As far as internal combustion engines go, V12 engines are at the zenith. This is while still acknowledging the omnipotent W16 motors seen in today’s Bugatti hypercars, while not forgetting the likes of mainstream automakers – such as BMW and Mercedes-Benz – also having flirted with the idea of series-production V16 engines in the past. With the 16-cylinder power plants essentially synonymous with the French automaker, the V12 is the de facto ruler for the broader spectrum of ultra-high-performance automobiles.
The diversity of this list fully demonstrates the universal appeal that V12s have around the world, to both producers and consumers alike. This unanimous and long-spanning support for the technology has helped to spawn some of the most impressive engines ever produced. The usual suspects are at play here, with Ferrari and Lamborghini making their totally not unexpected appearances. The British – via Aston Martin, Jaguar, and GMA – have shared their own highly impressive interpretations as well, while more conventional brands such as BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and even Toyota have had their say.
For the most part, these engines are naturally aspirated and characteristically rev all the way to the moon. In totality, each and every one of them is nothing short of a legend.
Here’s the shortlist of 10 such engines, curated for your reading pleasure:
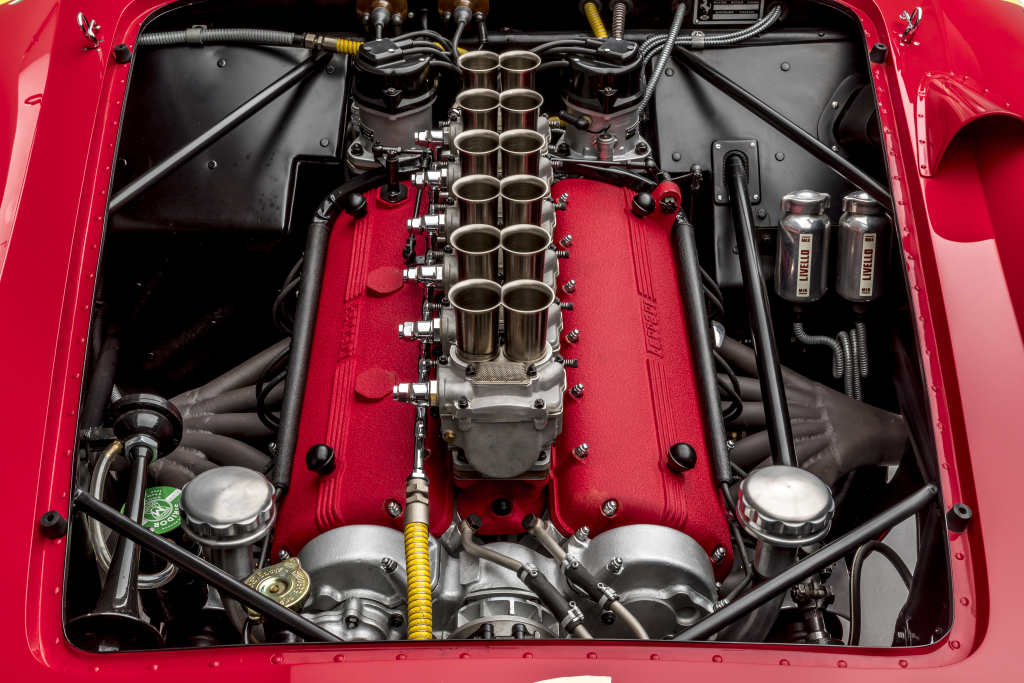
Ferrari Colombo V12
Originally designed by Gioacchino Colombo, this engine can trace its roots back to the very first Ferrari-branded model designed by Ferrari Enzo – the 1947 Ferrari 125 S – where it debuted as a 1.5L V12. The core design of the engine would persevere for more than 4 decades; along the way growing in size, having various levels of forced induction, and becoming a dual-overhead-cam configuration with EFI. Many credit the motor’s longevity to its reputation for being bulletproof.
Successful in both road-going and race track derivatives, the list of Ferrari cars this engine has graced has no shortage of automotive icons; the Ferrari 250 Testa Rossa, Ferrari 250 GTO, and Ferrari 365 GTB/4, just to name a few.
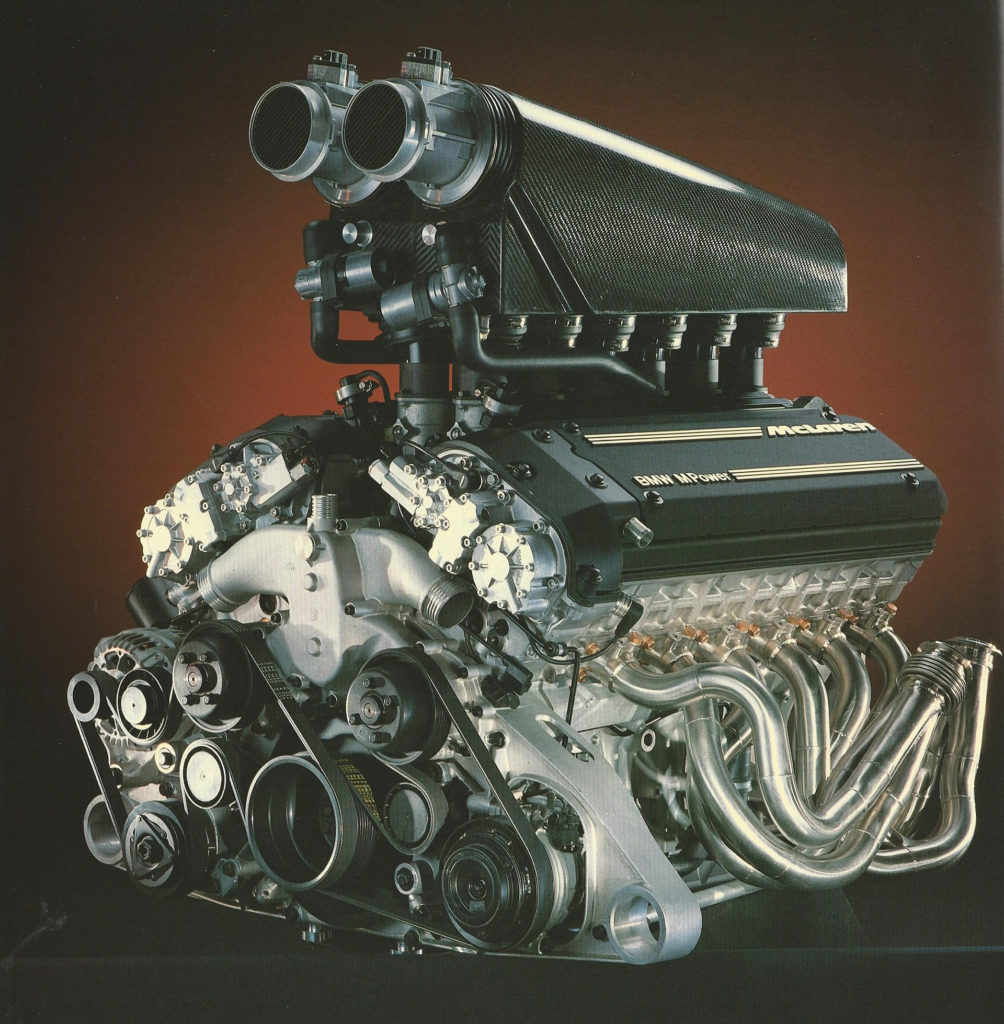
BMW S70/2
Despite being produced by BMW, the S70/2 didn’t feature in one of the Bavarian automaker’s own production cars. Nevertheless, it did end up powering none other than arguably the most iconic supercars ever made – the 1992-1998 McLaren F1. The 6.1L naturally-aspirated unit produced 627 hp and was capable of 0-60 mph in just 3.2 seconds, and had a top speed of 240 mph. It wouldn’t be until the next millennium before those figures could be surpassed.
Interestingly enough, BMW wasn’t Gordon Murray’s first choice to supply the engine for his groundbreaking supercar, with collaborations with the likes of Honda and Isuzu falling apart before they would opt for the Munich-built power plant. Whatever might’ve happened if things turned out differently, who’s to know? But what we do know is that BMW got things absolutely spot-on with the S70/2, which continues to be regarded as one of the true and timeless masterpieces in automotive history.
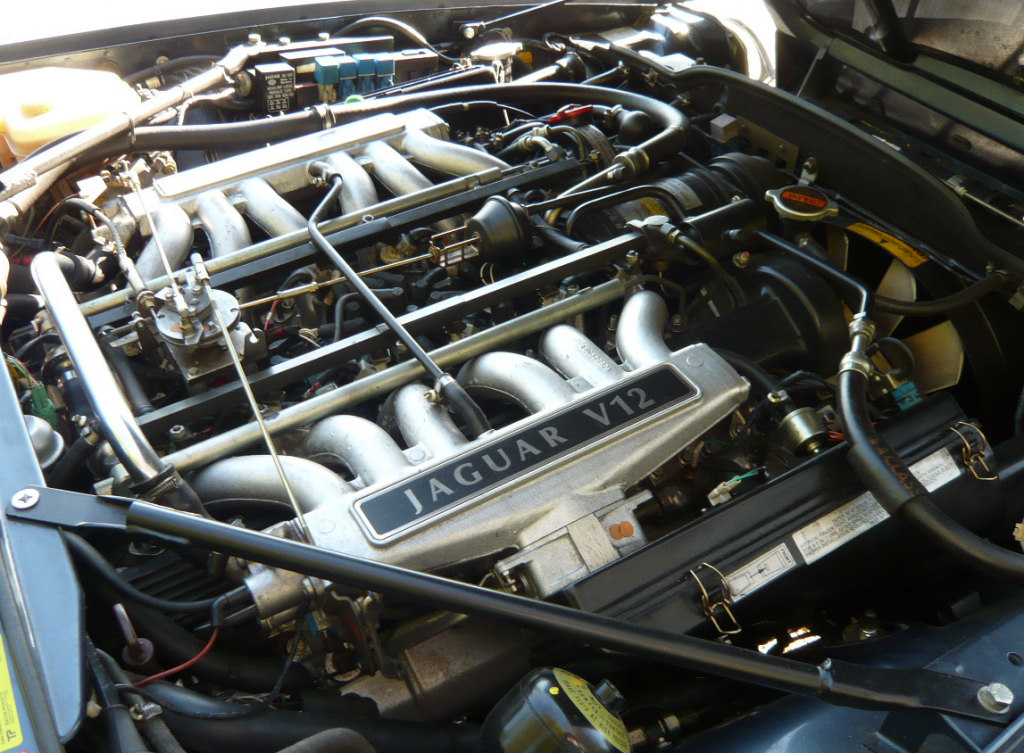
Jaguar V12
Jaguar’s first foray into the world of V12 engines began in motorsport as early as 1951, with its 1964 XJ13 Le Mans race car eventually serving as the trickle-down technology source for its production cars. For the latter, this would begin with a 5.3L naturally-aspirated unit in the 1971 Jaguar E-Type and would even go on to be used by other automakers such as Daimler and Panther. An HE (or “high-efficiency”) version of this engine would be released in 1981 – featuring on the XJ12, XJ-S, and Daimler Double-Six – which improved fuel economy by almost 50% compared to its predecessor, without affecting performance.
In its final iteration, the V12 would evolve into a 6.0L HE unit which produced as much as 333 hp and 365 lb-ft of torque. It was likely to be some variation of this engine which was initially being marketed for use on the Jaguar XJ220, before the British automaker controversially decided on a 3.5L twin-turbocharged V6 engine instead. The last Jaguar V12 engined was produced on April 17, 1997.
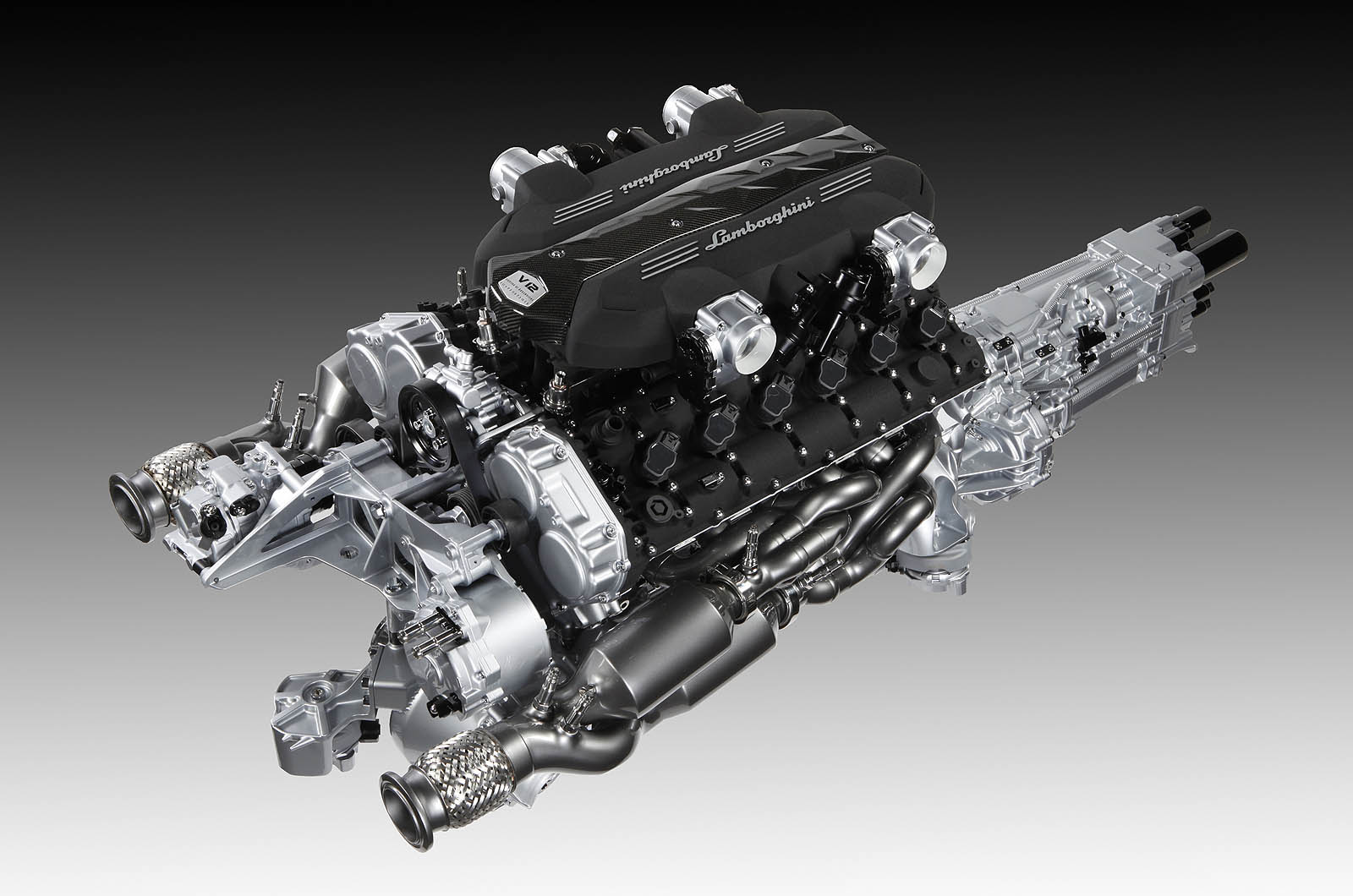
Lamborghini V12 L539
Like Ferrari, Lamborghini also has a long and storied history with V12 engines, having created its very own first version of this power plant for its mid-’60s era Lamborghini 350GT production car. Starting off as a considerably brawny 270 hp 3.5L naturally-aspirated unit, the “Bizzarrini” engine would evolve into a 661 hp 6.5L naturally-aspirated unit and be fashioned by models as recent as the 2010 Lamborghini Murciélago LP-670 SV.
As long as the Bizzarrini engine persisted, we feel that the most significant statement of Lamborghini’s V12 mastery comes in the form of its latest iteration of the engine, dubbed ‘L539’. This power plant would share its debut with the 2011 Lamborghini Aventador, of which it initially powered with 690 hp via a 6.5L naturally-aspirated configuration. With a fresh design, the new engine was over 18 kg lighter than its predecessor and was programmed with a new firing order. The all-wheel-drive supercar would see significant improvements during its lifecycle, with the latest iteration of the L539 car producing 770 hp in the limited-edition 2021 Lamborghini Aventador Ultimae.
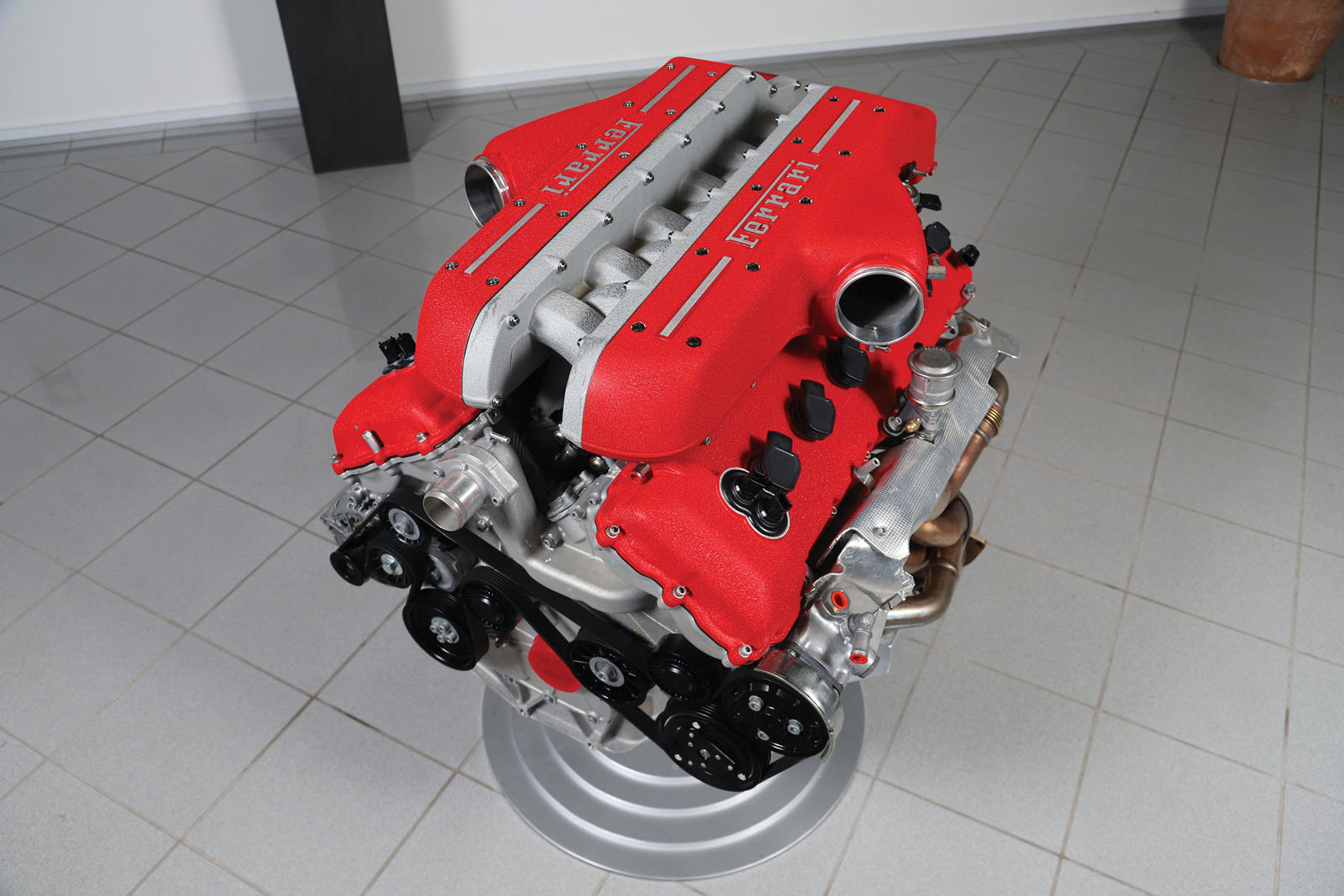
Ferrari F140
If the F140 had only powered the (2002-2005) Ferrari Enzo – the first Prancing Horse model where it featured – it would have been no less significant or legendary than it is today. The 65-degree V12 engine debuted on the Enzo as a 6.0L naturally-aspirated V12 unit which produced a staggering 651 hp @ 7,800 rpm and 458 lb-ft of torque @ 5,500 rpm. Over the years, 6.3L versions of the F140 have powered the likes of the hybrid LaFerrari and the F12berlinetta.
It has since evolved to its current peak as a 6.5L power plant – dubbed the F140 GA – which produces 789 hp @ 8,500 rpm and 530 lb-ft of torque @ 7,000 rpm in the 812 Superfast; this makes it the most powerful naturally-aspirated production car engine ever produced to this day. It is likely that this could be one of the final generations of Ferrari V12 engines – whether it be naturally aspirated, turbocharged, or even hybridized – so appreciate it while it’s still around!
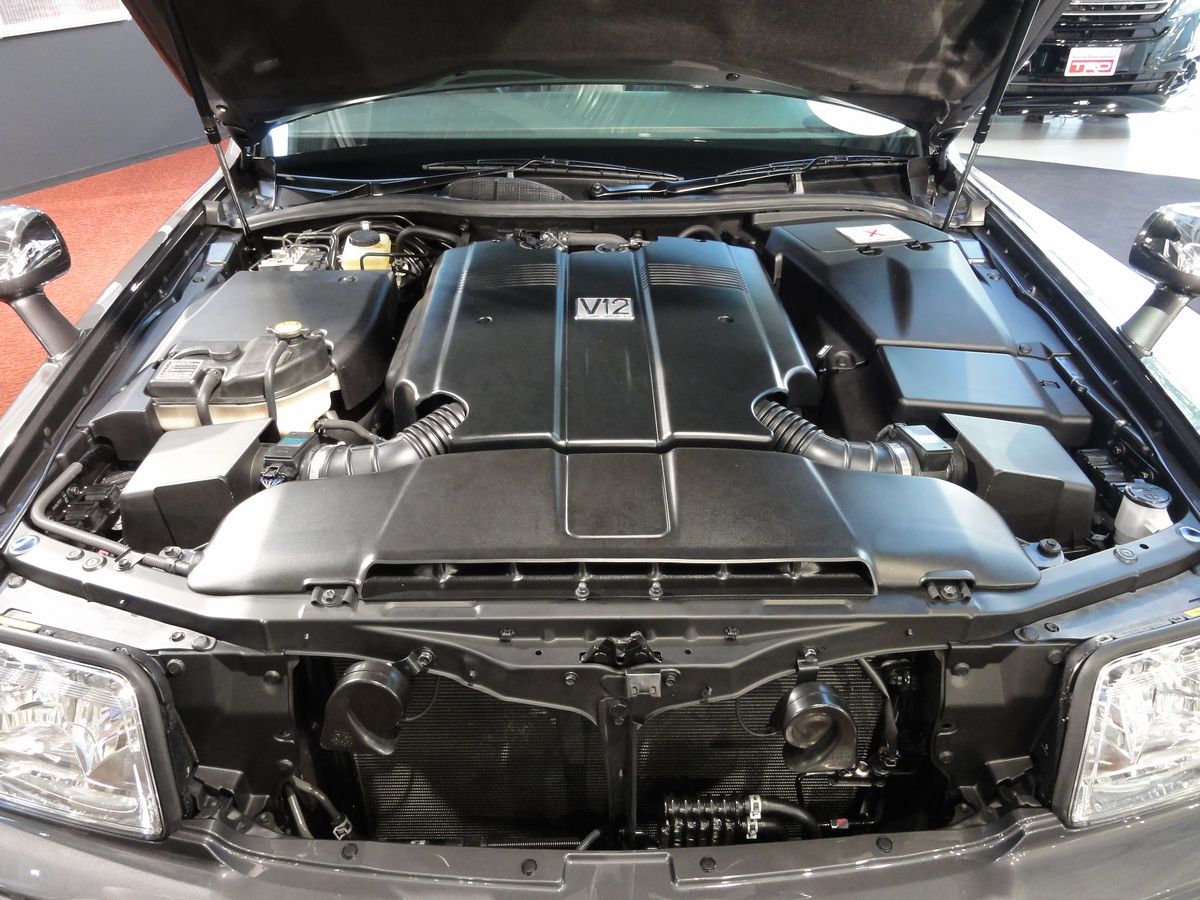
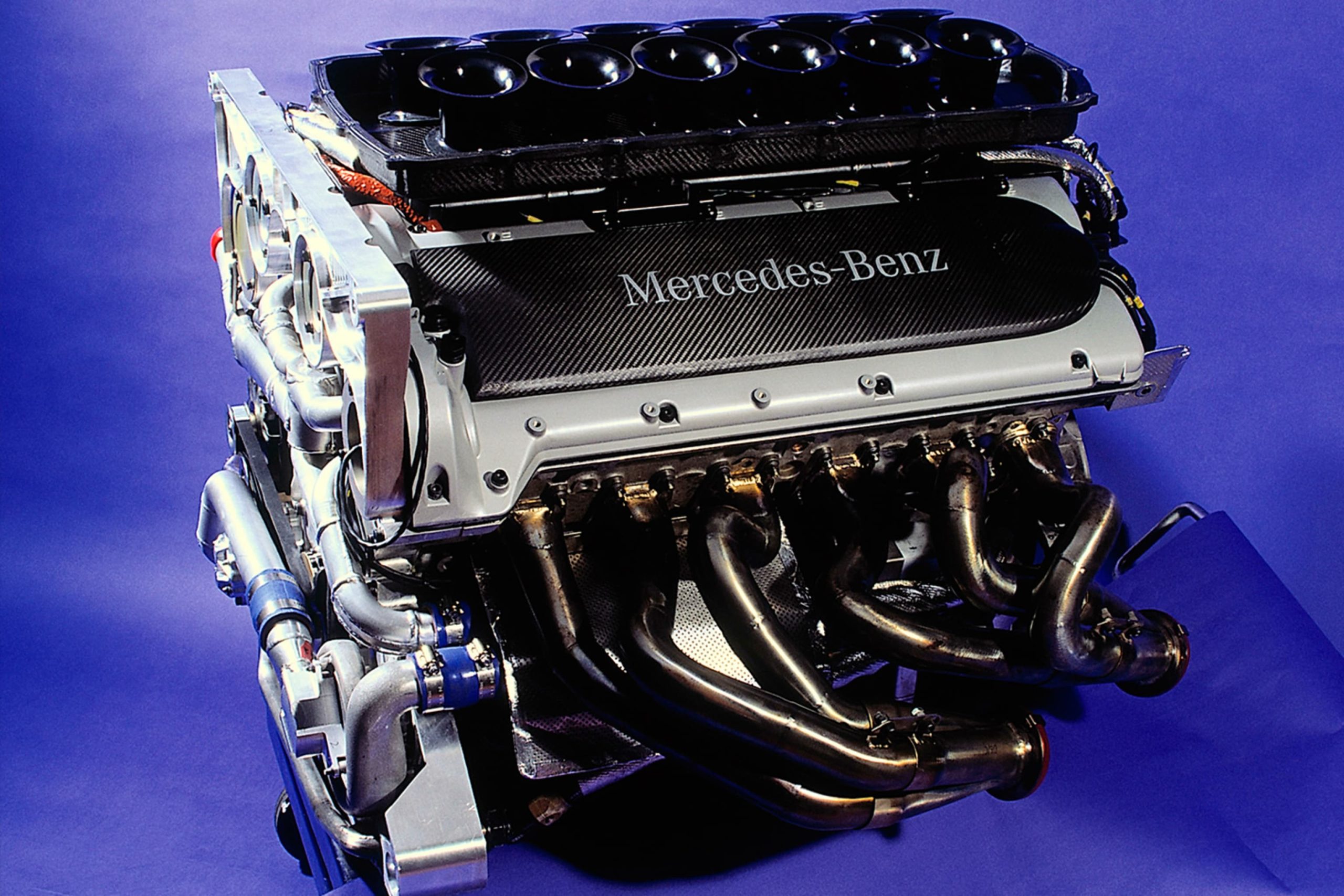
Mercedes-Benz M120 / M297
When Mercedes-Benz caught wind of archrival BMW’s side-hustle with Gordon Murray, let’s just say that there was no resting on any laurels going on at their Stuttgart headquarters. With a clever riposte, Mercedes would debut their first-ever V12 engine through the 1993 600 SEC (later to be renamed the S600 Coupé, and frequently referred to as the S-Class). The 6.0L naturally-aspirated power plant was good for 389 hp, 420 lb-ft of torque, and a top speed of 155 mph in its initial configuration.
Not only did Mercedes-Benz one-up BMW by using the engine for their own cars, but they also borrowed a page from their opponent’s playbook and had their M120 engine fashioned for use in the magnificent Pagani Zonda supercar as well. Hand-built and tuned by AMG, the M120 also featured on the Mercedes-Benz CLK GTR race car and also saw its displacement increased to 7.3L for use on the SL73 AMG and CL73 AMG – and at which point it was commonly referred to as the M297. The most powerful iteration of the M120 features in the Pagani Zonda Revolución, with the non-street-legal car good for 789 hp and 538 lb-ft of torque.
Aston Martin NA V12
With one of the best sounding V12s (and automobile engines, period), the story of how the Aston Martin (naturally-aspirated) V12 came to be is rather more peculiar and convoluted. The project had less, should we say, glamorous beginnings, when things basically started off with the development of a 2.5L naturally-aspirated V6 engine. This particular unit was essentially the brainchild of Suzuki and Mazda, with the latter’s then-majority owner, Ford, then taking the blueprint to Cosworth, who would go on to build the Duratec V6.
Needless to say, the story didn’t end there, and Aston Martin would end up bolting two of those engines together to create the 5.9L naturally-aspirated V12 it would stamp its name on (and market as a 6.0L). Having more in common with a Ford Taurus than owners or enthusiasts would like to admit, the motor produced 414 hp and 398 lb-ft of torque in the 1999 DB7 V12 Vantage. Aston Martin continues to employ a V12 engine to this day, with the 2017 DB11 having fashioned a 5.2L twin-turbocharged version. More recently, the company has referred back to the naturally-aspirated configuration, with a 6.5L unit designed to power its Valkyrie hypercar with over 1,000 hp @ 10,500 rpm (plus an additional 160 hp with its hybrid-electric system).
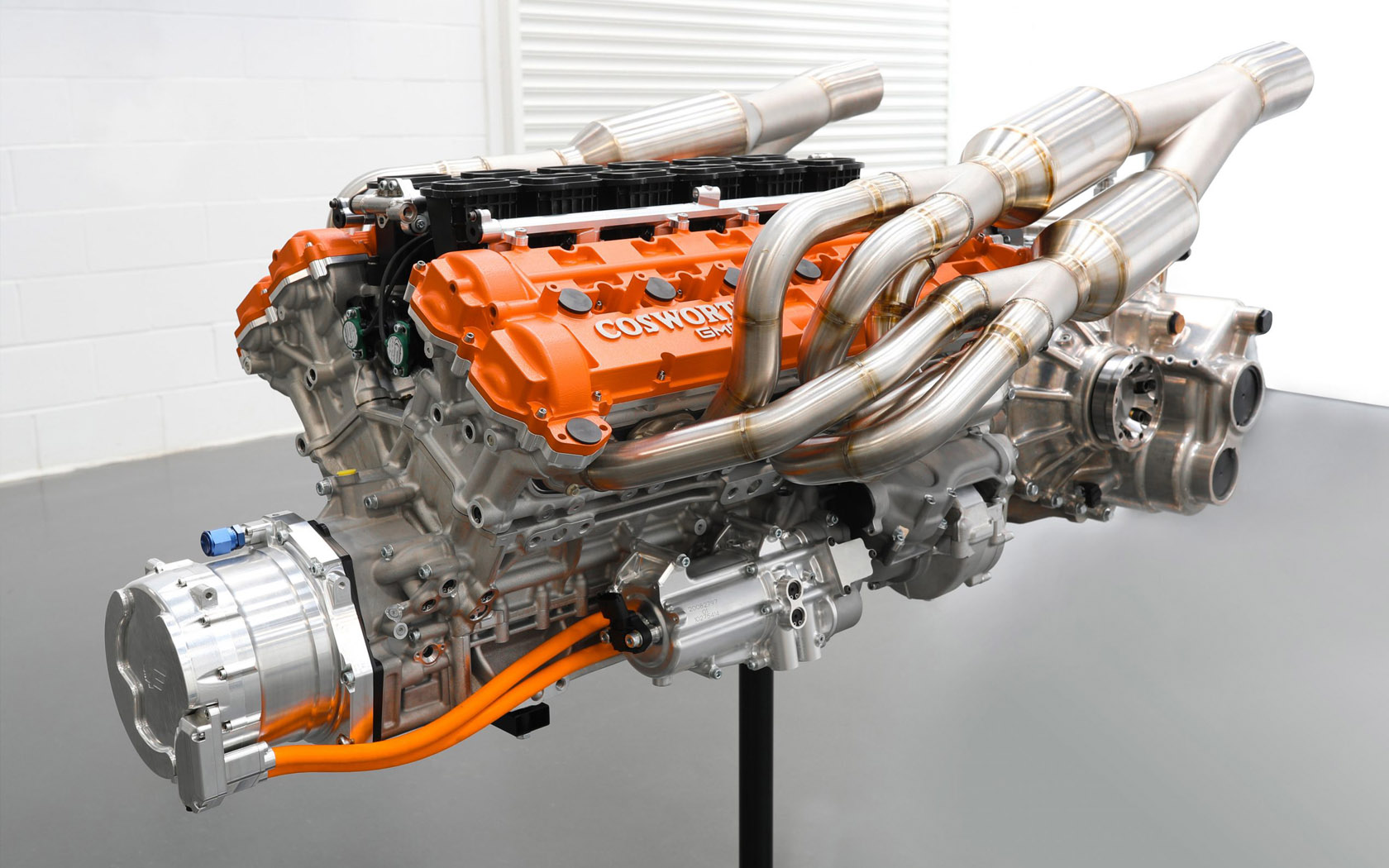
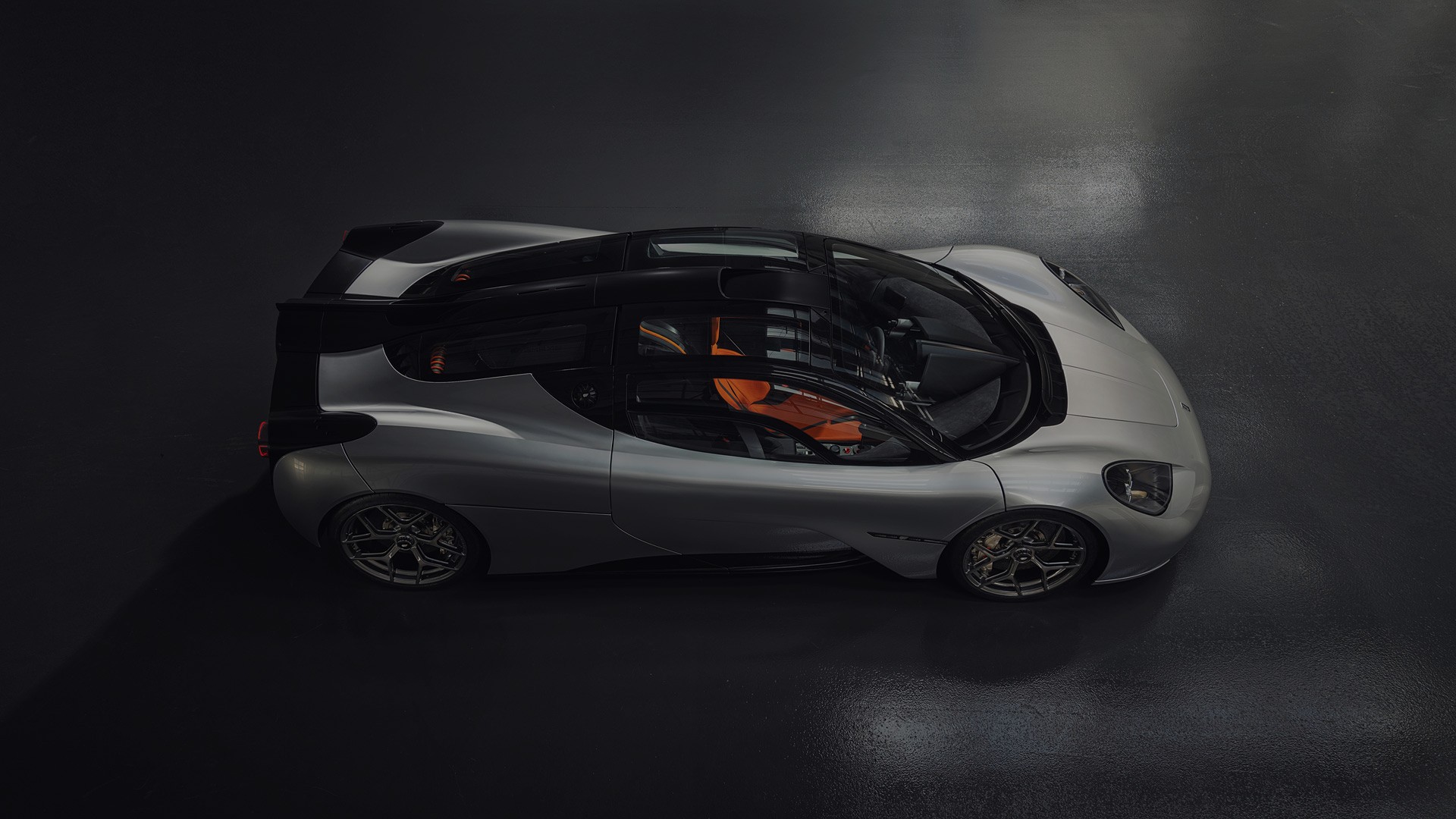
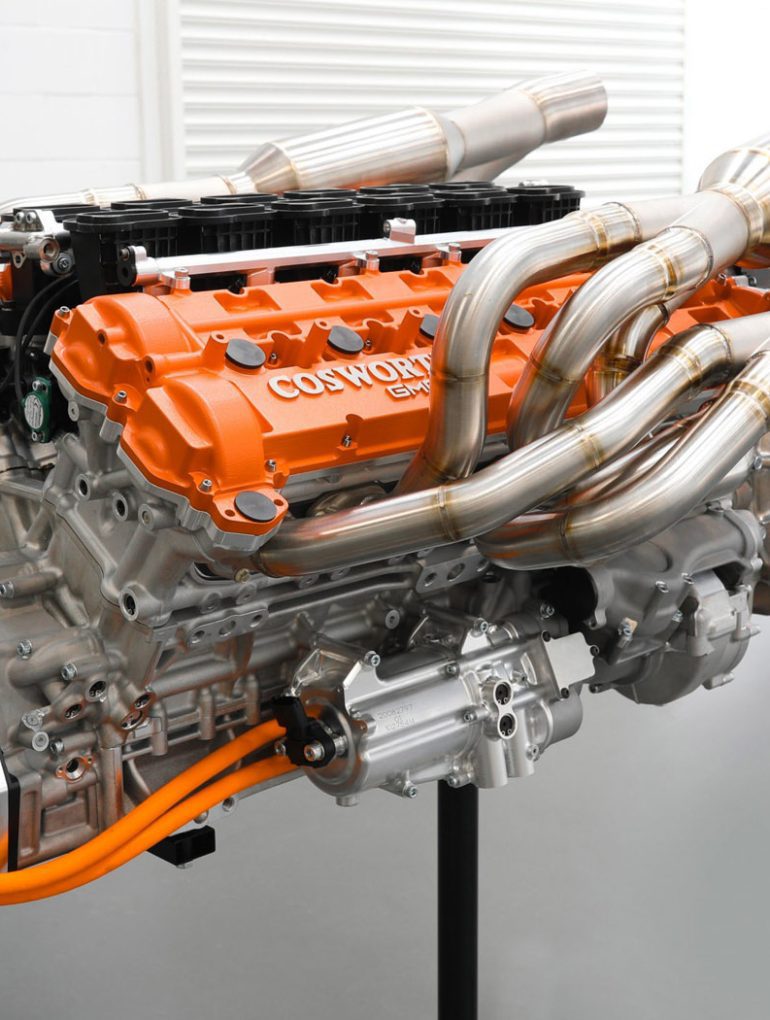
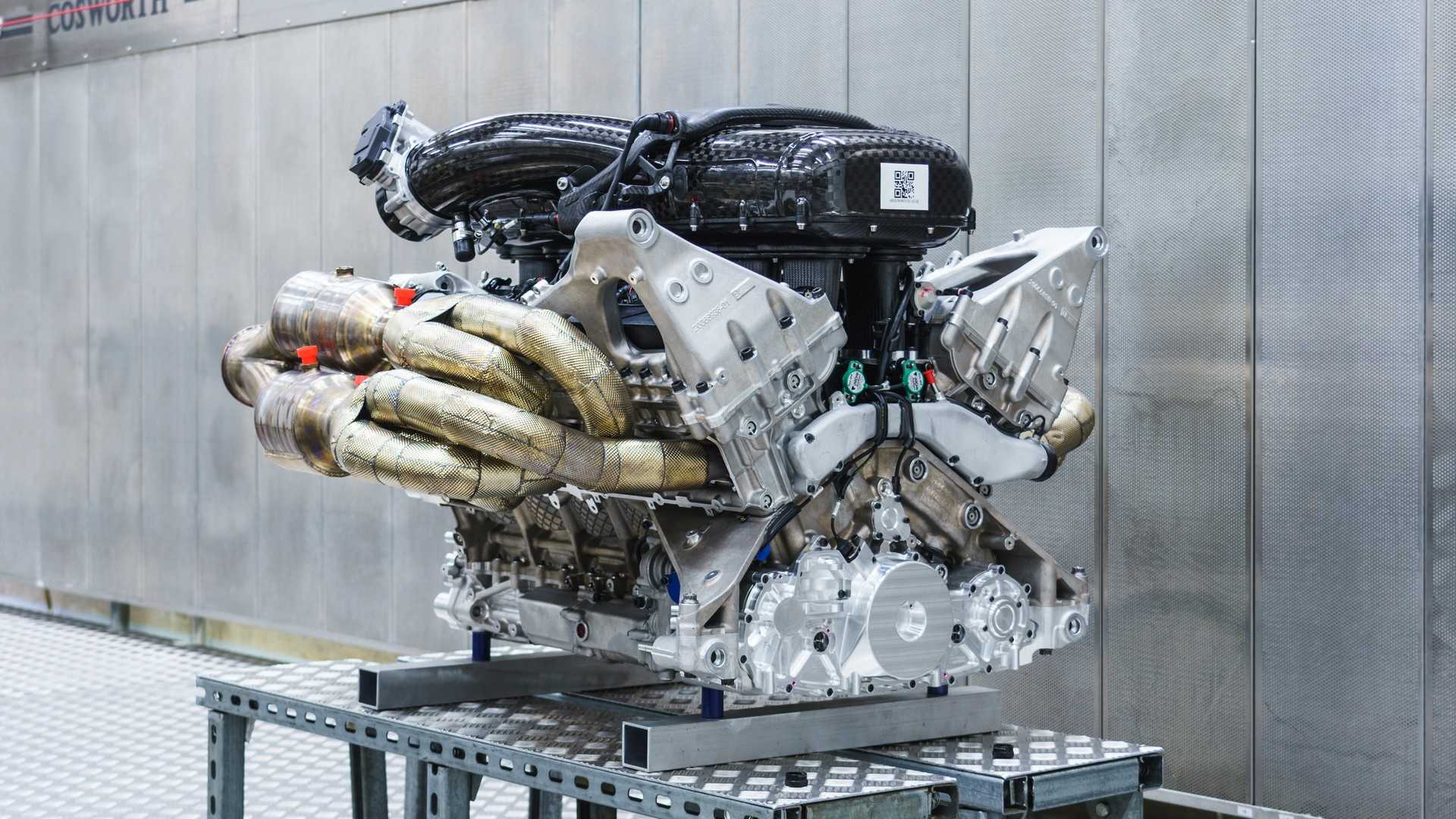
GMA Cosworth V12
It’s impossible to speak about the naturally-aspirated engine in the GMA T.50, without getting into how it’s involved in so much more than just spinning the new supercar’s rear wheels, or about how other design elements of the car are built around it. As impressive as a 12,100 rpm redline sounds, its 654 hp and 345 lb-ft of torque doesn’t sound extraordinary by today’s standards. But rest assured this engine, and this car, are on the cusp of a truly “redefining” moment in automotive history. Crucially weighing at just 178 kg, the engine plays a huge factor towards the T.50’s overall curb weight of just 980 kg – about one-third that of a contemporary supercar or hypercar.
The GMA T.50 is the culmination of decades of Gordon Murray’s aerodynamic and mechanical engineering experience. Part of what makes the T.50 so exciting, is that it incorporates the design and function of the infamous Brabham BT46 “Fan Car.” A gigantic fan – powered by the camshaft of the engine and coupled with the curved underbody of the BT46 – created an active venturi effect that quite literally vacuumed the car onto the road, and allowed it to corner at barely believable speeds and levels of grip. The T.50 will feature something similar, and likely more advanced. On a road car. We can’t wait to see this in the flesh.
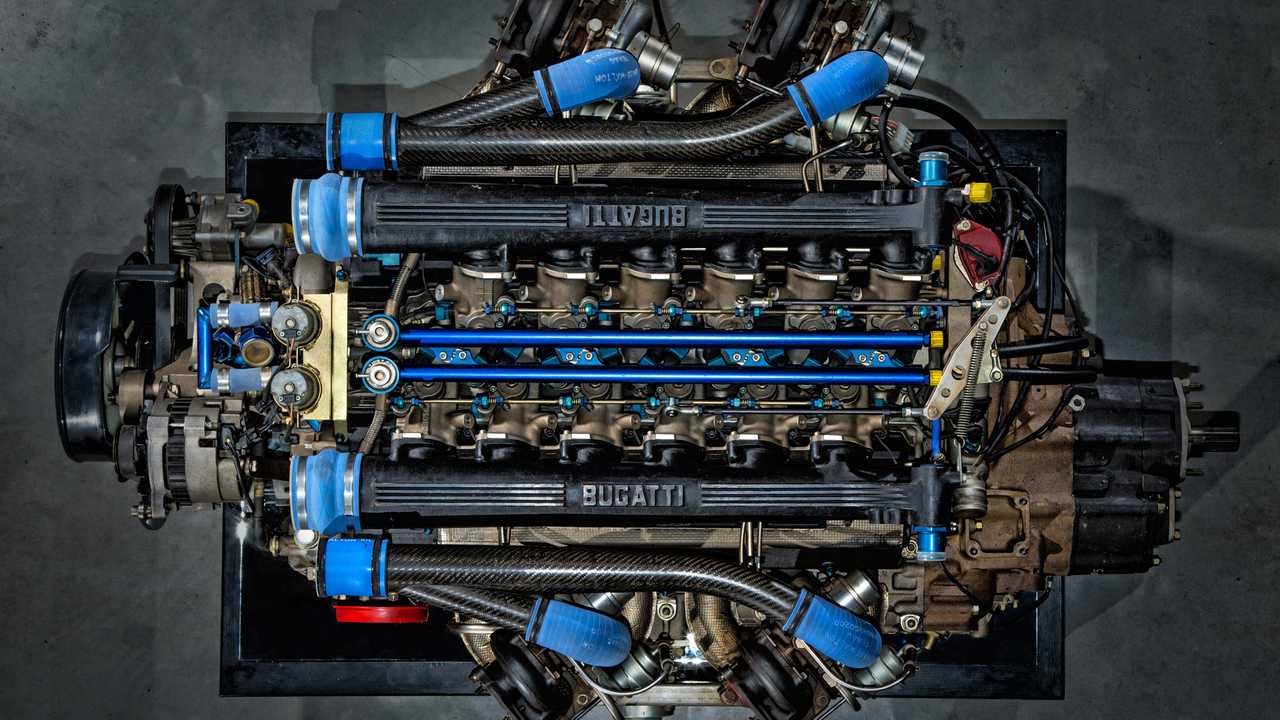
Bugatti 3.5L Quad-Turbocharged V12
This Bugatti engine has had a very decorated career, albeit a short one, which makes it all the more impressive. Featured exclusively on the (1991-1995) Bugatti EB110, this 3.5L quad-turbocharged V12 is responsible for some very notable distinctions. First, it is widely regarded as being one of the catalysts in the revival of the French marque even though it failed to be directly responsible for this. It became the world’s fastest production car of its time, beating the Jaguar XJ220 in the process.
Suffice to say, it grabbed all the headlines, and really, that was the whole point. I mean, for what other purposes would the use of four turbochargers be given the green light for? Sure, it produced a whopping 553 hp and 450 lb-ft of torque, but you would have to argue that this likely could’ve been achieved with a more conventional design. After all, quad-turbocharged engines never really proliferated, and there’s probably good science behind why that’s been the case. Nevertheless, there’s nothing un-iconic about a V12 engine with almost as many turbochargers as you can count on one hand; and we love it all the same.