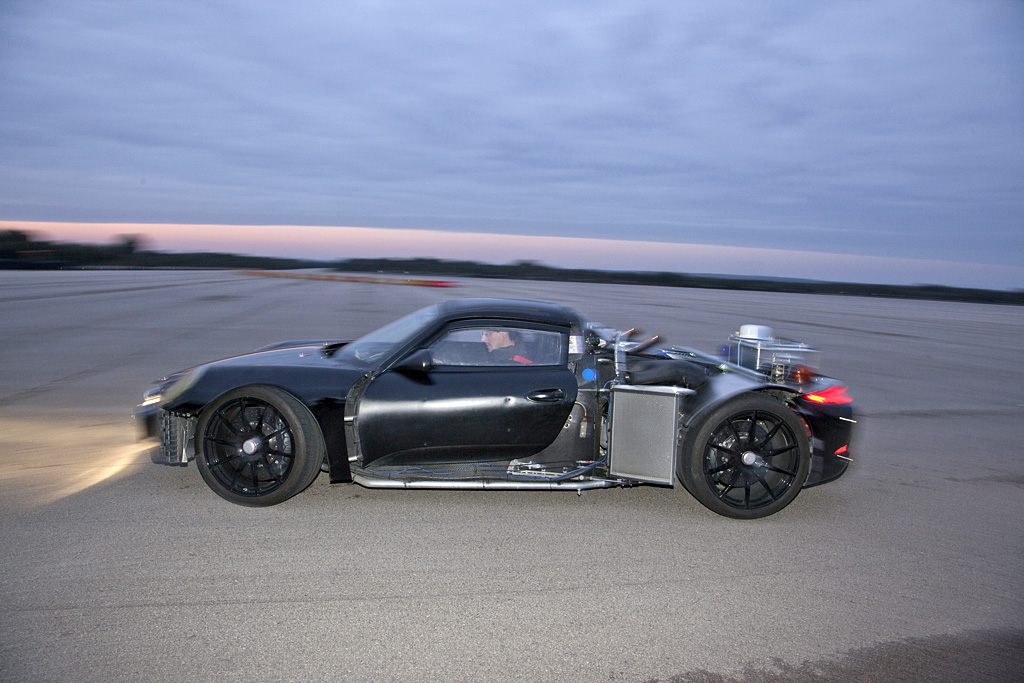
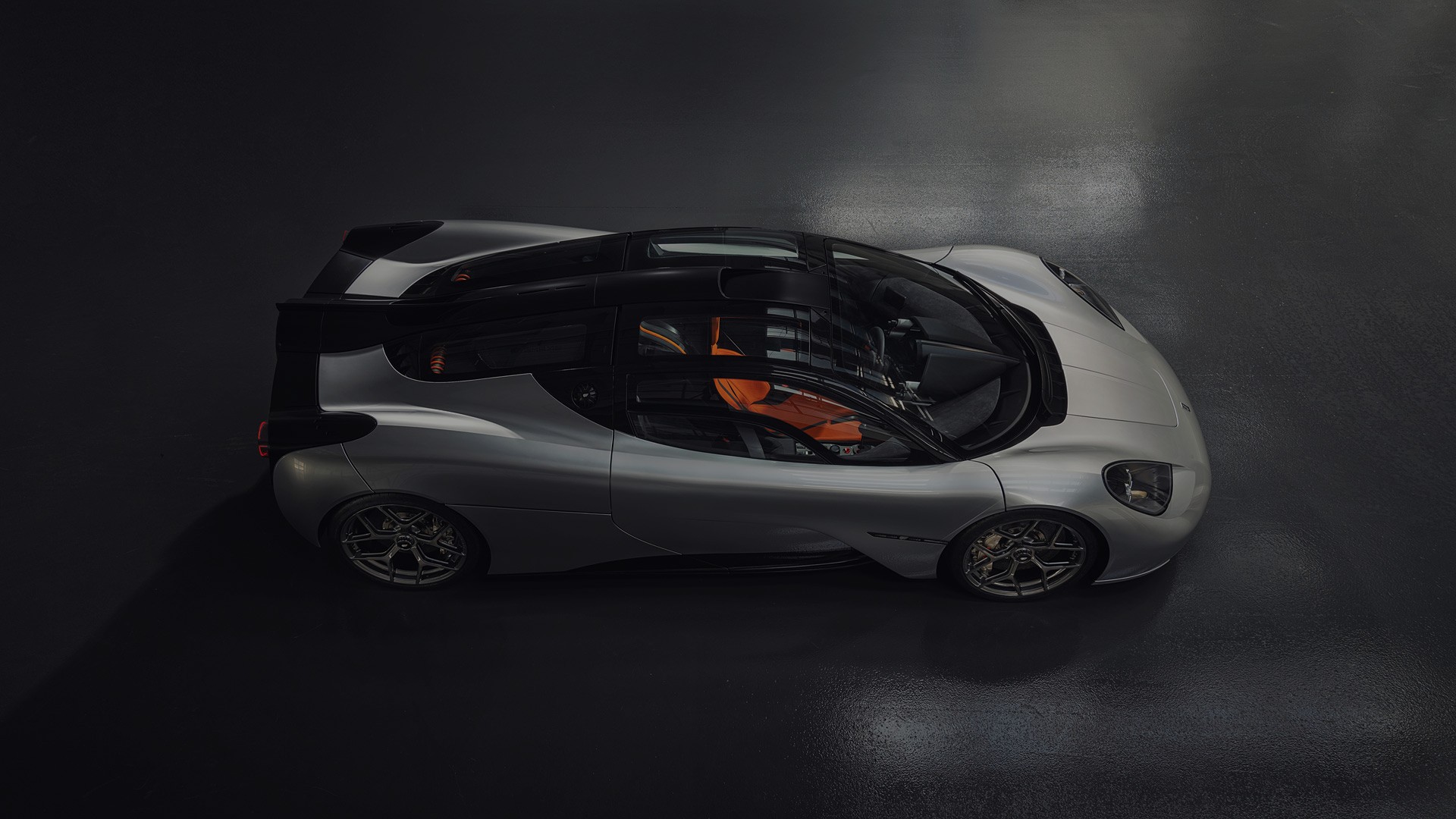
2012 Porsche 918 Spyder Prototyp
With two electric engines and a V8 based of their RS Spyder Le Mans prototype, Porsche will offer one of the world’s first plug-in electric supercars in 2013.
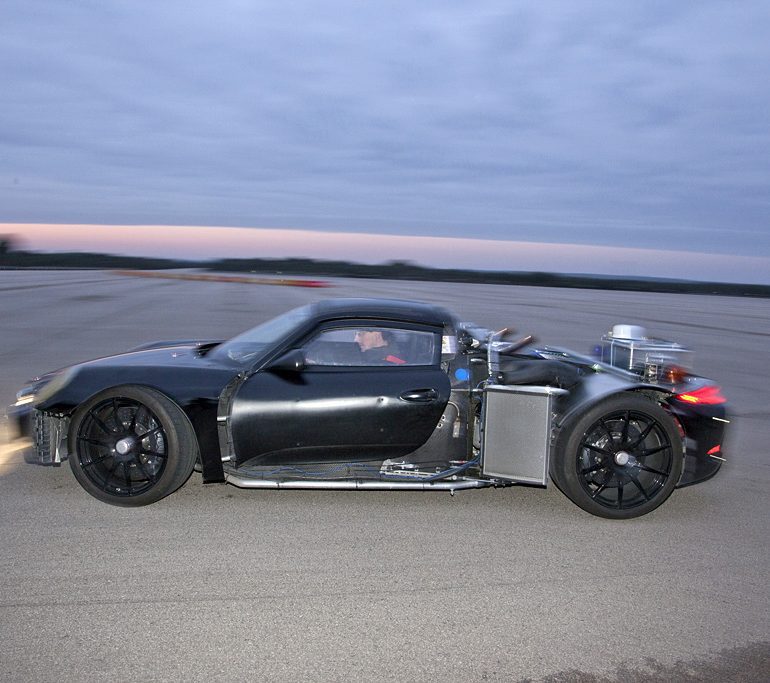
The 918 is the result of many years development by Porsche to offer a performance car that can handle the inherent weight of a lithium ion battery.
At the core of the 918 is a dry-sump V8 that can offer 570 genuine bhp. This is aided by an inline electric engine coupled to the transmission to the rear wheels and a separate electric engine and decoupler that handles the front axle. This offers a total output of 770 bhp while the car is in Hot Lap mode.
Press Release.
The future is taking shape: with more than half of its development time completed, the Porsche 918 Spyder is firmly on course to become the super sports car of tomorrow. As a plug-in hybrid vehicle, it logically combines a high-performance combustion engine with cutting-edge electric motors to deliver performance that is beyond extraordinary: the best of both worlds endows the 918 with the dynamics of a racing car packing more than 770 hp of power accompanied by fuel consumption, which at approximately three litres per 100 kilo -metres, is less than that of most modern compact cars. Moreover, Porsche is breaking yet more new ground with the technology demonstrator with spectacular solutions such as the full carbon fibre reinforced plastic (CFRP) body, fully adaptive aerodynamics, adaptive rear-axle steering and the upward-venting “top pipes” exhaust system. In the process, the 918 Spyder is offering a glimpse of what Porsche Intelligent Performance may be capable of in future.
The 918 Spyder has been designed as a super sports car and the legitimate successor to the Carrera GT. As such, the first goal was obvious: improving yet again on the Carrera GT’s performance. As far as is currently known, the 918 Spyder will be significantly faster – both in terms of acceleration and also performance on the racing circuit: less than three seconds from zero to 100 km/h (Carrera GT: 3.9 seconds) and less than 7:22 minutes on the Nürburgring Nordschleife (Carrera GT: 7:32 minutes) is an unmistakable statement. However, the uniqueness of the 918 Spyder is best represented by the union of outstan -ding performance with a level of efficiency never seen before in the super sports car sector.Fuel consumption of approximately three litres per 100 kilometres and an electric rangein excess of 25 kilometres are unprecedented.
five modes for three motors
The core of the 918 Spyder concept is the distribution of propulsive power across three power units, collaboration between which is controlled by an intelligent management system using five pre-selectable modes. This operating strategy is a core competency of the 918 Spyder. It takes the best possible account of the different requirements between an efficiency-orientated driving profile on the one hand and maximum performance on the other. In order to make the best possible use of these different approaches, the Porsche developers defined a total of five operating modes that can be activated via a “map switch” in the steering wheel, just like in motor sports cars.
When the vehicle is started up, the “E-Power” mode is the default operating mode as long as the battery is sufficiently charged. In ideal conditions, the 918 Spyder can cover more than 25 kilometres on purely electric power. In this mode, the combustion engine is only used when needed: maximum engine power is available at a moment’s notice by means of the kick-down function. If the charge state of the battery falls below a set minimum value, the vehicle automatically switches to hybrid mode.
“Race Hybrid” is the mode for the highest possible performance and especially sporty dri -ving style. The combustion engine is chiefly used under high load, and charges the battery when the driver is not utilising the maximum output. The electric motors provide additional support as necessary in the form of a boost when the driver requires even more power. The electric motors are used up to the maximum power output limit in order to provide the best possible performance for the race track. In this mode, the battery charge state is not kept constant, but instead fluctuates across the entire charge range. In contrast to Sport Hybrid mode, the electric motors run at their maximum power output limits for a short time, thus ensuring better boosting. This increased output is balanced out by the combustion engine charging the battery more powerfully.
The “Hot Lap” button in the middle of the map switch releases the 918 Spyder’s last reserves and can only be activated in “Race Hybrid” mode. Similar to a qualification mode, this pushes the traction battery to its maximum power output limits for a few fast laps. This mode uses all of the available energy in the battery.
Main propulsion
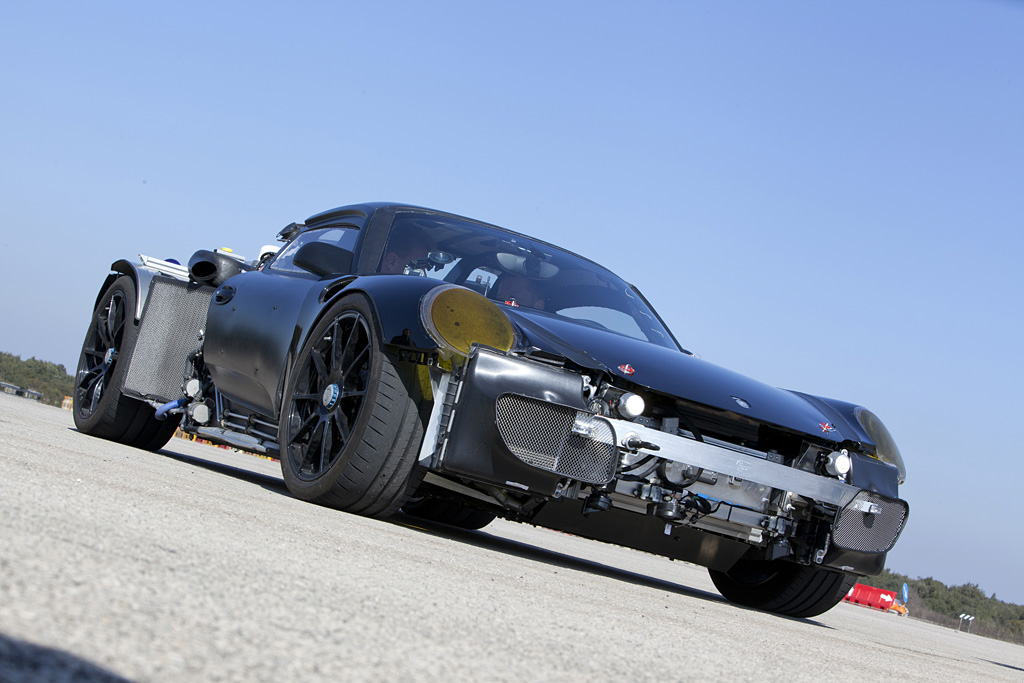
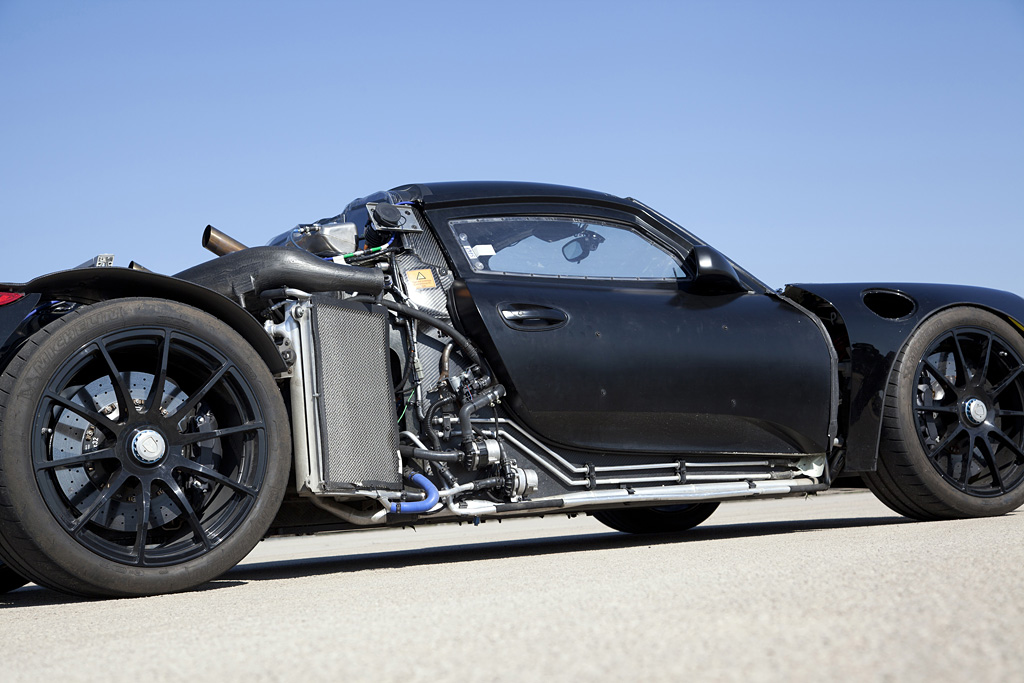
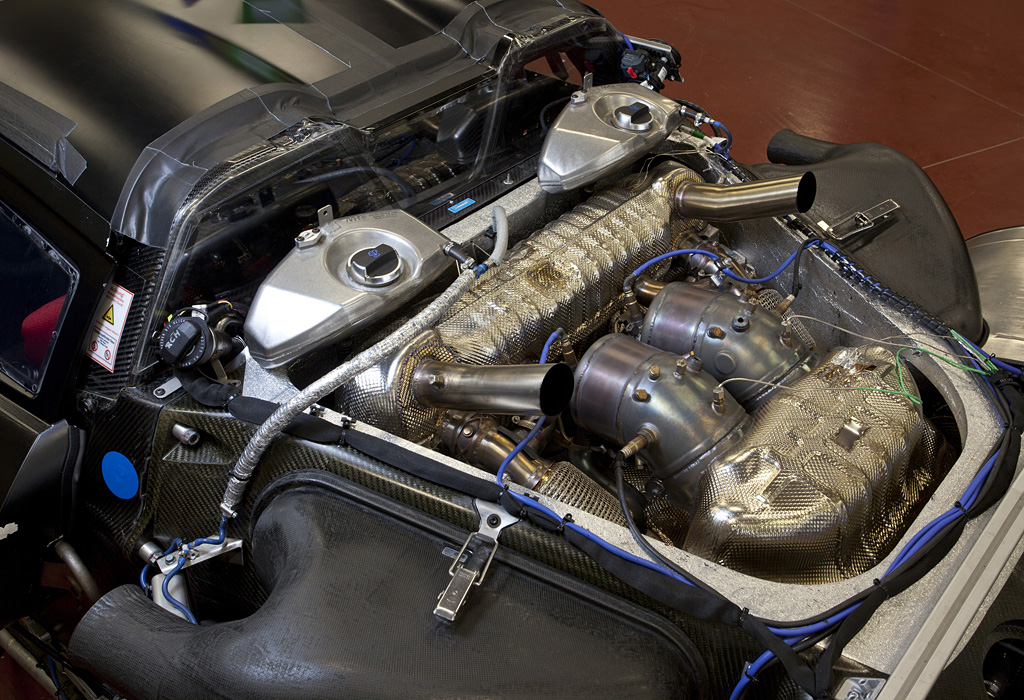
The main source of propulsion is the 4.6-litre, eight cylinder engine delivering more than 570 hp of power, which was directly derived from the power unit in the successful RS Spyder and explains why it delivers engine speeds of up to 9,000 rpm. Like the RS Spyder’s racing engine, the 918 Spyder power unit features dry-sump lubrication with a separate oil tank and oil extraction. In order to save weight, the four extraction pumps are made of plastic. Further extensive lightweight design measures resulted in, for example, titanium connec -ting rods, thin-wall, low-pressure casting on the crank case and the cylinder heads, a high-strength, light-weight steel crankshaft and the extremely thin-walled, alloy steel exhaust system. The result of the weight and performance optimisations is a power output per litre of approx. 125 hp/l, which is significantly higher than that of the Carrera GT (106 hp/l) and outstanding for a naturally aspirated engine.
The V8 engine is coupled to the hybrid module, the 918 Spyder being designed as a parallel hybrid like Porsche’s current hybrid models. Essentially, the hybrid module comprises a 90 kW electric motor and a decoupler acting as the connection with the combustion engine.As a result of the parallel hybrid configuration, the 918 Spyder can be powered at the rear axle both individually by the combustion engine or electric motor or via both drives jointly. As is typical for a Porsche super sports car, the power pack in the 918 Spyder has been placed in front of the rear axle, and does not have any direct mechanical connection to the front axle.
Top Pipes
It isn’t just this engine’s performance but also the sound it makes that stokes the emotionality of the 918 Spyder.
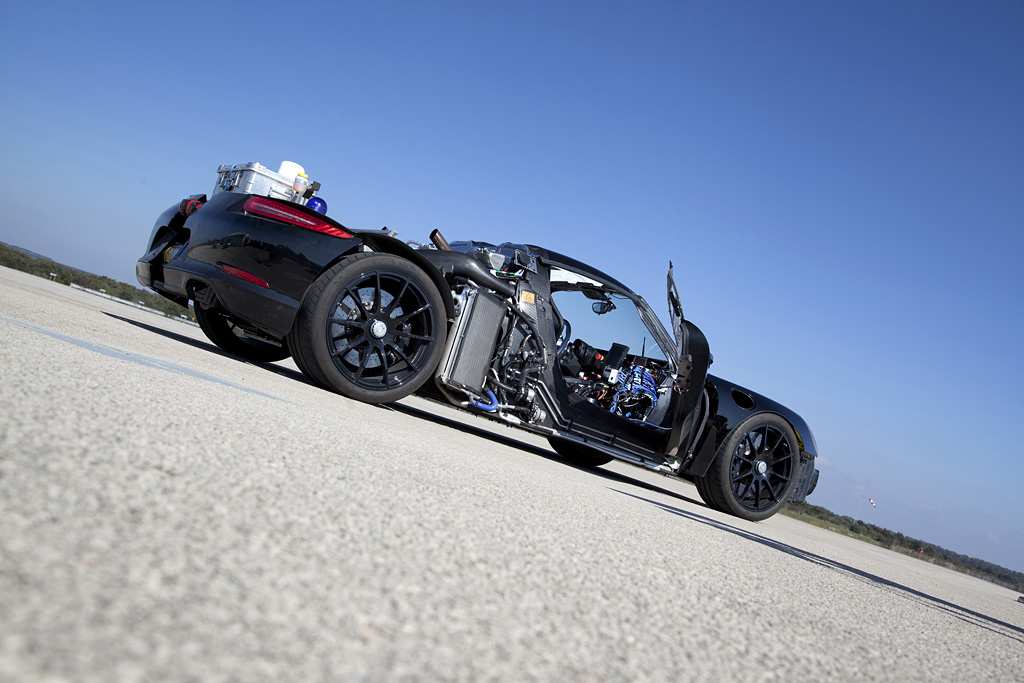
This is attributable first and foremost to the so-called top pipes: the tail -pipes terminate in the upper part of the rear end immediately above the engine. No other production vehicle exhibits this solution. The top pipes’ greatest benefit are the extremely short distances, as the hot exhaust gases are evacuated by the shortest, direct route and the exhaust gas back pressure remains low. This design requires a new, thermodynamic air channelling concept: With the HSI engine, the hot side is located inside in the cylinder V, the intake tracts are outside. There’s a further benefit: the engine compartment remains cooler. This is especially beneficial to the lithium-ion hybrid battery, as it provides optimum perfor -manceat temperatures between 20 and 40 degrees Celsius. As such, less energy needs to be used for active cooling of the battery.
A seven-speed Doppelkupplungsgetriebe (PDK) transmission takes care of power transmission to the rear axle. The high-performance transmission based on the PDK in the 911 Turbo has undergone a complete overhaul for the 918 Spyder and was further optimised for high performance. In order to ensure that the installation position and thus the centre of gravity of the entire vehicle were kept low, the gear unit was turned “on its head”, by rotating it 180 degrees about its longitudinal axis, in contrast to the mid-engine, two-seater Boxster, for example. If no propulsive power is required on the rear axle, the two motors can be decoupled by opening the decoupler and PDK clutches. This is what is behind the Porsche hybrid drive’s trademark “coasting” with the combustion engine switched off.
Lithium-ion battery
The electric energy for the electric motors is stored by a liquid-cooled lithium-ion battery comprising 312 individual cells with an energy content of approximately seven kilowatt hours. The battery of the 918 Spyder has a performance-orientated design in terms of both power charging and output in order to fulfil the performance requirements of the electric motor. The power capacity and the operating life of the lithium-ion traction battery are dependent on several factors, including thermal conditions. That is why the 918 Spyder’s battery is liquid-cooled by a dedicated cooling circuit.
To supply it with energy, Porsche developed a new system with a plug-in charging inter face and multiplied recuperation potential. The plug-in interface in the B-column on the front passenger side enables the storage battery to be connected directly with the home mains supply and charged. The charging interface is standardised for the country of purchase. The charger is located close to the traction battery. It converts the alternating current of the mains supply into direct current with a maximum charge output of 3.6 kW. For example, using the charging cable supplied with it, the battery can be charged within four hours from a ten ampere rated, fused power socket on the German 230 Volt mains supply. A compact charging station is also supplied as standard with the 918 Spyder. This can be installed permanently in the driver’s garage. It permits rapid and convenient charging within approximately two hours, irrespective of regional conditions.
Energy recuperation trebled: recuperation
In order to convert the kinetic energy of the vehicle into electric current when braking signi -ficantly more effectively than today, Porsche’s developers created a new generation of the recuperation system. A modern-day Porsche hybrid recovers braking energy up to a dece -leration of 0.15 g. That corresponds to a braking manoeuvre in which the driver applies approximately 1.5 kilograms of pedal force. The 918 Spyder can recover up to 0.5 g, equa -ting to eleven kilograms of pedal force – that is more than three times the amount of energy. The 918 Spyder can brake using both electric motors and thus recuperate energy for the traction battery. The super sports car features a ceramic braking system (PCCB) as standard.
CFRP Monocoque
Despite, or rather because of the heavy components in the electric motor, the 918 Spyder is a model of lightweight design. The load-bearing structure of its body comprises a mono -coque with a unit carrier, both of them made of carbon fibre reinforced plastic (CFRP). This concept has a critical part to play in the curb weight of less than 1,700 kilograms, an outstandingly low value for a hybrid vehicle in this performance class. A system of adjustable aerodynamic elements ensures unique, fully adaptive aerodynamics that automatically re -con cile optimal efficiency and maximum downforce.
The drivetrain components and all components weighing more than 50 kilograms are loca -ted as low down and as centrally as possible within the vehicle. The result is a slightly rear end biased axle load distribution of 57 per cent on the rear axle and 43 per cent on the front axle, combined with an extremely low centre of gravity, ideal for driving dynamics. The central and low position of the traction battery directly behin the driver not only supports the concentration of masses and the lowering of the centre of gravity; it also provides the best temperature conditions for optimum battery functioning.
Rear-axle steering
The Porsche 918 Spyder’s multi-link chassis is inspired by racing car construction, comple -mented by additional systems such as the adaptive shock-absorber system PASM and rear-axle steering. Basically, this comprises an electro-mechanical adjustment system on each rear wheel. The adjustment is speed-sensitive and executes steering angles of a few degrees in each direction. The rear axle can therefore be steered in the same direction or the opposite direction to the front wheels. At low speeds, the system steers the rear wheels in the opposite direction to the front wheels. This makes cornering even more direct, faster and more precise, and reduces the turning circle. At higher speeds, the system steers the rear wheels in the same direction as the front wheels. This minimises the “pushing” of the vehicle’s rear end when changing lanes quickly. The result is very secure and stable handling.
In Detail
| type | Concept / Prototype Car |
| built at | Germany |
| engine | Hybrid V8 w/2 Electric Motors |
| position | Mid, Longitudinal w./ |
| block material | Aluminum |
| valvetrain | DOHC, 4 Valves per Cyl |
| fuel feed | Direct Fuel Injection |
| displacement | 4600 cc / 280.71 in³ |
| power | 574.2 kw / 770 bhp |
| specific output | 167.39 bhp per litre |
| bhp/weight | 452.94 bhp per tonne |
| torque | 750 nm / 553.2 ft lbs |
| redline | 9000 |
| body / frame | Carbon Fiber Panels over Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastic Monocoque |
| driven wheels | 4WD |
| front brakes | PCCB Ceramic Disc Brakes |
| rear brakes | PCCB Ceramic Disc Brakes |
| steering | Electro-Mechanical Power Assist |
| f suspension | Double Wishbones w/PASM Dampers |
| r suspension | Multi-Link w/Rear-Wheel Steering, PASM Dampers |
| curb weight | 1700 kg / 3749 lbs |
| wheelbase | 2730 mm / 107.5 in |
| length | 4643 mm / 182.8 in |
| width | 1940 mm / 76.4 in |
| height | 1167 mm / 45.9 in |
| transmission | 7-Speed PDK Automatic |
| top speed | ~325 kph / 201.82 mph |
| 0 – 100 kph | ~3.0 seconds |
| 0 – 200 kph | ~9.0 seconds |
| combined fuel econ eu | 3.0 L/100 km or 78.40 mpg-us |
| emission | 70 g/km |