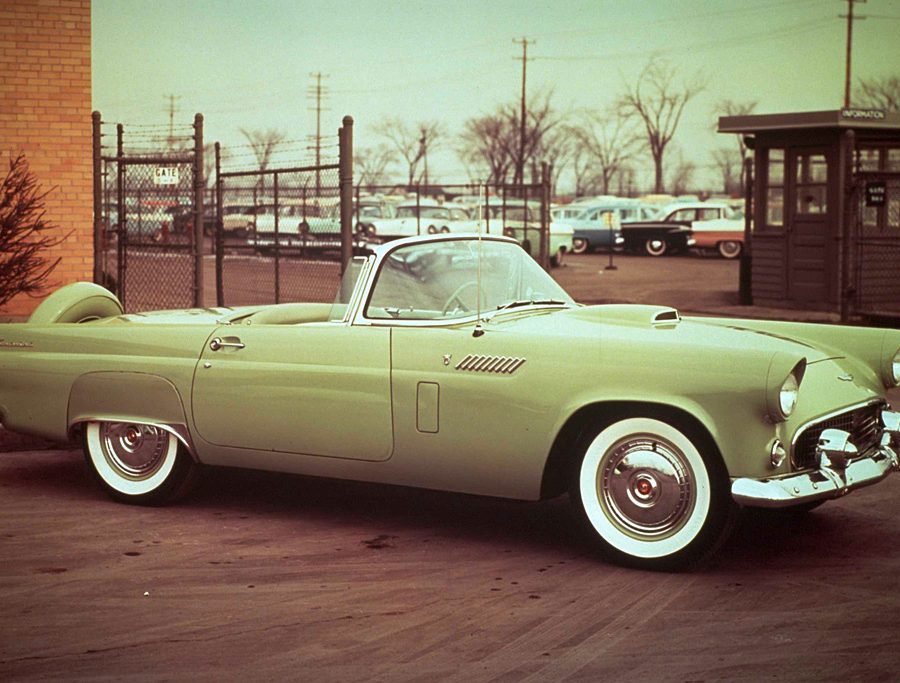
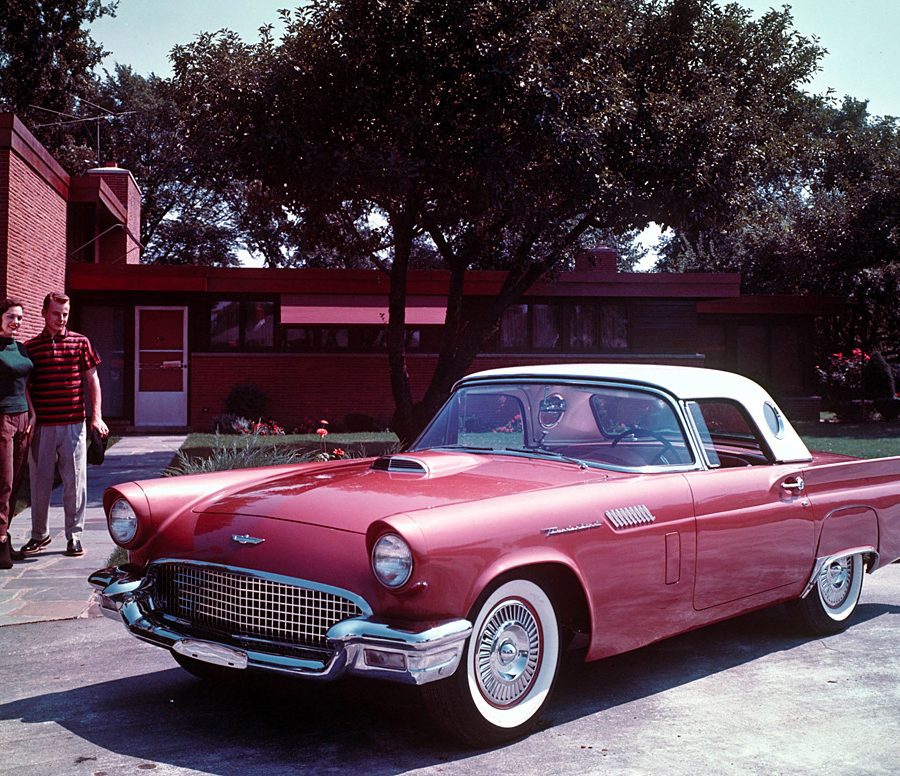
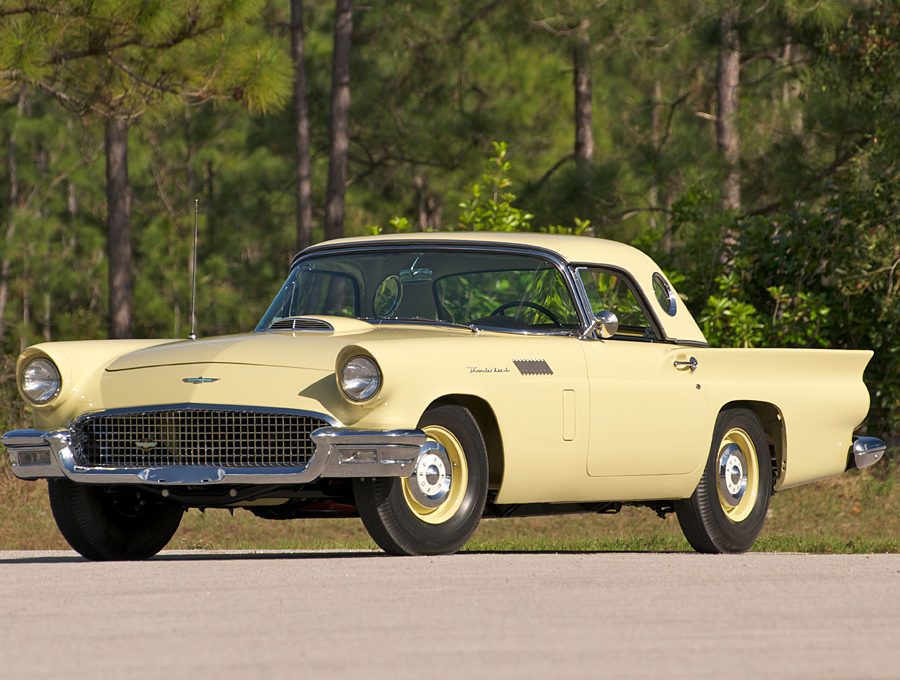
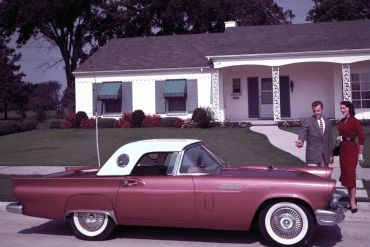
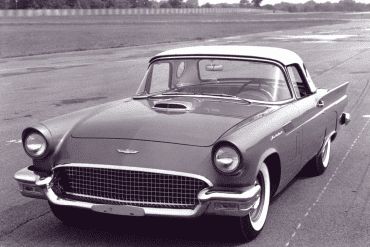
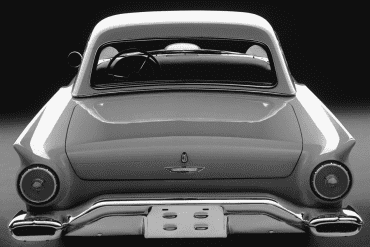
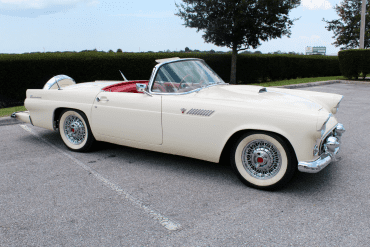
Ford Thunderbird (1955 - 1957)
First Generation Thunderbird
The first-generation Ford Thunderbird, launched in 1955, marked Ford’s entry into the burgeoning market for stylish, sporty personal cars. Initially inspired by European roadsters, the Thunderbird was Ford’s response to Chevrolet’s Corvette, though it was conceived as more of a “personal luxury” car than a pure sports car. With its sleek lines, removable hardtop, and distinctive porthole windows, the Thunderbird appealed to buyers seeking both style and comfort. Its iconic front grille and chrome details added to its appeal, making it a fashionable yet approachable car, often described as a “personal car of distinction.”
Powering the 1955 Thunderbird was a 4.8-liter V8 engine producing 193 horsepower, offering solid performance without compromising comfort. By 1956, Ford upgraded the model, adding a 5.1-liter V8 option with up to 215 horsepower and introducing the signature porthole windows in the hardtop to improve rearward visibility. Ford also addressed concerns about trunk space and weight balance by moving the spare tire to an external “Continental Kit” on the rear bumper. These enhancements bolstered the Thunderbird's reputation as a powerful, refined vehicle that prioritized a smooth driving experience.
In 1957, Ford continued refining the Thunderbird, giving it a more extended body and a reshaped grille, making the car even more distinguished on the road. This model year also introduced the option of a supercharged V8 engine, pushing performance to an impressive 300 horsepower. The Thunderbird’s increased power and refined styling made it a favorite among celebrities, furthering its status as an American automotive icon. With this last year of the first-generation, Ford emphasized both luxury and performance, a balance that would define the Thunderbird in years to come.
This first-generation Thunderbird was highly successful, selling over 53,000 units across three years. It was more than just a competitor to the Corvette—it carved out its own niche, combining elegance and power with an everyday practicality that appealed to a wide audience. The 1955-1957 Thunderbirds are now beloved collector’s items, cherished for their timeless design and for introducing the world to the Thunderbird name, a legacy that would span decades.
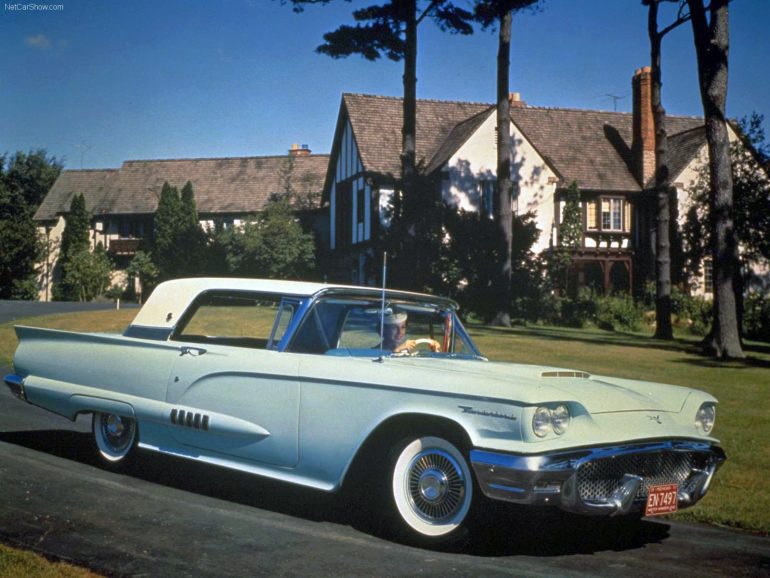
Ford Thunderbird (1958 - 1960)
Second Generation Thunderbird
The second-generation Ford Thunderbird, introduced in 1958, marked a bold shift for the model, transforming it from a sporty two-seater into a more luxurious four-seater known as the “Square Bird.” This redesign was a response to market research indicating that buyers wanted more seating capacity in their personal cars, aligning with the growing trend for larger, more versatile vehicles. With its wider stance, longer body, and angular lines, the 1958 Thunderbird retained its distinctive style while emphasizing increased comfort and space, making it a pioneering entry in the “personal luxury car” segment.
Under the hood, the second-generation Thunderbird was equipped with a 5.8-liter V8 engine, producing 300 horsepower—an upgrade that provided strong performance to match the car’s upscale image. In 1959, Ford introduced a larger 7.0-liter V8 option, boosting horsepower further to cater to drivers seeking more power. The new Thunderbird not only delivered on performance but also featured innovative engineering, like unit-body construction, which increased rigidity and improved handling. This approach also contributed to a quieter, smoother ride, underscoring Ford’s commitment to luxury.
This generation’s success was undeniable, earning the Thunderbird a place in American culture as the first personal luxury car to receive the prestigious Motor Trend Car of the Year award in 1958. Buyers were drawn to its unique combination of luxury, space, and power, a mix that was relatively rare for its time. The Thunderbird’s spacious interior, luxurious trim, and advanced options—such as power windows, air conditioning, and power seats—furthered its appeal, making it an aspirational choice for many consumers in the late 1950s.
By 1960, the Thunderbird’s reputation was well established, and its popularity showed in the sales figures, with this generation achieving record sales compared to its predecessor. The second-generation Thunderbird not only helped solidify the brand’s shift toward a luxurious, stylish identity but also influenced the direction of Ford’s other models and competitors in the industry. Today, the 1958-1960 Thunderbirds remain a cherished part of automotive history, celebrated for introducing a new genre of personal luxury cars and setting the stage for the Thunderbird’s continued evolution.

2nd Gen Basics
Also called: Square Bird
Production: Dec 1957–1960
Model years: 1958–1960
Designer: Joe Oros
Body style: 2-door hardtop coupe, 2-door convertible
Layout: Front-engine, RWD
Engine: 352 cu in (5.8 L) FE V8, 430 cu in (7.0 L) MEL V8
Transmission: 3-speed manual, 3-speed auto
Wheelbase: 112 in (2,845 mm)
Length: 205.4 in (5,217 mm)
Width: 77 in (1,956 mm)
Curb weight: 3,957 lb (1,795 kg)
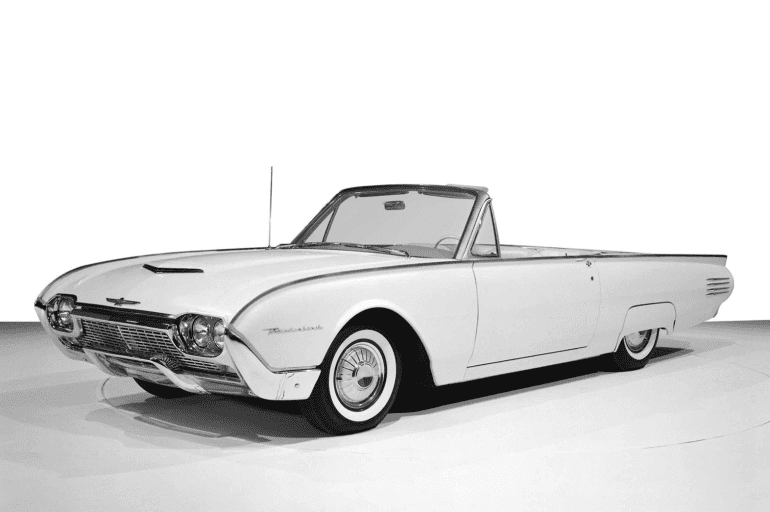
3rd Gen Basics
Production: 1961–1963
Model Years: 1961-1963
Designer: Bill Boyer
Body style: 2-door hardtop coupe, 2-door convertible
Layout: Front-engine, RWD
Engine: 390 cu in (6.4 L) FE V8, 406 cu in (6.7 L) FE V8, 427 cu in (7.0 L) FE V8
Transmission: 3-speed auto
Wheelbase: 113.2 in (2,875 mm)
Length: 205 in (5,207 mm)
Width: 75.9 in (1,928 mm)
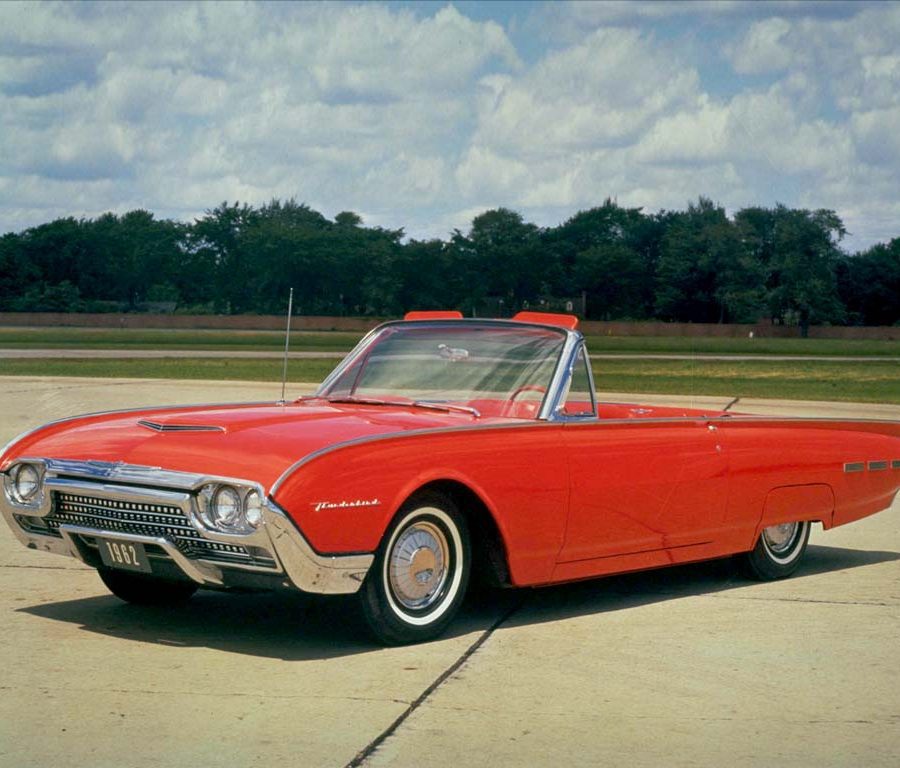
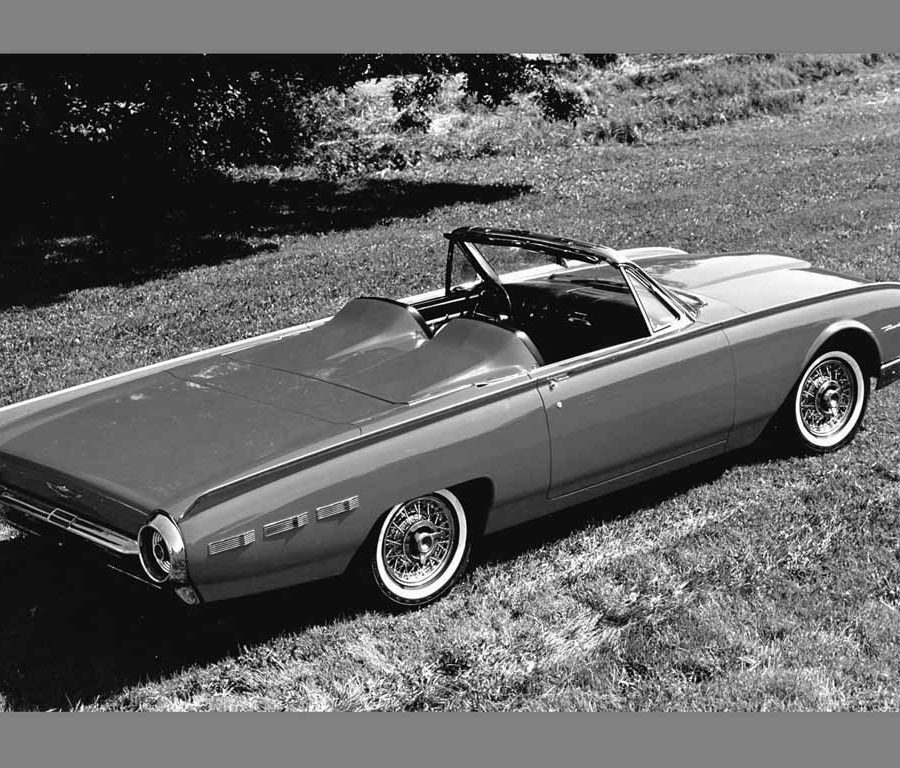
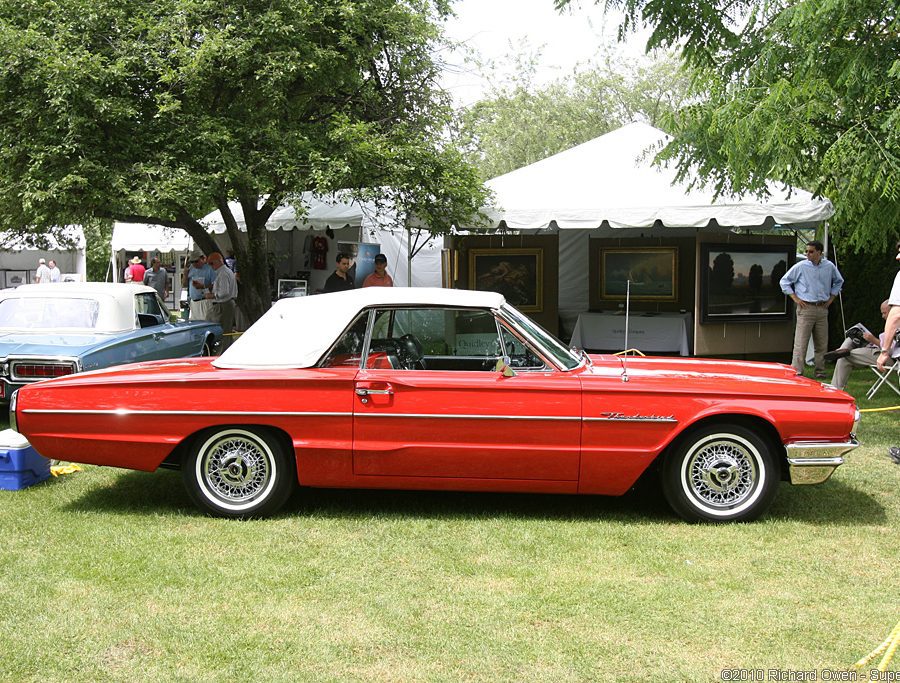
Ford Thunderbird (1961 - 1963)
Third Generation Thunderbird
The third-generation Ford Thunderbird, launched in 1961, introduced a sleek, aerodynamic design that departed from the “Square Bird” aesthetic of its predecessor. Known as the “Bullet Bird” for its streamlined, rocket-inspired shape, the 1961 Thunderbird emphasized modernity and sophistication. With its rounded lines, forward-leaning stance, and distinctive pointed front grille, the third-generation model reflected the futuristic design trends of the early 1960s, capturing the spirit of an era enamored with space-age styling. This Thunderbird was an instant hit among buyers who wanted a high-style, luxurious car that still retained a sense of sportiness.
Under the hood, the third-generation Thunderbird offered a 6.4-liter V8 engine delivering 300 horsepower, ensuring robust performance to match its bold design. In 1962, Ford introduced the Thunderbird Sports Roadster package, which featured a removable fiberglass tonneau cover that turned the four-seater into a sleek two-seater, along with Kelsey-Hayes wire wheels for added style. This package was marketed to those who wanted a Thunderbird with a more exclusive, high-performance look, while the car’s regular lineup continued to cater to drivers seeking luxury and comfort.
Another defining feature of this Thunderbird generation was the introduction of Ford’s unique “Swing-Away” steering wheel, which could pivot to the right to allow easier entry and exit for the driver. This innovative feature became a signature of the model, highlighting Ford’s focus on driver convenience and cutting-edge technology. The interior design also reflected this emphasis, with premium materials, ample instrumentation, and an aircraft-inspired dashboard that added to the car’s futuristic appeal. The third-generation Thunderbird was a showcase of both luxury and innovation, making it one of the most stylish cars of its time.
With its bold design and advanced features, the 1961-1963 Thunderbird solidified the model’s reputation as a leading personal luxury car. Sales continued to thrive, and the Thunderbird became a cultural symbol, even appearing in movies and television as an aspirational vehicle. The third-generation Thunderbird successfully balanced luxury with sporty appeal, setting a new standard for personal luxury cars in the industry and securing its place in automotive history. Today, it remains a beloved classic, admired for its style, innovation, and cultural significance.
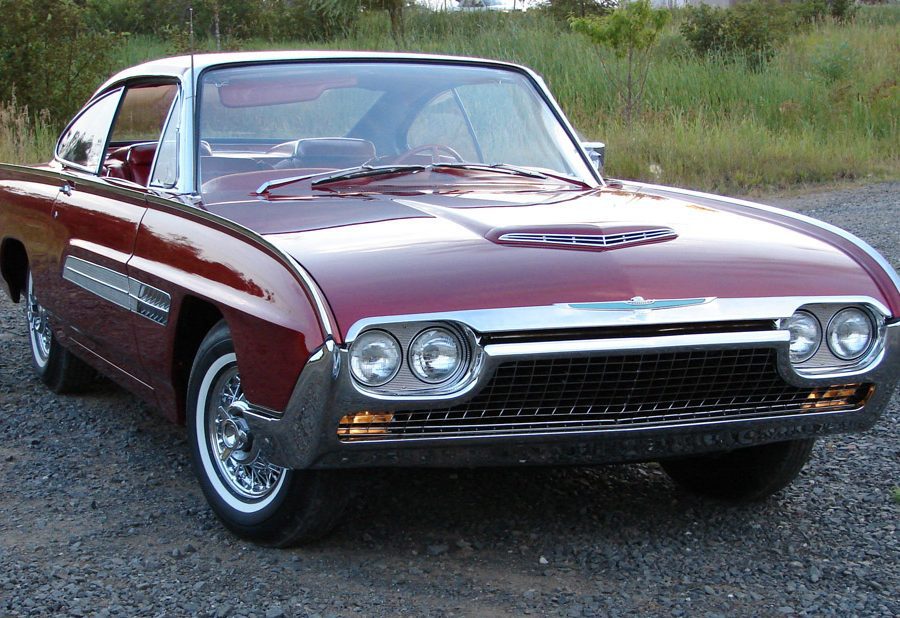
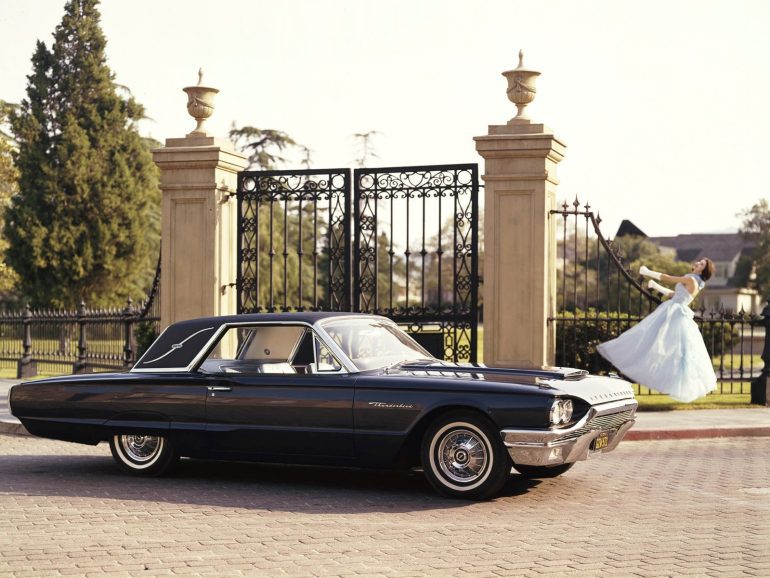
Ford Thunderbird (1964 - 1966)
Fourth Generation Thunderbird
The fourth-generation Ford Thunderbird, produced from 1964 to 1966, brought a fresh, elegant redesign that emphasized clean lines and a more formal look. Moving away from the curvaceous, jet-age styling of the previous “Bullet Bird,” Ford introduced a Thunderbird with a squared-off, more refined aesthetic, often referred to as the “Flair Bird.” This generation featured a distinct, boxy grille, subtle chrome accents, and sharper edges that conveyed a sense of sophistication. The new look was aimed at appealing to a mature, affluent market interested in a luxurious personal car with both presence and comfort.
Underneath its sleek exterior, the fourth-generation Thunderbird was equipped with a powerful 6.4-liter V8 engine that offered a smooth and quiet ride, perfectly complementing its luxury-oriented design. For 1966, Ford upgraded the engine options, introducing a 7.0-liter V8 for those seeking more power. The Thunderbird also boasted advanced features for its time, such as sequential turn signals, a first for an American production car, and “floating” rear taillights that enhanced its stylish, futuristic look. These small but innovative touches helped reinforce the Thunderbird’s reputation for combining luxury with a hint of performance.
Inside, Ford continued its focus on driver comfort and innovation with a luxurious, aircraft-inspired interior. The fourth-generation Thunderbird’s cabin was spacious, with a wrap-around dashboard, reclining passenger seats, and high-quality materials throughout. An optional Landau trim, which included a vinyl-covered roof and Landau bars on the C-pillars, added an extra layer of elegance and exclusivity. The Landau models quickly became some of the most popular versions of the Thunderbird, cementing its image as a prestigious vehicle with an air of classic American style.
By the end of the 1966 model year, the Thunderbird had firmly established itself as a top contender in the personal luxury car market. Its blend of style, innovation, and comfort set it apart from other models, and its distinctive design continued to draw a loyal following. The fourth-generation Thunderbird became a cultural icon, symbolizing American automotive elegance and sophistication. Today, it is cherished by collectors and enthusiasts who appreciate its unique place in the evolution of the Thunderbird line and its influence on luxury car design during the 1960s.

4th Gen Basics
Production: 1964–1966
Model Years: 1964–1966
Body style: 2-door hardtop coupe, 2-door landau, 2-door convertible
Layout: Front-engine, RWD
Engine: 390 cu in (6.4 L) FE V8, 427 cu in (7.0 L) FE V8, 428 cu in (7.0 L) FE V8
Transmission: 3-speed Cruise-O Matic MX auto, 3-speed Ford C6 auto

5th Gen Basics
Production: 1966−1971
Model years: 1967−1971
Body style: 2-door hardtop coupe, 2-door landau, 4-door pillared hardtop landau sedan
Layout: Front-engine, RWD
Engine: 390 cu in (6.4 L) FE V8, 428 cu in (7.0 L) FE V8, 429 cu in (7.0 L) 385 V8
Transmission: 3-speed Cruise-o-Matic auto
Wheelbase: 2-door models: 115 in (2,921 mm), 4-door Landau: 117.2 in (2977 mm)
Length: 2-door models: 206.9 in (5,255 mm), 4-door Landau: 209.4 in (5,319 mm)
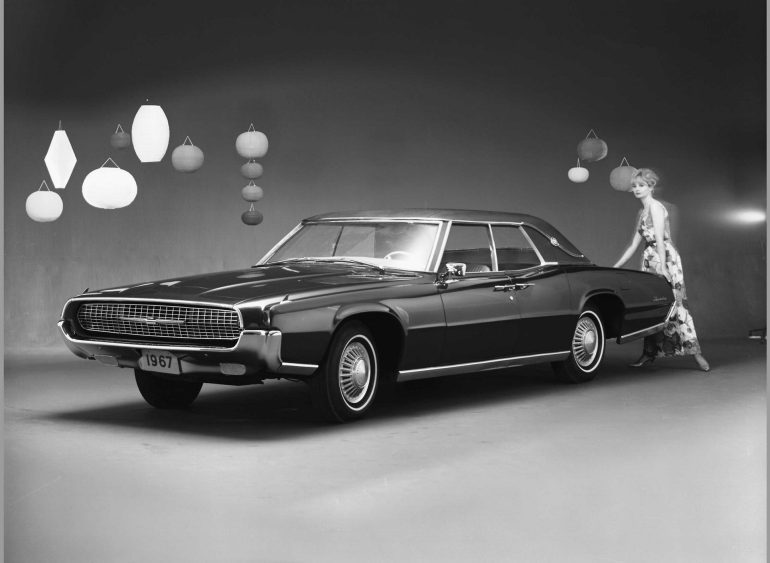
Ford Thunderbird (1967 - 1971)
Fifth Generation Thunderbird
The fifth-generation Ford Thunderbird, produced from 1967 to 1971, marked another significant transformation for the iconic model, taking it further into the realm of luxury and size. This generation introduced a larger body style, aligning the Thunderbird more closely with full-sized luxury vehicles. The move to increase the Thunderbird’s dimensions allowed Ford to cater to a growing demand for roomier, more comfortable cars. With this model, the Thunderbird began to blur the line between a personal luxury coupe and a grand tourer, providing ample space for passengers without compromising its unique sense of style.
In terms of design, the fifth-generation Thunderbird featured a bold, aggressive look that deviated from its predecessor’s refined style. It adopted a new front-end design with hidden headlights—a popular feature in late 1960s American luxury cars—adding a mysterious, upscale quality to the Thunderbird’s appearance. The “fuselage” styling, with sleek lines and a tapered rear end, gave the car a streamlined, aerodynamic look despite its size. The overall design struck a balance between elegance and muscle, a trend in American automotive design at the time, making the Thunderbird both imposing and appealing.
Performance-wise, the fifth-generation Thunderbird offered a range of powerful V8 engines, including a standard 390 cubic inch (6.4-liter) V8 and, later, the more potent 429 cubic inch (7.0-liter) Thunder Jet V8. These engines provided the car with ample power for highway cruising, maintaining a smooth, controlled ride that appealed to drivers looking for luxury performance. For the first time, Ford also offered a four-door version of the Thunderbird in 1967, with rear “suicide” doors similar to those found on Lincoln Continentals. This new option appealed to buyers who wanted the Thunderbird’s style and luxury in a more practical family-oriented layout.
The fifth generation saw the Thunderbird continuing to evolve with changing consumer preferences, moving further away from its origins as a sporty two-seater to embrace a more luxurious, substantial identity. Although some traditional Thunderbird fans missed the sportiness of earlier models, this generation found a new audience among drivers who valued luxury, space, and style. Today, the fifth-generation Thunderbird is appreciated for its bold styling and unique place in Thunderbird history, representing an era when personal luxury cars reigned supreme in the American automotive landscape.
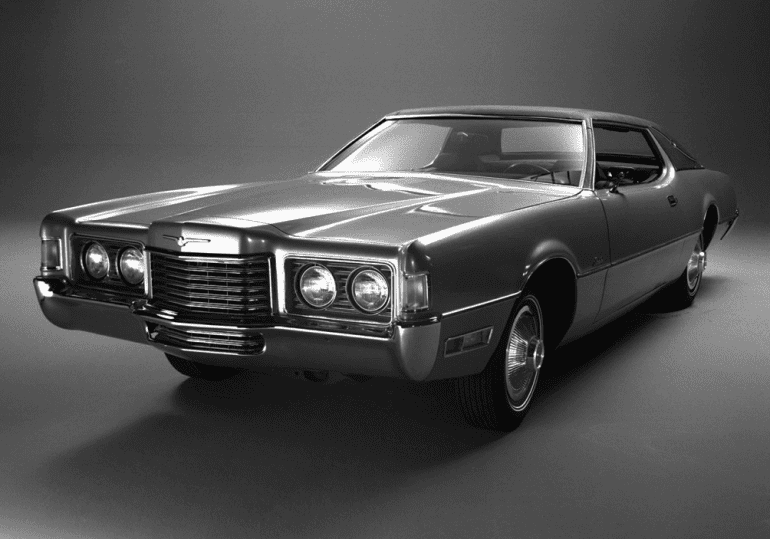
Ford Thunderbird (1972 - 1976)
Sixth Generation Thunderbird
The sixth-generation Ford Thunderbird, produced from 1972 to 1976, marked the Thunderbird’s continued evolution into a large, luxurious personal car, catering to the American market's appetite for bigger, more opulent vehicles. This generation saw the Thunderbird sharing a platform with the Lincoln Continental Mark IV, further positioning it as a high-end option within Ford’s lineup. The shift to an even larger body style resulted in a car that was almost 19 feet long, making this Thunderbird one of the most substantial vehicles in its class. The 1972-1976 models embraced the trends of the era with their imposing size, abundant chrome accents, and dramatic styling.
Underneath its bold exterior, the sixth-generation Thunderbird came equipped with a powerful lineup of engines to ensure that its considerable weight didn’t compromise performance. A standard 7.0-liter (429 cubic inch) V8 was available initially, followed by an even larger 7.5-liter (460 cubic inch) V8 in later years. These engines delivered a smooth yet powerful driving experience, well-suited for highway cruising, although they weren’t known for fuel efficiency—something that became increasingly relevant with the oil crisis of the 1970s. The Thunderbird’s size and engine options appealed to drivers who prioritized comfort and power, making it a favorite among those seeking a grand, long-distance cruiser.
The interior of the sixth-generation Thunderbird was designed to match its luxurious exterior, offering a spacious cabin outfitted with high-quality materials and a wealth of features. Buyers could choose from plush upholstery options, including cloth and vinyl, and were treated to wood-grain trim, deep-pile carpeting, and padded seating. Ford continued to innovate with this generation, including features like power windows, adjustable seats, and air conditioning as standard or optional upgrades. The “Brougham” trim level, introduced later in the generation, added even more upscale touches, enhancing the Thunderbird’s image as a luxurious, premium vehicle.
Despite its appeal as a comfortable, stylish cruiser, the sixth-generation Thunderbird faced challenges as the fuel crisis took hold and consumer preferences began shifting towards smaller, more fuel-efficient vehicles. However, this model solidified the Thunderbird's role as a symbol of 1970s luxury and Americana, remembered today for its grand proportions, distinctive styling, and emphasis on comfort over sportiness. Collectors and enthusiasts now view the 1972-1976 Thunderbirds as emblematic of an era when personal luxury cars represented the pinnacle of automotive sophistication and indulgence

6th Gen Basics
Production: 1972–1976
Model Year: 1972–1976
Body style: 2-door hardtop coupe
Layout: Front-engine, RWD
Engine: 400 cu in (6.6 L) 400 V8, 429 cu in (7.0 L) 385 V8, 460 cu in (7.5 L) 385 V8
Transmission: 3-speed Cruise-o-Matic auto
Wheelbase: 120.4 in (3,058 mm)
Length: 225 in (5,715 mm)
Width: 79.7 in (2,024 mm)
Curb weight: 5,000 lb (2,268 kg)

7th Gen Basics
Production: 1977–1979
Model Years: 1977–1979
Body style: 2-door coupe
Layout: Front-engine, RWD
Engine: 302 cu in (4.9 L) Windsor V8, 351 cu in (5.8 L) 351W V8, 351 cu in (5.8 L) 351M V8, 400 cu in (6.6 L) Cleveland V8
Wheelbase: 114.0 in (2,896 mm)
Length: 217.7 in (5,530 mm)
Width: 78.5 in (1,994 mm)
Height: 52.6 in (1,336 mm)
Ford Thunderbird (1977 - 1979)
Seventh Generation Thunderbird
The seventh-generation Ford Thunderbird, produced from 1977 to 1979, represented a significant shift for the model, as Ford sought to respond to changing market demands and the economic realities of the late 1970s. Downsized from its predecessor, this Thunderbird was built on a more compact platform shared with the Ford Torino and LTD II. This shift was part of a broader trend among American automakers to create vehicles that were smaller and more fuel-efficient in response to the fuel crisis and rising gas prices. Although the seventh-generation Thunderbird was more modest in size compared to its predecessor, it still retained the distinctive style and luxury that defined the model.
The design of the seventh-generation Thunderbird combined a sleeker, more aerodynamic profile with classic luxury car elements. While the overall length and weight were reduced, the car maintained its signature Thunderbird flair, with a bold front grille, hidden headlights, and a distinctive, sculpted body. The car’s “opera windows” in the rear pillars and optional vinyl roof added a touch of elegance, keeping with the personal luxury aesthetic Ford had cultivated for the Thunderbird. This styling struck a balance, appealing to buyers who wanted a refined, luxurious car without the excessive bulk of earlier models.
Under the hood, the seventh-generation Thunderbird came equipped with a series of smaller V8 engines, starting with a 5.0-liter (302 cubic inch) V8 as standard, though options for a 5.8-liter (351 cubic inch) and 6.6-liter (400 cubic inch) V8 were also available. These engines offered solid performance while prioritizing fuel efficiency—a critical concern during this period. Although the performance was more restrained than in earlier generations, the Thunderbird delivered a smooth, comfortable driving experience, which continued to resonate with drivers seeking a luxury car with practical appeal.
The seventh-generation Thunderbird was a commercial success, becoming one of the best-selling Thunderbirds to date and helping Ford maintain a competitive edge in the shifting automotive landscape. By focusing on luxury and style in a smaller, more economical package, Ford succeeded in reimagining the Thunderbird for a new era. This generation is remembered fondly for its unique blend of efficiency and elegance, marking a pivotal point in Thunderbird history as it adapted to the economic challenges of the late 1970s without losing its identity as a stylish, luxurious vehicle.
Ford Thunderbird (1980 - 1982)
Eighth Generation Thunderbird
The eighth-generation Ford Thunderbird, produced from 1980 to 1982, marked another transition for the model as Ford continued to adapt to shifting economic realities and changing consumer demands. Built on Ford’s midsize Fox platform, which it shared with the Ford Fairmont, this Thunderbird was lighter and more compact than previous generations. This shift reflected the industry-wide trend toward downsizing in response to fuel efficiency standards and consumer interest in smaller, more economical vehicles. The new platform allowed the Thunderbird to offer a more agile driving experience while aligning with the demand for improved fuel economy.
Stylistically, the eighth-generation Thunderbird retained its luxury car identity, though it took on a more understated look compared to the flamboyant designs of earlier generations. The lines were smoother and less imposing, giving the car a more contemporary feel. Notable features included a squared-off front end and a cleaner, more refined silhouette that emphasized simplicity over bold styling. This change helped position the Thunderbird as a modern personal luxury car for the 1980s, though some fans of the model missed the dramatic styling that had characterized earlier versions.
In terms of powertrain options, Ford offered a range of engines that prioritized fuel efficiency over sheer power. The base engine was a 3.3-liter inline-six, while a 4.2-liter V8 was also available. For those who wanted more performance, a 5.0-liter V8 option provided additional power. Despite the smaller engines, the Thunderbird was designed to provide a comfortable and smooth ride, appealing to drivers who valued refinement and efficiency. The interior of the eighth-generation Thunderbird was tailored to reflect this focus, with options for plush seating, wood trim, and other luxury touches that kept the Thunderbird’s image as an upscale vehicle intact.
Although the eighth-generation Thunderbird faced mixed reactions due to its conservative styling and reduced performance, it fulfilled Ford’s goal of producing a fuel-efficient, practical car that maintained a sense of luxury. This generation laid the groundwork for the major redesign that would come with the next iteration, as Ford prepared to reimagine the Thunderbird once again. Today, the 1980-1982 Thunderbird is remembered as a product of its time, embodying the balance between luxury and practicality that defined the early 1980s automotive market.
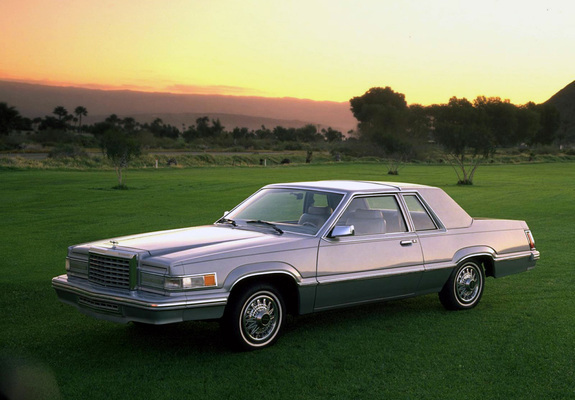

8th Gen Basics
Production: 1979–1982
Model years: 1980–1982
Body style: 2-door coupe
Layout: Front-engine, RWD
Engine: 200 cu in (3.3 L) Thriftpower Six I6, 232 cu in (3.8 L) Essex V6, 255 cu in (4.2 L) Windsor V8, 302 cu in (4.9 L) Windsor V8
Transmission: 4-speed Ford AOD overdrive auto, 3-speed auto
Wheelbase: 108.4 in (2,750 mm)
Length: 200.4 in (5,090 mm)
Width: 74.1 in (1,880 mm)
Height: 53.0 in (1,350 mm)
Curb weight: 3,166–3,477 lb (1,436.1–1,577.1 kg)
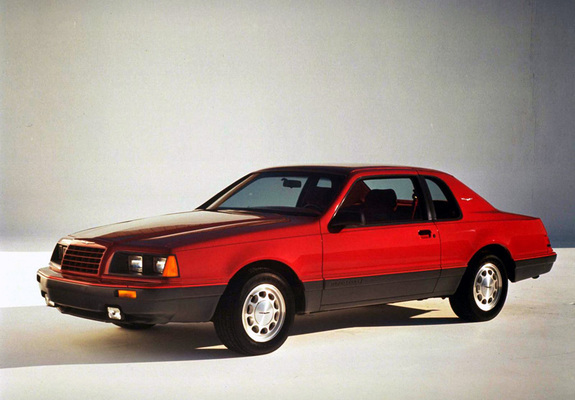

9th Gen Basics
Production: 1982–1988
Model years: 1983–1988
Designer: Dave Royer
Body style: 2-door coupe
Layout: Front-engine, RWD
Engine: 2.3 L Lima turbo I4, 3.8 L Essex V6, 5.0 L Windsor V8
Transmission: 3-speed Ford C3 auto, 4-speed A4LD auto, 3-speed Ford C5 auto, 4-speed Ford AOD auto, 5-speed Borg-Warner T-5 manual
Wheelbase: 104.2 in (2,647 mm)
Length: 1983–1986: 197.6 in (5,019 mm), 1987–1988: 202.1 in (5,133 mm),
Width: 71.1 in (1,806 mm)
Height: 1983–1986: 53.2 in (1,351 mm), 1987–1988: 53.4 in (1,356 mm)
Ford Thunderbird (1983 - 1988)
Ninth Generation Thunderbird
The ninth-generation Ford Thunderbird, produced from 1983 to 1988, marked a bold reinvention of the model, both in terms of design and engineering. This generation introduced a dramatically sleeker, more aerodynamic shape that set it apart from its boxier predecessors and helped define a new design language for Ford. The Thunderbird’s new “aero” look, with its rounded lines and sloped roofline, represented a shift towards more streamlined, fuel-efficient cars that also captured the spirit of 1980s automotive style. This generation was well-received by the public, revitalizing interest in the Thunderbird and making it one of Ford’s most popular models during this period.
Under the hood, the ninth-generation Thunderbird offered a variety of engine options that catered to both efficiency and performance-oriented drivers. The base model came with a 3.8-liter V6 engine, while a 5.0-liter V8 was available for those seeking more power. However, the standout option was the turbocharged 2.3-liter inline-four found in the Thunderbird Turbo Coupe, which was introduced in 1983. This high-performance variant, with its turbocharged engine, sport-tuned suspension, and more aggressive styling cues, appealed to enthusiasts and marked a return to the Thunderbird’s sporty roots. In 1987, the Turbo Coupe was further enhanced with an intercooler, boosting its power to 190 horsepower, making it one of the most exciting Thunderbird models in years.
The ninth-generation Thunderbird’s interior continued to emphasize comfort and luxury, with a focus on driver-centric features. It offered plush seating, a spacious cabin, and advanced technology for the time, including digital dashboards and an optional premium audio system. The Turbo Coupe, in particular, stood out with its sporty interior details, such as bolstered seats and unique instrumentation. Ford’s commitment to both luxury and sportiness in this generation allowed the Thunderbird to attract a broader range of buyers, from those seeking a comfortable cruiser to enthusiasts interested in a high-performance experience.
The success of the ninth-generation Thunderbird reinforced Ford’s decision to embrace modern design and technology, proving that the brand could adapt to contemporary trends while honoring the model’s legacy. The “aero” Thunderbird left a lasting impression on the market, as it balanced innovative style with performance and comfort. Today, the 1983-1988 Thunderbird remains a celebrated example of 1980s automotive design, valued by collectors and enthusiasts who appreciate its unique blend of sportiness and sophistication.
Ford Thunderbird (1989 - 1997)
Tenth Generation Thunderbird
The tenth-generation Ford Thunderbird, produced from 1989 to 1997, represented one of the most advanced redesigns in the model's history, blending innovation, performance, and luxury in a more refined package. Built on Ford’s all-new MN12 platform, this Thunderbird was designed to offer improved handling and a smoother ride, incorporating independent rear suspension—an unusual and sophisticated feature for American cars of the time. The model’s updated aerodynamic design also reflected contemporary trends, with a smooth, rounded profile, flush headlights, and a sloping hood that gave it a modern, sleek look while keeping the Thunderbird’s unmistakable identity.
Under the hood, the tenth-generation Thunderbird initially offered two engine options: a naturally aspirated 3.8-liter V6 for the base model and a 3.8-liter supercharged V6 for the Thunderbird Super Coupe (SC). The Super Coupe, a high-performance variant, featured 210 horsepower and 315 lb-ft of torque, delivering impressive power for its class and ensuring the Thunderbird retained its performance heritage. The Super Coupe also included a variety of performance upgrades, such as a sport-tuned suspension, four-wheel disc brakes, and wider tires, which together made it one of the most capable American sport coupes of the era. Later in the model’s run, Ford also introduced a 4.6-liter V8 option in 1994, which provided a smoother, more relaxed driving experience for those seeking power with comfort.
Inside, the tenth-generation Thunderbird offered a comfortable and high-tech environment, aimed at drivers who valued luxury and modern amenities. The interior was spacious, featuring supportive bucket seats and a driver-oriented dashboard. Ford included several advanced features for the time, such as keyless entry, a premium audio system, and digital climate controls. The Super Coupe variant further emphasized driver engagement with bolstered sport seats and unique interior touches. This generation struck a balance between comfort and sportiness, attracting a wide range of buyers looking for either a relaxed grand tourer or a performance-oriented coupe.
The tenth-generation Thunderbird achieved considerable success during its production run, appealing to drivers who appreciated its combination of style, performance, and technology. However, as the 1990s progressed, consumer preferences began to shift toward SUVs and trucks, which ultimately impacted the Thunderbird’s market position. Despite its eventual discontinuation in 1997, the tenth-generation Thunderbird left a legacy as one of the model’s most innovative iterations, and it remains popular among enthusiasts who value its blend of performance, luxury, and sophisticated design.
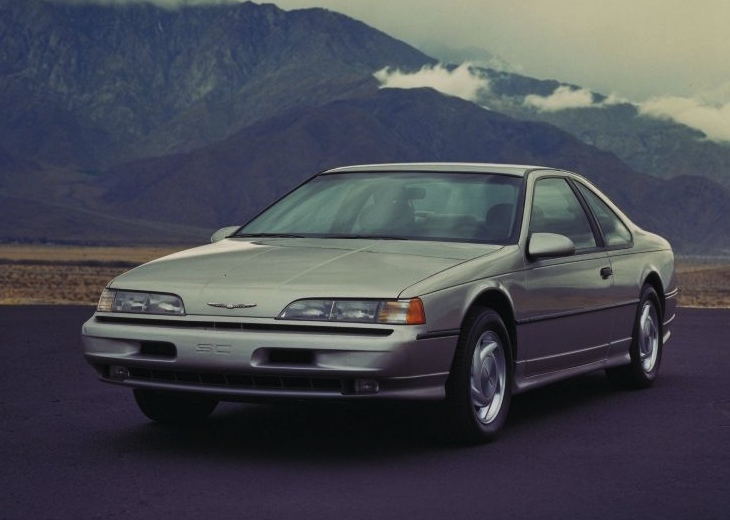

10th Gen Basics
Production: Oct 1988–Sep 1997
Model Years: 1989- 1997
Designer: Jack Telnack
Body style: 2-door coupe
Layout: Front-engine, RWD
Engine: 3.8 L Essex V6 (1989–1997), 3.8 L Essex supercharged V6 (1989–1995), 4.9 L small block V8 (1991–1993), 4.6 L Ford Modular V8 (1994–1997)
Transmission: 4-speed Ford AOD auto (1989–1993), 4-speed Ford AOD 4R70W auto (1994–1997), 5-speed Mazda M5R2 manual (1989–1995 Super Coupe only)
Wheelbase: 113.0 in (2,870 mm)
Length: 1989–1993: 198.7 in (5,047 mm), 1994–97: 200.3 in (5,088 mm)
Width: 1989–1995: 72.7 in (1,847 mm), 1996–1997: 73.2 in (1,859 mm)
Height: 1994–1997: 52.5 in (1,334 mm), 1994–1995 Super Coupe: 53.0 in (1,346 mm), 1989–1993: 52.7 in (1,339 mm), 1991–1993, Upper End Models: 53.1 in (1,349 mm)
Curb weight: 3,536 lb (1,604 kg) (1989 V6 model), 3,725 lb (1,690 kg) (1995 V8 model)
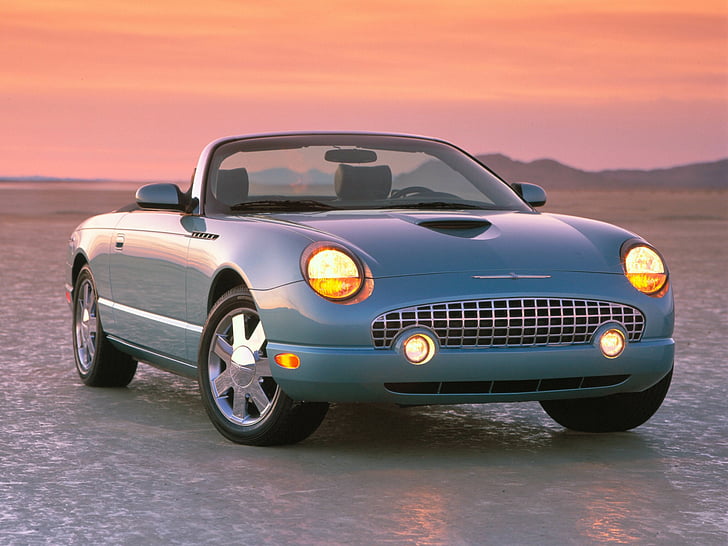

11th Gen Basics
Production: Jun 2001 – Jul 2005
Model years: 2002–2005
Designer: Jack Telnack
Body style: 2-door convertible
Layout: Front-engine, RWD
Engine: 3.9 L Jaguar AJ35 V8
Transmission: 5-speed Ford Bordeaux 5R44E auto
Wheelbase: 107.1 in (2,720 mm)
Length: 186.3 in (4,732 mm)
Width: 72 in (1,829 mm)
Height: 52.1 in (1,323 mm)
Curb weight: 3,775 lb (1,712 kg)
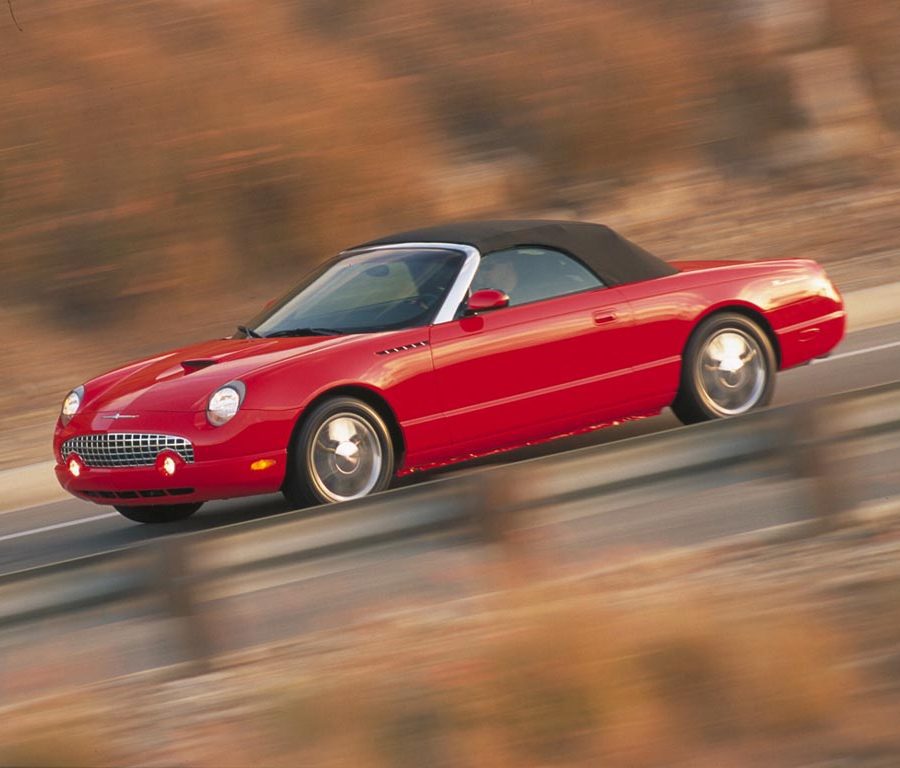
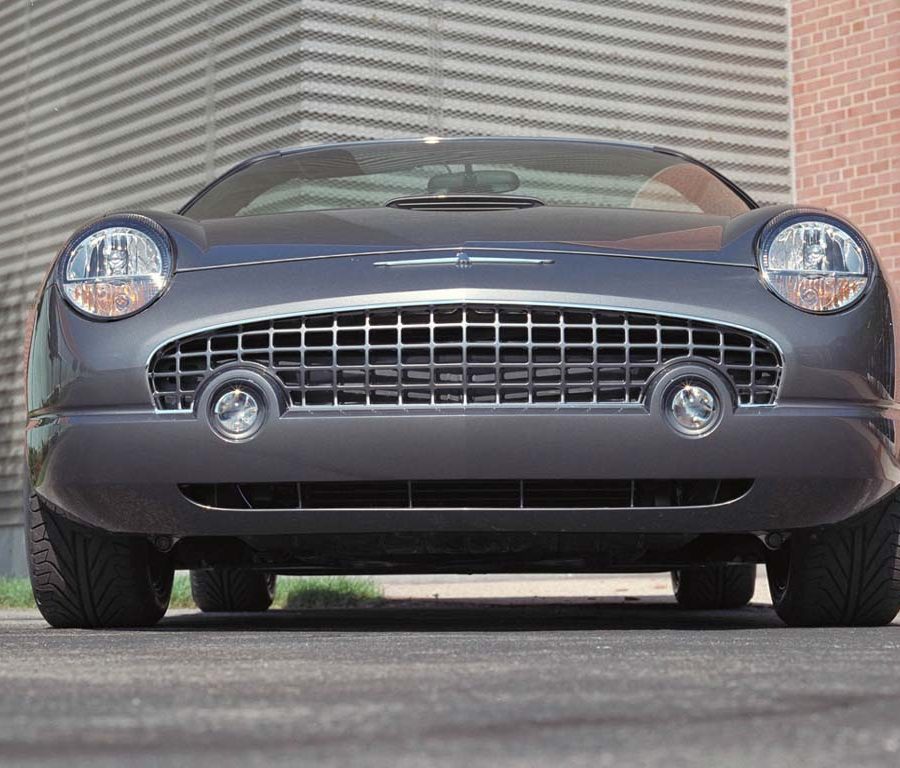
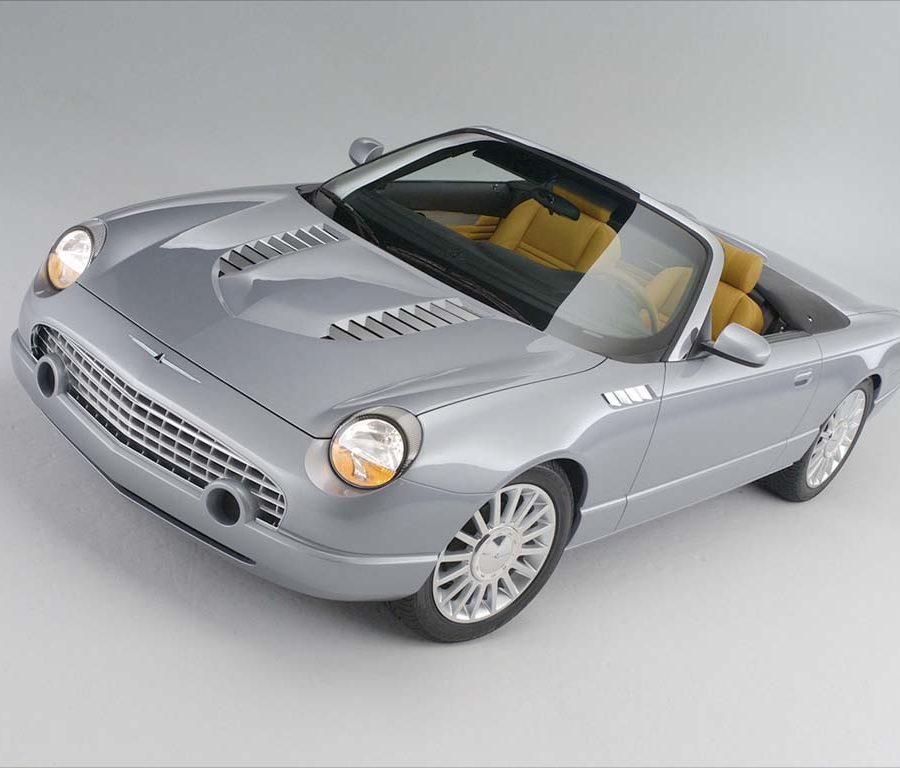
Ford Thunderbird (2002 - 2005)
Eleventh Generation Thunderbird
The eleventh-generation Ford Thunderbird, produced from 2002 to 2005, marked a nostalgic return to the model’s roots with a modern take on the classic two-seat convertible design that defined the original Thunderbird in the 1950s. Inspired by the styling cues of the iconic first-generation models, this Thunderbird featured retro elements such as round headlights, porthole windows on the hardtop, and a bold front grille. These design choices resonated with buyers who appreciated its tribute to Thunderbird heritage, and the car quickly became a statement of style, appealing to fans of both classic and modern aesthetics.
Under the hood, Ford equipped the eleventh-generation Thunderbird with a 3.9-liter V8 engine, producing 252 horsepower and paired with a five-speed automatic transmission. This powertrain allowed the Thunderbird to deliver a smooth and refined driving experience, ideal for cruising rather than aggressive performance. With rear-wheel drive and a comfortable, well-tuned suspension, the Thunderbird provided an enjoyable, relaxed ride reminiscent of the leisurely driving experiences that characterized early Thunderbirds. The combination of power and comfort made it a compelling choice for buyers seeking a unique personal luxury car with a hint of nostalgia.
Inside, the eleventh-generation Thunderbird emphasized comfort and style, featuring leather seats, brushed aluminum accents, and retro-inspired details that mirrored the car’s exterior design. Buyers could personalize their Thunderbirds with a range of bold color combinations, both inside and out, reflecting the playful spirit of the original model. The cabin offered advanced amenities for the time, including a premium audio system, power-adjustable seats, and modern safety features. These touches allowed the Thunderbird to compete in the personal luxury segment, combining a classic design ethos with contemporary convenience.
Though the eleventh-generation Thunderbird captured significant attention upon its release, it struggled to maintain momentum in a rapidly changing market increasingly dominated by SUVs and sports cars. Ford ultimately discontinued the Thunderbird in 2005, putting the model back on hiatus. However, this generation left a lasting impression as a beloved tribute to Thunderbird’s rich heritage, celebrated by collectors and enthusiasts who admire its design, luxurious cruising capability, and role in reviving a classic American icon for a new generation.
"From sleek coupes to powerful convertibles, the Thunderbird always evolved with the times, yet remained undeniably itself."
Sports Car Digest